The application of Tet repressor in prokaryotic gene regulation and expression
- PMID: 21261817
- PMCID: PMC3864427
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2007.00001.x
The application of Tet repressor in prokaryotic gene regulation and expression
Abstract
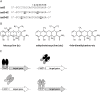
Inducible gene expression based upon Tet repressor (tet regulation) is a broadly applied tool in molecular genetics. In its original environment, Tet repressor (TetR) negatively controls tetracycline (tc) resistance in bacteria. In the presence of tc, TetR is induced and detaches from its cognate DNA sequence tetO, so that a tc antiporter protein is expressed. In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview about tet regulation in bacteria and illustrate the parameters of different regulatory architectures. While some of these set-ups rely on natural tet-control regions like those found on transposon Tn10, highly efficient variations of this system have recently been adapted to different Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Novel tet-controllable artificial or hybrid promoters were employed for target gene expression. They are controlled by regulators expressed at different levels either in a constitutive or in an autoregulated manner. The resulting tet systems have been used for various purposes. We discuss integrative elements vested with tc-sensitive promoters, as well as tet regulation in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria for analytical purposes and for protein overproduction. Also the use of TetR as an in vivo biosensor for tetracyclines or as a regulatory device in synthetic biology constructs is outlined. Technical specifications underlying different regulatory set-ups are highlighted, and finally recent developments concerning variations of TetR are presented, which may expand the use of prokaryotic tet systems in the future.
Figures
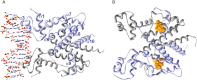



Similar articles
-
Status quo of tet regulation in bacteria.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Apr;15(4):1101-1119. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13926. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34713957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying expression of Tn10 encoded tetracycline resistance.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:345-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.002021. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7826010 Review.
-
New architectures for Tet-on and Tet-off regulation in Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Feb;76(3):680-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02416-09. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19966017 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation by tetracyclines. Constraints of resistance regulation in bacteria shape TetR for application in eukaryotes.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Aug;270(15):3109-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03694.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12869186 Review.
-
Thermodynamic analysis of tetracycline-mediated induction of Tet repressor by a quantitative methylation protection assay.Anal Biochem. 1995 Dec 10;232(2):190-6. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.0006. Anal Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8747474
Cited by
-
A dual-inducible control system for multistep biosynthetic pathways.J Biol Eng. 2024 Nov 20;18(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13036-024-00462-z. J Biol Eng. 2024. PMID: 39568033 Free PMC article.
-
Development of inducible promoter and CRISPRi plasmids functional in Rickettsia rickettsii.J Bacteriol. 2024 Oct 24;206(10):e0036724. doi: 10.1128/jb.00367-24. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 39347571 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and application of LacI mutants with stringent expressions.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;17(3):e14427. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14427. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38465475 Free PMC article.
-
Rendezvous with Vaccinia Virus in the Post-smallpox Era: R&D Advances.Viruses. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):1742. doi: 10.3390/v15081742. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPRi-mediated tunable control of gene expression level with engineered single-guide RNA in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 22;51(9):4650-4659. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad234. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36999618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agerso Y., Guardabassi L. Identification of Tet 39, a novel class of tetracycline resistance determinant in Acinetobacter spp. of environmental and clinical origin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;55:566–569. - PubMed
-
- Bae T., Schneewind O. Allelic replacement in Staphylococcus aureus with inducible counter‐selection. Plasmid. 2006;55:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Bahl M.I., Hansen L.H., Sorensen S.J. Construction of an extended range whole‐cell tetracycline biosensor by use of the tet(M) resistance gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;253:201–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


