MAGEB2 is activated by promoter demethylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23029077
- PMCID: PMC3454438
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045534
MAGEB2 is activated by promoter demethylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Although promoter hypermethylation has been an accepted means of tumor suppressor gene inactivation, activation of otherwise normally repressed proto-oncogenes by promoter demethylation has been infrequently documented.
Experimental design: In this study we performed an integrative, whole-genome analysis for discovery of epigenetically activated proto-oncogenes in head and neck cancer tumors. We used the 47K GeneChip U133 Plus 2.0 Affymetrix expression microarray platform to obtain re-expression data from 5-aza treated normal cell line and expression data from primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumor tissues and normal mucosa tissues. We then investigated candidate genes by screening promoter regions for CpG islands and bisulfite sequencing followed by QUMSP and RT PCR for the best candidate genes. Finally, functional studies were performed on the top candidate gene.
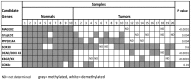
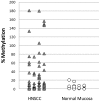
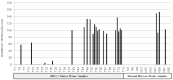
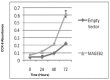
Results: From the top 178 screened candidates 96 had CpG islands in their promoter region. Seven candidate genes showed promoter region methylation in normal mucosa samples and promoter demethylation in a small cohort of primary HNSCC tissues. We then studied the demethylation of the top 3 candidate genes in an expanded cohort of 76 HNSCC tissue samples and 17 normal mucosa samples. We identified MAGEB2 as having significant promoter demethylation in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma tissues. We then found significantly higher expression of MAGEB2 in tumors in a separate cohort of 73 primary HNSCC tissues and 31 normal tissues. Finally, we found that MAGEB2 has growth promoting effects on minimally transformed oral keratinocyte cell lines but not a definite effect on HNSCC cell lines.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we identified MAGEB2 as activated by promoter demethylation in HNSCCand demonstrates growth promoting effects in a minimally transformed oral keratinocyte cell line. More studies are needed to evaluate MAGBE2's exact role in HNSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoter methylation of MGMT, MLH1 and RASSF1A tumor suppressor genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: pharmacological genome demethylation reduces proliferation of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;27(4):1135-41. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1624. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22246327 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated activation of candidate proto-oncogenes and cancer testes antigens via promoter demethylation in head and neck cancer and lung cancer.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004961. Epub 2009 Mar 23. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19305507 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic screen of human DNA repair genes identifies aberrant promoter methylation of NEIL1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2012 Dec 6;31(49):5108-16. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.660. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22286769
-
Delineating an epigenetic continuum in head and neck cancer.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jan 28;342(2):178-84. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 22388100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frequent chromosomal aberrations and candidate genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Mar;273(3):537-45. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3339-1. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 25355032 Review.
Cited by
-
The m6A and immune regulatory gene signature predicts the prognosis and correlates with immune infiltration of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 24;10(21):e39758. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39758. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524706 Free PMC article.
-
MAGEB2-Mediated Degradation of EGR1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Spermatogonial Stem Cell Lines.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Jun 2;2023:3610466. doi: 10.1155/2023/3610466. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 37304127 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Proteomic Profiles for Elucidating Cisplatin Resistance in Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;14(22):5511. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225511. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428603 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF276 promotes the malignant phenotype of breast carcinoma by activating the CYP1B1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 10;13(9):781. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05223-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36085146 Free PMC article.
-
Role and Clinical Utility of Cancer/Testis Antigens in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;13(22):5690. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225690. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brieger J, Pongsapich W, Mann SA, Hedrich J, Fruth K, et al. (2010) Demethylation treatment restores hic1 expression and impairs aggressiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 46: 678–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


