Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
 Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) satellite | |
| Names | Explorer 80 MAP Microwave Anisotropy Probe MIDEX-2 WMAP |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Cosmic microwave background Astronomy |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 2001-027A |
| SATCAT no. | 26859 |
| Website | http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/ |
| Mission duration | 27 months (planned) 9 years (achieved)[1] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer LXXX |
| Spacecraft type | Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe |
| Bus | WMAP |
| Manufacturer | NRAO |
| Launch mass | 840 kg (1,850 lb)[2] |
| Dry mass | 763 kg (1,682 lb) |
| Dimensions | 3.6 × 5.1 m (12 × 17 ft) |
| Power | 419 watts |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 30 June 2001, 19:46:46 UTC[3] |
| Rocket | Delta II 7425-10 (Delta 246) |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral, SLC-17B |
| Contractor | Boeing Launch Services |
| Entered service | 1 October 2001 |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Graveyard orbit |
| Deactivated | 20 October 2010[4] |
| Last contact | 19 August 2010 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Sun-Earth L2 orbit |
| Regime | Lissajous orbit |
| Main telescope | |
| Type | Gregorian |
| Diameter | 1.4 × 1.6 m (4 ft 7 in × 5 ft 3 in) |
| Wavelengths | 23 GHz to 94 GHz |
| Instruments | |
| Pseudo-Correlation Radiometer | |
 Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe mission patch Explorer program | |
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – the radiant heat remaining from the Big Bang.[5][6] Headed by Professor Charles L. Bennett of Johns Hopkins University, the mission was developed in a joint partnership between the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Princeton University.[7] The WMAP spacecraft was launched on 30 June 2001 from Florida. The WMAP mission succeeded the COBE space mission and was the second medium-class (MIDEX) spacecraft in the NASA Explorer program. In 2003, MAP was renamed WMAP in honor of cosmologist David Todd Wilkinson (1935–2002),[7] who had been a member of the mission's science team. After nine years of operations, WMAP was switched off in 2010, following the launch of the more advanced Planck spacecraft by European Space Agency (ESA) in 2009.
WMAP's measurements played a key role in establishing the current Standard Model of Cosmology: the Lambda-CDM model. The WMAP data are very well fit by a universe that is dominated by dark energy in the form of a cosmological constant. Other cosmological data are also consistent, and together tightly constrain the Model. In the Lambda-CDM model of the universe, the age of the universe is 13.772±0.059 billion years. The WMAP mission's determination of the age of the universe is to better than 1% precision.[8] The current expansion rate of the universe is (see Hubble constant) 69.32±0.80 km·s−1·Mpc−1. The content of the universe currently consists of 4.628%±0.093% ordinary baryonic matter; 24.02%+0.88%
−0.87% cold dark matter (CDM) that neither emits nor absorbs light; and 71.35%+0.95%
−0.96% of dark energy in the form of a cosmological constant that accelerates the expansion of the universe.[9] Less than 1% of the current content of the universe is in neutrinos, but WMAP's measurements have found, for the first time in 2008, that the data prefer the existence of a cosmic neutrino background[10] with an effective number of neutrino species of 3.26±0.35. The contents point to a Euclidean flat geometry, with curvature () of −0.0027+0.0039
−0.0038. The WMAP measurements also support the cosmic inflation paradigm in several ways, including the flatness measurement.
The mission has won various awards: according to Science magazine, the WMAP was the Breakthrough of the Year for 2003.[11] This mission's results papers were first and second in the "Super Hot Papers in Science Since 2003" list.[12] Of the all-time most referenced papers in physics and astronomy in the INSPIRE-HEP database, only three have been published since 2000, and all three are WMAP publications. Bennett, Lyman A. Page Jr., and David N. Spergel, the latter both of Princeton University, shared the 2010 Shaw Prize in astronomy for their work on WMAP.[13] Bennett and the WMAP science team were awarded the 2012 Gruber Prize in cosmology. The 2018 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics was awarded to Bennett, Gary Hinshaw, Norman Jarosik, Page, Spergel, and the WMAP science team.
In October 2010, the WMAP spacecraft was derelict in a heliocentric graveyard orbit after completing nine years of operations.[14] All WMAP data are released to the public and have been subject to careful scrutiny. The final official data release was the nine-year release in 2012.[15][16]
Some aspects of the data are statistically unusual for the Standard Model of Cosmology. For example, the largest angular-scale measurement, the quadrupole moment, is somewhat smaller than the Model would predict, but this discrepancy is not highly significant.[17] A large cold spot and other features of the data are more statistically significant, and research continues into these.
Objectives
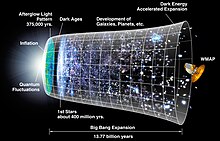

The WMAP objective was to measure the temperature differences in the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation. The anisotropies then were used to measure the universe's geometry, content, and evolution; and to test the Big Bang model, and the cosmic inflation theory.[18] For that, the mission created a full-sky map of the CMB, with a 13 arcminutes resolution via multi-frequency observation. The map required the fewest systematic errors, no correlated pixel noise, and accurate calibration, to ensure angular-scale accuracy greater than its resolution.[18] The map contains 3,145,728 pixels, and uses the HEALPix scheme to pixelize the sphere.[19] The telescope also measured the CMB's E-mode polarization,[18] and foreground polarization.[10] Its service life was 27 months; 3 to reach the L2 position, and 2 years of observation.[18]
Development
The MAP mission was proposed to NASA in 1995, selected for definition study in 1996, and approved for development in 1997.[20][21]
The WMAP was preceded by two missions to observe the CMB; (i) the Soviet RELIKT-1 that reported the upper-limit measurements of CMB anisotropies, and (ii) the U.S. COBE satellite that first reported large-scale CMB fluctuations. The WMAP was 45 times more sensitive, with 33 times the angular resolution of its COBE satellite predecessor.[22] The successor European Planck mission (operational 2009–2013) had a higher resolution and higher sensitivity than WMAP and observed in 9 frequency bands rather than WMAP's 5, allowing improved astrophysical foreground models.
Spacecraft


The telescope's primary reflecting mirrors are a pair of Gregorian 1.4 × 1.6 m (4 ft 7 in × 5 ft 3 in) dishes (facing opposite directions), that focus the signal onto a pair of 0.9 × 1.0 m (2 ft 11 in × 3 ft 3 in) secondary reflecting mirrors. They are shaped for optimal performance: a carbon fibre shell upon a Korex core, thinly-coated with aluminium and silicon oxide. The secondary reflectors transmit the signals to the corrugated feedhorns that sit on a focal plane array box beneath the primary reflectors.[18]
The receivers are polarization-sensitive differential radiometers measuring the difference between two telescope beams. The signal is amplified with High-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) low-noise amplifiers, built by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO). There are 20 feeds, 10 in each direction, from which a radiometer collects a signal; the measure is the difference in the sky signal from opposite directions. The directional separation azimuth is 180°; the total angle is 141°. To improve subtraction of foreground signals from our Milky Way galaxy, the WMAP used five discrete radio frequency bands, from 23 GHz to 94 GHz.[18]
| Property | K-band | Ka-band | Q-band | V-band | W-band |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central wavelength (mm) | 13 | 9.1 | 7.3 | 4.9 | 3.2 |
| Central frequency (GHz) | 23 | 33 | 41 | 61 | 94 |
| Bandwidth (GHz) | 5.5 | 7.0 | 8.3 | 14.0 | 20.5 |
| Beam size (arcminutes) | 52.8 | 39.6 | 30.6 | 21 | 13.2 |
| Number of radiometers | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| System temperature (K) | 29 | 39 | 59 | 92 | 145 |
| Sensitivity (mK s) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
The WMAP's base is a 5.0 m (16.4 ft)-diameter solar panel array that keeps the instruments in shadow during CMB observations, (by keeping the craft constantly angled at 22°, relative to the Sun). Upon the array sit a bottom deck (supporting the warm components) and a top deck. The telescope's cold components: the focal-plane array and the mirrors, are separated from the warm components with a cylindrical, 33 cm (13 in)-long thermal isolation shell atop the deck.[18]
Passive thermal radiators cool the WMAP to approximately 90 K (−183.2 °C; −297.7 °F); they are connected to the low-noise amplifiers. The telescope consumes 419 W of power. The available telescope heaters are emergency-survival heaters, and there is a transmitter heater, used to warm them when off. The WMAP spacecraft's temperature is monitored with platinum resistance thermometers.[18]
The WMAP's calibration is effected with the CMB dipole and measurements of Jupiter; the beam patterns are measured against Jupiter. The telescope's data are relayed daily via a 2-GHz transponder providing a 667 kbit/s downlink to a 70 m (230 ft) Deep Space Network station. The spacecraft has two transponders, one a redundant backup; they are minimally active – about 40 minutes daily – to minimize radio frequency interference. The telescope's position is maintained, in its three axes, with three reaction wheels, gyroscopes, two star trackers and Sun sensors, and is steered with eight hydrazine thrusters.[18]
Launch, trajectory, and orbit
The WMAP spacecraft arrived at the Kennedy Space Center on 20 April 2001. After being tested for two months, it was launched via Delta II 7425 launch vehicle on 30 June 2001.[20][22] It began operating on its internal power five minutes before its launching, and continued so operating until the solar panel array deployed. The WMAP was activated and monitored while it cooled. On 2 July 2001, it began working, first with in-flight testing (from launching until 17 August 2001), then began constant, formal work.[22] Afterwards, it effected three Earth-Moon phase loops, measuring its sidelobes, then flew by the Moon on 30 July 2001, en route to the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point, arriving there on 1 October 2001, becoming the first CMB observation mission posted there.[20]
Locating the spacecraft at Lagrange 2, (1,500,000 km (930,000 mi) from Earth) thermally stabilizes it and minimizes the contaminating solar, terrestrial, and lunar emissions registered. To view the entire sky, without looking to the Sun, the WMAP traces a path around L2 in a Lissajous orbit ca. 1.0° to 10°,[18] with a 6-month period.[20] The telescope rotates once every 2 minutes 9 seconds (0.464 rpm) and precesses at the rate of 1 revolution per hour.[18] WMAP measured the entire sky every six months, and completed its first, full-sky observation in April 2002.[21]
-
WMAP launches from Kennedy Space Center, 30 June 2001
-
The WMAP's trajectory and orbit
-
WMAP's orbit and sky scan strategy
Experiment
Pseudo-Correlation Radiometer
The WMAP instrument consists of pseudo-correlation differential radiometers fed by two back-to-back 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) primary Gregorian reflectors. This instrument uses five frequency bands from 22 GHz to 90 GHz to facilitate rejection of foreground signals from our own Galaxy. The WMAP instrument has a 3.5° x 3.5° field of view (FoV).[23]
Foreground radiation subtraction
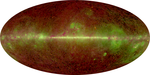
The WMAP observed in five frequencies, permitting the measurement and subtraction of foreground contamination (from the Milky Way and extra-galactic sources) of the CMB. The main emission mechanisms are synchrotron radiation and free-free emission (dominating the lower frequencies), and astrophysical dust emissions (dominating the higher frequencies). The spectral properties of these emissions contribute different amounts to the five frequencies, thus permitting their identification and subtraction.[18]
Foreground contamination is removed in several ways. First, subtract extant emission maps from the WMAP's measurements; second, use the components' known spectral values to identify them; third, simultaneously fit the position and spectra data of the foreground emission, using extra data sets. Foreground contamination was reduced by using only the full-sky map portions with the least foreground contamination, while masking the remaining map portions.[18]
 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 23 GHz | 33 GHz | 41 GHz | 61 GHz | 94 GHz |
Measurements and discoveries
One-year data release

On 11 February 2003, NASA published the first-year's worth of WMAP data. The latest calculated age and composition of the early universe were presented. In addition, an image of the early universe, that "contains such stunning detail, that it may be one of the most important scientific results of recent years" was presented. The newly released data surpass previous CMB measurements.[7]
Based upon the Lambda-CDM model, the WMAP team produced cosmological parameters from the WMAP's first-year results. Three sets are given below; the first and second sets are WMAP data; the difference is the addition of spectral indices, predictions of some inflationary models. The third data set combines the WMAP constraints with those from other CMB experiments (ACBAR and CBI), and constraints from the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey and Lyman alpha forest measurements. There are degenerations among the parameters, the most significant is between and ; the errors given are at 68% confidence.[24]
| Parameter | Symbol | Best fit (WMAP only) | Best fit (WMAP, extra parameter) | Best fit (all data) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of the universe (Ga) | 13.4±0.3 | – | 13.7±0.2 | |
| Hubble's constant ( km⁄Mpc·s ) | 72±5 | 70±5 | 71+4 −3 | |
| Baryonic content | 0.024±0.001 | 0.023±0.002 | 0.0224±0.0009 | |
| Matter content | 0.14±0.02 | 0.14±0.02 | 0.135+0.008 −0.009 | |
| Optical depth to reionization | 0.166+0.076 −0.071 |
0.20±0.07 | 0.17±0.06 | |
| Amplitude | A | 0.9±0.1 | 0.92±0.12 | 0.83+0.09 −0.08 |
| Scalar spectral index | 0.99±0.04 | 0.93±0.07 | 0.93±0.03 | |
| Running of spectral index | — | −0.047±0.04 | −0.031+0.016 −0.017 | |
| Fluctuation amplitude at 8h−1 Mpc | 0.9±0.1 | — | 0.84±0.04 | |
| Total density of the universe | – | – | 1.02±0.02 |
Using the best-fit data and theoretical models, the WMAP team determined the times of important universal events, including the redshift of reionization, 17±4; the redshift of decoupling, 1089±1 (and the universe's age at decoupling, 379+8
−7 kyr); and the redshift of matter/radiation equality, 3233+194
−210. They determined the thickness of the surface of last scattering to be 195±2 in redshift, or 118+3
−2 kyr. They determined the current density of baryons, (2.5±0.1)×10−7 cm−1, and the ratio of baryons to photons, 6.1+0.3
−0.2×10−10. The WMAP's detection of an early reionization excluded warm dark matter.[24]
The team also examined Milky Way emissions at the WMAP frequencies, producing a 208-point source catalogue.
Three-year data release

The three-year WMAP data were released on 17 March 2006. The data included temperature and polarization measurements of the CMB, which provided further confirmation of the standard flat Lambda-CDM model and new evidence in support of inflation.
The 3-year WMAP data alone shows that the universe must have dark matter. Results were computed both only using WMAP data, and also with a mix of parameter constraints from other instruments, including other CMB experiments (Arcminute Cosmology Bolometer Array Receiver (ACBAR), Cosmic Background Imager (CBI) and BOOMERANG), Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey, the Supernova Legacy Survey and constraints on the Hubble constant from the Hubble Space Telescope.[25]
| Parameter | Symbol | Best fit (WMAP only) |
|---|---|---|
| Age of the universe (Ga) | 13.73+0.16 −0.15 | |
| Hubble's constant ( km⁄Mpc·s ) | 73.2+3.1 −3.2 | |
| Baryonic content | 0.0229±0.00073 | |
| Matter content | 0.1277+0.0080 −0.0079 | |
| Optical depth to reionization [a] | 0.089±0.030 | |
| Scalar spectral index | 0.958±0.016 | |
| Fluctuation amplitude at 8h−1 Mpc | 0.761+0.049 −0.048 | |
| Tensor-to-scalar ratio [b] | r | <0.65 |
[a] ^ Optical depth to reionization improved due to polarization measurements.[26]
[b] ^ <0.30 when combined with SDSS data. No indication of non-gaussianity.[25]
Five-year data release

The five-year WMAP data were released on 28 February 2008. The data included new evidence for the cosmic neutrino background, evidence that it took over half billion years for the first stars to reionize the universe, and new constraints on cosmic inflation.[27]
The improvement in the results came from both having an extra two years of measurements (the data set runs between midnight on 10 August 2001 to midnight of 9 August 2006), as well as using improved data processing techniques and a better characterization of the instrument, most notably of the beam shapes. They also make use of the 33-GHz observations for estimating cosmological parameters; previously only the 41-GHz and 61-GHz channels had been used.
Improved masks were used to remove foregrounds.[10] Improvements to the spectra were in the 3rd acoustic peak, and the polarization spectra.[10]
The measurements put constraints on the content of the universe at the time that the CMB was emitted; at the time 10% of the universe was made up of neutrinos, 12% of atoms, 15% of photons and 63% dark matter. The contribution of dark energy at the time was negligible.[27] It also constrained the content of the present-day universe; 4.6% atoms, 23% dark matter and 72% dark energy.[10]
The WMAP five-year data was combined with measurements from Type Ia supernova (SNe) and Baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO).[10]
The elliptical shape of the WMAP skymap is the result of a Mollweide projection.[28]
| Parameter | Symbol | Best fit (WMAP only) | Best fit (WMAP + SNe + BAO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of the universe (Ga) | 13.69±0.13 | 13.72±0.12 | |
| Hubble's constant ( km⁄Mpc·s ) | 71.9+2.6 −2.7 |
70.5±1.3 | |
| Baryonic content | 0.02273±0.00062 | 0.02267+0.00058 −0.00059 | |
| Cold dark matter content | 0.1099±0.0062 | 0.1131±0.0034 | |
| Dark energy content | 0.742±0.030 | 0.726±0.015 | |
| Optical depth to reionization | 0.087±0.017 | 0.084±0.016 | |
| Scalar spectral index | 0.963+0.014 −0.015 |
0.960±0.013 | |
| Running of spectral index | −0.037±0.028 | −0.028±0.020 | |
| Fluctuation amplitude at 8h−1 Mpc | 0.796±0.036 | 0.812±0.026 | |
| Total density of the universe | 1.099+0.100 −0.085 |
1.0050+0.0060 −0.0061 | |
| Tensor-to-scalar ratio | r | <0.43 | <0.22 |
The data puts limits on the value of the tensor-to-scalar ratio, r <0.22 (95% certainty), which determines the level at which gravitational waves affect the polarization of the CMB, and also puts limits on the amount of primordial non-gaussianity. Improved constraints were put on the redshift of reionization, which is 10.9±1.4, the redshift of decoupling, 1090.88±0.72 (as well as age of universe at decoupling, 376.971+3.162
−3.167 kyr) and the redshift of matter/radiation equality, 3253+89
−87.[10]
The extragalactic source catalogue was expanded to include 390 sources, and variability was detected in the emission from Mars and Saturn.[10]
 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 23 GHz | 33 GHz | 41 GHz | 61 GHz | 94 GHz |
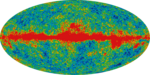
Seven-year data release
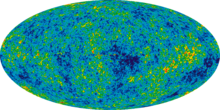
The seven-year WMAP data were released on 26 January 2010. As part of this release, claims for inconsistencies with the standard model were investigated.[29] Most were shown not to be statistically significant, and likely due to a posteriori selection (where one sees a weird deviation, but fails to consider properly how hard one has been looking; a deviation with 1:1000 likelihood will typically be found if one tries one thousand times). For the deviations that do remain, there are no alternative cosmological ideas (for instance, there seem to be correlations with the ecliptic pole). It seems most likely these are due to other effects, with the report mentioning uncertainties in the precise beam shape and other possible small remaining instrumental and analysis issues.
The other confirmation of major significance is of the total amount of matter/energy in the universe in the form of dark energy – 72.8% (within 1.6%) as non 'particle' background, and dark matter – 22.7% (within 1.4%) of non baryonic (sub-atomic) 'particle' energy. This leaves matter, or baryonic particles (atoms) at only 4.56% (within 0.16%).
| Parameter | Symbol | Best fit (WMAP only) | Best fit (WMAP + BAO[31] + H0[32]) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of the universe (Ga) | 13.75±0.13 | 13.75±0.11 | |
| Hubble's constant ( km⁄Mpc·s ) | 71.0±2.5 | 70.4+1.3 −1.4 | |
| Baryon density | 0.0449±0.0028 | 0.0456±0.0016 | |
| Physical baryon density | 0.02258+0.00057 −0.00056 |
0.02260±0.00053 | |
| Dark matter density | 0.222±0.026 | 0.227±0.014 | |
| Physical dark matter density | 0.1109±0.0056 | 0.1123±0.0035 | |
| Dark energy density | 0.734±0.029 | 0.728+0.015 −0.016 | |
| Fluctuation amplitude at 8h−1 Mpc | 0.801±0.030 | 0.809±0.024 | |
| Scalar spectral index | 0.963±0.014 | 0.963±0.012 | |
| Reionization optical depth | 0.088±0.015 | 0.087±0.014 | |
| *Total density of the universe | 1.080+0.093 −0.071 |
1.0023+0.0056 −0.0054 | |
| *Tensor-to-scalar ratio, k0 = 0.002 Mpc−1 | r | < 0.36 (95% CL) | < 0.24 (95% CL) |
| *Running of spectral index, k0 = 0.002 Mpc−1 | −0.034±0.026 | −0.022±0.020 | |
| Note: * = Parameters for extended models (parameters place limits on deviations from the Lambda-CDM model)[30] |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 23-GHz | 33-GHz | 41-GHz | 61-GHz | 94-GHz |
Nine-year data release
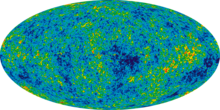
On 29 December 2012, the nine-year WMAP data and related images were released. 13.772±0.059 billion-year-old temperature fluctuations and a temperature range of ± 200 microkelvins are shown in the image. In addition, the study found that 95% of the early universe is composed of dark matter and dark energy, the curvature of space is less than 0.4% of "flat" and the universe emerged from the cosmic Dark Ages "about 400 million years" after the Big Bang.[15][16][33]
| Parameter | Symbol | Best fit (WMAP only) | Best fit (WMAP + eCMB + BAO + H0) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of the universe (Ga) | 13.74±0.11 | 13.772±0.059 | |
| Hubble's constant ( km⁄Mpc·s ) | 70.0±2.2 | 69.32±0.80 | |
| Baryon density | 0.0463±0.0024 | 0.04628±0.00093 | |
| Physical baryon density | 0.02264±0.00050 | 0.02223±0.00033 | |
| Cold dark matter density | 0.233±0.023 | 0.2402+0.0088 −0.0087 | |
| Physical cold dark matter density | 0.1138±0.0045 | 0.1153±0.0019 | |
| Dark energy density | 0.721±0.025 | 0.7135+0.0095 −0.0096 | |
| Density fluctuations at 8h−1 Mpc | 0.821±0.023 | 0.820+0.013 −0.014 | |
| Scalar spectral index | 0.972±0.013 | 0.9608±0.0080 | |
| Reionization optical depth | 0.089±0.014 | 0.081±0.012 | |
| Curvature | 1 | −0.037+0.044 −0.042 |
−0.0027+0.0039 −0.0038 |
| Tensor-to-scalar ratio (k0 = 0.002 Mpc−1) | r | < 0.38 (95% CL) | < 0.13 (95% CL) |
| Running scalar spectral index | −0.019±0.025 | −0.023±0.011 |
Main result
The main result of the mission is contained in the various oval maps of the CMB temperature differences. These oval images present the temperature distribution derived by the WMAP team from the observations by the telescope during the mission. Measured is the temperature obtained from a Planck's law interpretation of the microwave background. The oval map covers the whole sky. The results are a snapshot of the universe around 375,000 years after the Big Bang, which happened about 13.8 billion years ago. The microwave background is very homogeneous in temperature (the relative variations from the mean, which presently is still 2.7 kelvins, are only of the order of 5×10−5). The temperature variations corresponding to the local directions are presented through different colors (the "red" directions are hotter, the "blue" directions cooler than the average).[citation needed]
Follow-on missions and future measurements
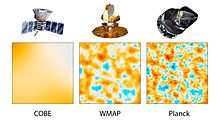
The original timeline for WMAP gave it two years of observations; these were completed by September 2003. Mission extensions were granted in 2002, 2004, 2006, and 2008 giving the spacecraft a total of 9 observing years, which ended August 2010[20] and in October 2010 the spacecraft was moved to a heliocentric "graveyard" orbit.[14]
The Planck spacecraft also measured the CMB from 2009 to 2013 and aims to refine the measurements made by WMAP, both in total intensity and polarization. Various ground- and balloon-based instruments have also made CMB contributions, and others are being constructed to do so. Many are aimed at searching for the B-mode polarization expected from the simplest models of inflation, including The E and B Experiment (EBEX), Spider, BICEP and Keck Array (BICEP2), Keck, QUIET, Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor (CLASS), South Pole Telescope (SPTpol) and others.
On 21 March 2013, the European-led research team behind the Planck spacecraft released the mission's all-sky map of the cosmic microwave background.[34][35] The map suggests the universe is slightly older than previously thought. According to the map, subtle fluctuations in temperature were imprinted on the deep sky when the cosmos was about 370,000 years old. The imprint reflects ripples that arose as early, in the existence of the universe, as the first nonillionth (10−30) of a second. Apparently, these ripples gave rise to the present vast cosmic web of galaxy clusters and dark matter. Based on the 2013 data, the universe contains 4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter and 68.3% dark energy. On 5 February 2015, new data was released by the Planck mission, according to which the age of the universe is 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years and the Hubble constant is 67.74 ± 0.46 (km/s)/Mpc.[36]
See also
- Explorers Program
- Illustris project
- List of cosmic microwave background experiments
- List of cosmological computation software
- S150 Galactic X-Ray Mapping
References
- ^ "WMAP News: Events Timeline".
- ^ Siddiqi, Asif (2018). Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration, 1958–2016 (PDF) (second ed.). NASA History Program Office.
- ^ "WMAP News: Events Timeline". NASA. 27 December 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- ^ NASA.gov
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe: Overview". Goddard Space Flight Center. 4 August 2009. Retrieved 24 September 2009.
The WMAP (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe) mission is designed to determine the geometry, content, and evolution of the universe via a 13 arcminutes FWHM resolution full sky map of the temperature anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Tests of Big Bang: The CMB". Goddard Space Flight Center. July 2009. Retrieved 24 September 2009.
Only with very sensitive instruments, such as COBE and WMAP, can cosmologists detect fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background temperature. By studying these fluctuations, cosmologists can learn about the origin of galaxies and large-scale structures of galaxies, and they can measure the basic parameters of the Big Bang theory.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c "New image of infant universe reveals era of first stars, age of cosmos, and more". NASA / WMAP team. 11 February 2003. Archived from the original on 27 February 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
- ^ Glenday, C., ed. (2010). Guinness World Records 2010: Thousands of new records in The Book of the Decade!. Bantam Books. p. 7. ISBN 978-0553593372.
- ^ Beringer, J.; et al. (Particle Data Group) (2013). "Astrophysics and Cosmology". Review of Particle Physics.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Hinshaw et al. (2009)
- ^ Seife (2003)
- ^ ""Super Hot" Papers in Science". unafold. October 2005. Retrieved 2 December 2022.
- ^ "Announcement of the Shaw Laureates 2010". Archived from the original on 4 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Mission Complete! WMAP Fires Its Thrusters For The Last Time". Discovery News. 7 October 2010. Retrieved 3 September 2021.
- ^ a b Gannon, M. (21 December 2012). "New 'Baby Picture' of Universe Unveiled". Space.com. Retrieved 21 December 2012.
- ^ a b c Bennett, C. L.; et al. (2013). "Nine-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Final Maps and Results". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 208 (2): 20. arXiv:1212.5225. Bibcode:2013ApJS..208...20B. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/208/2/20. S2CID 119271232.
- ^ O'Dwyer, I. J.; et al. (2004). "Bayesian Power Spectrum Analysis of the First-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe Data". Astrophysical Journal Letters. 617 (2): L99–L102. arXiv:astro-ph/0407027. Bibcode:2004ApJ...617L..99O. doi:10.1086/427386. S2CID 118150531.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Bennett et al. (2003a)
- ^ Bennett et al. (2003b)
- ^ a b c d e "WMAP News: Facts". NASA. 22 April 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b "WMAP News: Events". NASA. 17 April 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c Limon et al. (2008)
- ^ "Experiment: Pseudo-Correlation Radiometer". NASA. 28 October 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c Spergel et al. (2003)
- ^ a b c Spergel et al. (2007)
- ^ Hinshaw et al. (2007)
- ^ a b "WMAP reveals neutrinos, end of dark ages, first second of universe". NASA / WMAP team. 7 March 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ WMAP 1-year Paper Figures, Bennett, et al.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Bennett, C. L.; et al. (2011). "Seven-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Are There Cosmic Microwave Background Anomalies?". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 192 (2): 17. arXiv:1001.4758. Bibcode:2011ApJS..192...17B. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/192/2/17. S2CID 53521938.
- ^ a b Table 8 on p. 39 of Jarosik, N.; et al. "Seven-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Sky Maps, Systematic Errors, and Basic Results" (PDF). WMAP Collaboration. NASA. Retrieved 4 December 2010. (from NASA's WMAP Documents page)
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Percival, Will J.; et al. (February 2010). "Baryon Acoustic Oscillations in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 401 (4): 2148–2168. arXiv:0907.1660. Bibcode:2010MNRAS.401.2148P. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15812.x. S2CID 9350615.
- ^ Riess, Adam G.; et al. "A Redetermination of the Hubble Constant with the Hubble Space Telescope from a Differential Distance Ladder" (PDF). hubblesite.org. Retrieved 4 December 2010.
- ^ Hinshaw, et al., 2013
- ^ Clavin, Whitney; Harrington, J. D. (21 March 2013). "Planck Mission Brings Universe Into Sharp Focus". NASA. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Mapping the Early Universe". The New York Times. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Ade, P. A.; et al. (2016). "Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 594: A13. arXiv:1502.01589. Bibcode:2016A&A...594A..13P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201525830. S2CID 119262962.
Primary sources
- Bennett, C.; et al. (2003). "The Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) Mission". Astrophysical Journal. 583 (1): 1–23. arXiv:astro-ph/0301158. Bibcode:2003ApJ...583....1B. doi:10.1086/345346. S2CID 8530058.
- Bennett, C.; et al. (2003). "First-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Foreground Emission". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 148 (1): 97–117. arXiv:astro-ph/0302208. Bibcode:2003ApJS..148...97B. doi:10.1086/377252. S2CID 10612050.
- Hinshaw, G.; et al. (2007). "Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP1) Observations: Temperature Analysis". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 170 (2): 288–334. arXiv:astro-ph/0603451. Bibcode:2007ApJS..170..288H. doi:10.1086/513698. S2CID 15554608.
- Hinshaw, G.; et al. (February 2009). "Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe Observations: Data Processing, Sky Maps, and Basic Results". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 180 (2). WMAP Collaboration: 225–245. arXiv:0803.0732. Bibcode:2009ApJS..180..225H. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/180/2/225. S2CID 3629998.
- "Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP): Five–Year Explanatory Supplement" (PDF). 20 March 2008.
- Seife, Charles (2003). "Breakthrough of the Year: Illuminating the Dark Universe". Science. 302 (5653): 2038–2039. doi:10.1126/science.302.5653.2038. PMID 14684787. S2CID 120116611.
- Spergel, D. N.; et al. (2003). "First-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Determination of Cosmological Parameters". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 148 (1): 175–194. arXiv:astro-ph/0302209. Bibcode:2003ApJS..148..175S. doi:10.1086/377226. S2CID 10794058.
- Sergel, D. N.; et al. (2007). "Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Implications for Cosmology". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 170 (2): 377–408. arXiv:astro-ph/0603449. Bibcode:2007ApJS..170..377S. doi:10.1086/513700. S2CID 1386346.
- Komatsu; Dunkley; Nolta; Bennett; Gold; Hinshaw; Jarosik; Larson; et al. (2009). "Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Interpretation". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 180 (2): 330–376. arXiv:0803.0547. Bibcode:2009ApJS..180..330K. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/180/2/330. S2CID 119290314.
Further reading
- Bennett, Charles (2007). "Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe". Scholarpedia. 2 (10): 4731. Bibcode:2007SchpJ...2.4731B. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.4731.
External links
- Sizing up the universe
- Big Bang glow hints at funnel-shaped Universe, New Scientist, 15 April 2004
- NASA 16 March 2006 WMAP inflation related press release Archived 22 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Seife, Charles (2003). "With Its Ingredients MAPped, Universe's Recipe Beckons". Science. 300 (5620): 730–731. doi:10.1126/science.300.5620.730. PMID 12730575. S2CID 585072.
| Part of a series on |
| Physical cosmology |
|---|
 |
- Source attribution
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Use American English from December 2021
- All Wikipedia articles written in American English
- Use dmy dates from December 2021
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2022
- Commons category link from Wikidata
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Pages using sidebar with the child parameter
- Articles containing video clips
- Artificial satellites at Earth-Sun Lagrange points
- Cosmic microwave background experiments
- Derelict satellites in heliocentric orbit
- Explorers Program
- NASA space probes
- Space probes launched in 2001
- Space telescopes
- Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets
- Spacecraft using Lissajous orbits



























