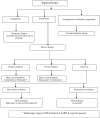
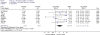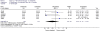European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients
- PMID: 19636493
- PMCID: PMC2719730
- DOI: 10.1007/s10029-009-0529-7
European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients
Abstract
The European Hernia Society (EHS) is proud to present the EHS Guidelines for the Treatment of Inguinal Hernia in Adult Patients. The Guidelines contain recommendations for the treatment of inguinal hernia from diagnosis till aftercare. They have been developed by a Working Group consisting of expert surgeons with representatives of 14 country members of the EHS. They are evidence-based and, when necessary, a consensus was reached among all members. The Guidelines have been reviewed by a Steering Committee. Before finalisation, feedback from different national hernia societies was obtained. The Appraisal of Guidelines for REsearch and Evaluation (AGREE) instrument was used by the Cochrane Association to validate the Guidelines. The Guidelines can be used to adjust local protocols, for training purposes and quality control. They will be revised in 2012 in order to keep them updated. In between revisions, it is the intention of the Working Group to provide every year, during the EHS annual congress, a short update of new high-level evidence (randomised controlled trials [RCTs] and meta-analyses). Developing guidelines leads to questions that remain to be answered by specific research. Therefore, we provide recommendations for further research that can be performed to raise the level of evidence concerning certain aspects of inguinal hernia treatment. In addition, a short summary, specifically for the general practitioner, is given. In order to increase the practical use of the Guidelines by consultants and residents, more details on the most important surgical techniques, local infiltration anaesthesia and a patient information sheet is provided. The most important challenge now will be the implementation of the Guidelines in daily surgical practice. This remains an important task for the EHS. The establishment of an EHS school for teaching inguinal hernia repair surgical techniques, including tips and tricks from experts to overcome the learning curve (especially in endoscopic repair), will be the next step. Working together on this project was a great learning experience, and it was worthwhile and fun. Cultural differences between members were easily overcome by educating each other, respecting different views and always coming back to the principles of evidence-based medicine. The members of the Working Group would like to thank the EHS board for their support and especially Ethicon for sponsoring the many meetings that were needed to finalise such an ambitious project.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Principles of the management of adult inguinal hernia--recommendations by the European Hernia Society].Magy Seb. 2010 Oct;63(5):287-96. doi: 10.1556/MaSeb.63.2010.5.1. Magy Seb. 2010. PMID: 20965861 Hungarian.
-
Update with level 1 studies of the European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients.Hernia. 2014 Apr;18(2):151-63. doi: 10.1007/s10029-014-1236-6. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Hernia. 2014. PMID: 24647885 Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
"One step procedure" local anaesthesia for inguinal hernia repair in ambulatory surgery conditions--district general hospital experience.Acta Chir Iugosl. 2012;59(1):87-93. Acta Chir Iugosl. 2012. PMID: 22924311
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of open mesh repairs in adults presenting with a clinically diagnosed primary unilateral inguinal hernia who are operated in an elective setting: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2015 Nov;19(92):1-142. doi: 10.3310/hta19920. Health Technol Assess. 2015. PMID: 26556776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quadruple Hernia: A Rare Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Oct 6;16(10):e70962. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70962. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39507131 Free PMC article.
-
Surgeons' Approach to Intraoperative Complications in Total Extraperitoneal (TEP) Hernia Repair.JSLS. 2024 Jul-Sep;28(3):e2024.00020. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2024.00020. JSLS. 2024. PMID: 39445074 Free PMC article.
-
Internal hernia after trans-abdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) hernia repair: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Nov;124:110445. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110445. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39418992 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Open Rives-Stoppa and Lichtenstein Repair Methods for Bilateral Inguinal Hernias: A Single-Centre Comparative Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Aug 27;16(8):e67946. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67946. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39328621 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective randomized study comparing mesh displacement in enhanced-view totally extraperitoneal versus totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair without mesh fixation.Hernia. 2024 Dec;28(6):2393-2401. doi: 10.1007/s10029-024-03181-y. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Hernia. 2024. PMID: 39325327 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3461421', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3461421/'}]}
- Aasvang E, Kehlet H (1986) Classification of chronic pain. Descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. Prepared by the International Association for the Study of Pain, Subcommittee on Taxonomy. Pain Suppl 3:S1–S226 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15531621', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15531621/'}]}
- Aasvang E, Kehlet H (2005) Chronic postoperative pain: the case of inguinal herniorrhaphy. Br J Anaesth 95:69–76 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15962258', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15962258/'}]}
- Aasvang E, Kehlet H (2005) Surgical management of chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 92:795–801 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16545910', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16545910/'}]}
- Aasvang EK, Møhl B, Bay-Nielsen M, Kehlet H (2006) Pain related sexual dysfunction after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Pain 122:258–263 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17667575', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17667575/'}]}
- Aasvang EK, Møhl B, Kehlet H (2007) Ejaculatory pain: a specific postherniotomy pain syndrome? Anesthesiology 107:298–304 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical