A millennial myosin census
- PMID: 11294886
- PMCID: PMC32266
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.780
A millennial myosin census
Abstract
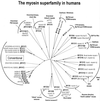
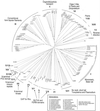
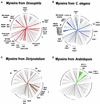
The past decade has seen a remarkable explosion in our knowledge of the size and diversity of the myosin superfamily. Since these actin-based motors are candidates to provide the molecular basis for many cellular movements, it is essential that motility researchers be aware of the complete set of myosins in a given organism. The availability of cDNA and/or draft genomic sequences from humans, Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorhabditis elegans, Arabidopsis thaliana, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and Dictyostelium discoideum has allowed us to tentatively define and compare the sets of myosin genes in these organisms. This analysis has also led to the identification of several putative myosin genes that may be of general interest. In humans, for example, we find a total of 40 known or predicted myosin genes including two new myosins-I, three new class II (conventional) myosins, a second member of the class III/ninaC myosins, a gene similar to the class XV deafness myosin, and a novel myosin sharing at most 33% identity with other members of the superfamily. These myosins are in addition to the recently discovered class XVI myosin with N-terminal ankyrin repeats and two human genes with similarity to the class XVIII PDZ-myosin from mouse. We briefly describe these newly recognized myosins and extend our previous phylogenetic analysis of the myosin superfamily to include a comparison of the complete or nearly complete inventories of myosin genes from several experimentally important organisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and phylogenetic analysis of Drosophila melanogaster myosins.Mol Biol Evol. 2002 Jul;19(7):1041-52. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004163. Mol Biol Evol. 2002. PMID: 12082124
-
Thirteen is enough: the myosins of Dictyostelium discoideum and their light chains.BMC Genomics. 2006 Jul 20;7:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-183. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16857047 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into myosin evolution and classification.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 7;103(10):3681-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506307103. Epub 2006 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16505385 Free PMC article.
-
How many is enough? Exploring the myosin repertoire in the model eukaryote Dictyostelium discoideum.Cell Biochem Biophys. 1999;30(3):389-411. doi: 10.1007/BF02738121. Cell Biochem Biophys. 1999. PMID: 10403058 Review.
-
Identification and analysis of the myosin superfamily in Drosophila: a database approach.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000;21(6):491-505. doi: 10.1023/a:1026589626422. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000. PMID: 11206129 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of the Pre-Powerstroke Myosin Lever Arm and the Effects of Omecamtiv Mecarbil.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10425. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910425. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408754 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the fastest myosin: Discovery history and structure-function relationships of algae Chara myosin XI.Biophys Physicobiol. 2024 Jul 17;21(3):e210016. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v21.0016. eCollection 2024. Biophys Physicobiol. 2024. PMID: 39234188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filamin A regulates platelet shape change and contractile force generation via phosphorylation of the myosin light chain.Biochem J. 2024 Oct 17;481(20):1395-1410. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240114. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 39189664 Free PMC article.
-
Myo5B plays a significant role in the hyphal growth and virulence of the human pathogenic fungus Mucor lusitanicus.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Jul;170(7):001482. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001482. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 39073411 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Unconventional myosins in motile and contractile functions: fifty years on the stage.Front Physiol. 2024 Jun 12;15:1439746. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1439746. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38933364 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, George RA, Lewis SE, Richards S, Ashburner M, Henderson SN, Sutton GG, Wortman JR, Yandell MD, Zhang Q, Chen LX, Brandon RC, Rogers YH, Blazej RG, Champe M, Pfeiffer BD, Wan KH, Doyle C, Baxter EG, Helt G, Nelson CR, Gabor GL, Abril JF, Agbayani A, An HJ, Andrews-Pfannkoch C, Baldwin D, Ballew RM, Basu A, Baxendale J, Bayraktaroglu L, Beasley EM, Beeson KY, Benos PV, Berman BP, Bhandari D, Bolshakov S, Borkova D, Botchan MR, Bouck J, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Bahler M. Are class III and class IX myosins motorized signaling molecules? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1496:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Baker JP, Titus MA. A family of unconventional myosins from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1997;272:523–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous


