PPM1A is a RelA phosphatase with tumor suppressor-like activity
- PMID: 23812431
- PMCID: PMC3897569
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2013.246
PPM1A is a RelA phosphatase with tumor suppressor-like activity
Abstract
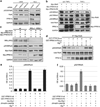
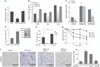
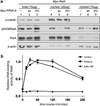
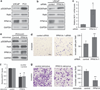
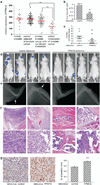
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling contributes to human disease processes, notably inflammatory diseases and cancer. NF-κB has a role in tumorigenesis and tumor growth, as well as promotion of metastases. Mechanisms responsible for abnormal NF-κB activation are not fully elucidated; however, RelA phosphorylation, particularly at serine residues S536 and S276, is critical for RelA function. Kinases that phosphorylate RelA promote oncogenic behaviors, suggesting that phosphatases targeting RelA could have tumor-inhibiting activities; however, few RelA phosphatases have been identified. Here, we identified tumor inhibitory and RelA phosphatase activities of the protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) phosphatase family member, PPM1A. We show that PPM1A directly dephosphorylated RelA at residues S536 and S276 and selectively inhibited NF-κB transcriptional activity, resulting in decreased expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 and interleukin-6, cytokines implicated in cancer metastasis. PPM1A depletion enhanced NF-κB-dependent cell invasion, whereas PPM1A expression inhibited invasion. Analyses of human expression data revealed that metastatic prostate cancer deposits had lower PPM1A expression compared with primary tumors without distant metastases. A hematogenous metastasis mouse model revealed that PPM1A expression inhibited bony metastases of prostate cancer cells after vascular injection. In summary, our findings suggest that PPM1A is a RelA phosphatase that regulates NF-κB activity and that PPM1A has tumor suppressor-like activity. Our analyses also suggest that PPM1A inhibits prostate cancer metastases and as neither gene deletions nor inactivating mutations of PPM1A have been described, increasing PPM1A activity in tumors represents a potential therapeutic strategy to inhibit NF-κB signaling or bony metastases in human cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PPM1A and PPM1B act as IKKbeta phosphatases to terminate TNFalpha-induced IKKbeta-NF-kappaB activation.Cell Signal. 2009 Jan;21(1):95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.09.012. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 18930133 Free PMC article.
-
The serine phosphatase SerB of Porphyromonas gingivalis suppresses IL-8 production by dephosphorylation of NF-κB RelA/p65.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003326. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003326. Epub 2013 Apr 18. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23637609 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of RelA phosphorylation: emerging players and their roles in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Feb;26(1):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 25438737 Review.
-
WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 May;11(5):659-66. doi: 10.1038/ncb1873. Epub 2009 Apr 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19377466
-
A comprehensive overview of PPM1A: From structure to disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Mar;247(6):453-461. doi: 10.1177/15353702211061883. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 34861123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRIM25, TRIM28 and TRIM59 and Their Protein Partners in Cancer Signaling Crosstalk: Potential Novel Therapeutic Targets for Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 25;46(10):10745-10761. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100638. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase PP2Cα S-glutathionylation regulates cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2024 Oct;300(10):107784. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107784. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39303918 Free PMC article.
-
Gypenosides Synergistically Reduce the Extracellular Matrix of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Ameliorate Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice.Molecules. 2023 Jul 17;28(14):5448. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145448. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513321 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel Small-Molecule Scaffolds for the Inhibition and Activation of WIP1 Phosphatase from a RapidFire Mass Spectrometry High-Throughput Screen.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Sep 28;5(10):993-1006. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00147. eCollection 2022 Oct 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36268125 Free PMC article.
-
Ampelopsin Suppresses Stem Cell Properties Accompanied by Attenuation of Oxidative Phosphorylation in Chemo- and Radio-Resistant MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 12;14(8):794. doi: 10.3390/ph14080794. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orlowski RZ, Baldwin J, Albert S. NF-[kappa]B as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:385–389. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, An H, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS, Yarbrough WG. LZAP a putative tumor suppressor, selectively inhibits NF-kappaB. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:239–251. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Karin M. NF-kappaB in mammary gland development and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003;8:215–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials


