Onset of breast and pubic hair development in 1231 preadolescent Lithuanian schoolgirls
- PMID: 15855182
- PMCID: PMC1720558
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2004.057612
Onset of breast and pubic hair development in 1231 preadolescent Lithuanian schoolgirls
Abstract
Background: Correct staging of puberty is essential in order to differentiate different pathologies, as various components of the endocrine system influence breast, pubic, and axillary hair development.
Aims: To determine the current timing of adrenarche and breast development in Lithuanian preadolescent schoolgirls.
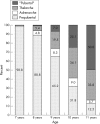
Methods: Cross-sectional study of 1231 schoolgirls aged 7.0-11.6 years. Puberty was staged according to the method of Tanner. Mean age at entry into each pubertal stage was calculated by probit analysis.
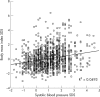
Results: Of the 255 girls aged 7 years, two had premature adrenarche (0.8%) and one premature thelarche (0.4%). Mean age of onset of pubic/axillary hair development was 11.0 years, and for breast development (Stage 2) 10.2 years. Breast Stage 3 development was attained at 11.3 years and Stage 4 at 13.9 years. Mean BMI, height, weight, and systolic blood pressure SD scores were higher in pubertal than in prepubertal girls. Skinfold thickness was also significantly higher in girls with isolated adrenarche than in prepubertal girls. The increase in BMI and weight resulted from an increase in body fat as evidenced by measures of subscapular and triceps skinfold thickness. Girls with only signs of adrenarche or thelarche did not differ from each other from the anthropometric standpoint.
Conclusions: Premature thelarche and premature adrenarche were relatively uncommon in this population. Pubertal onset was slightly earlier than the UK Tanner standards and tended to occur in girls with a higher BMI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pubertal maturation in girls and the relationship to anthropometric changes: pathways through puberty.J Pediatr. 2003 Jun;142(6):643-6. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2003.244. J Pediatr. 2003. PMID: 12838192
-
Thelarche, pubarche, and menarche attainment in children with normal and elevated body mass index.Pediatrics. 2009 Jan;123(1):84-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-0146. Pediatrics. 2009. PMID: 19117864
-
Age and anthropometric status of Nigerian girls at puberty: implication for the introduction of sex education into secondary schools.West Afr J Med. 1990 Jul-Sep;9(3):226-31. West Afr J Med. 1990. PMID: 2271438
-
Physical changes of puberty.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991 Mar;20(1):1-14. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991. PMID: 2029881 Review.
-
Premature adrenarche leads to polycystic ovary syndrome? Long-term consequences.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Dec;1092:148-57. doi: 10.1196/annals.1365.013. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17308141 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of cognitive behavioral therapy on stress and anxiety of mothers of girls with precocious puberty symptoms: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):738. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05216-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37817169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, birth size, adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in 7-year-old children.Pediatr Res. 2022 Jun;91(7):1897-1905. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01706-0. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34417562
-
Worldwide Secular Trends in Age at Pubertal Onset Assessed by Breast Development Among Girls: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 1;174(4):e195881. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5881. Epub 2020 Apr 6. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32040143 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and hormonal assessment of adolescent and young adult women with prior premature adrenarche.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74:e836. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2019/e836. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31241662 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between age of puberty onset and height at age 18 years in girls and boys.World J Pediatr. 2013 Aug;9(3):230-8. doi: 10.1007/s12519-013-0399-z. Epub 2013 Jan 18. World J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23335183
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical