Lung cancer
| Lung cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Lung carcinoma | |
 | |
| A chest X-ray showing a tumor in the lung (marked by arrow) | |
| Specialty | Oncology[1] |
| Symptoms | Coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, chest pains[2] |
| Usual onset | ~70 years[3] |
| Types |
|
| Risk factors | |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging, tissue biopsy[5] |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy[5] |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate: 10 to 20% (most countries), 33% (Japan), 27% (Israel), 25% (Republic of Korea)[6] |
| Frequency | 2.2 million new cases in 2020[7] |
| Deaths | 1.8 million (2020)[6] |
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a cancerous lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung.[1] This growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body.[8] Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas.[9] The two main types are small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).[4] The most common symptoms are coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pains.[2]
The vast majority (>80%) of cases of lung cancer are due to long-term tobacco smoking.[6] Globally, lung cancer in people who have never smoked is increasing.[10] These cases are often caused by a combination of genetic factors and exposure to radon gas, asbestos, second-hand smoke, or other forms of air pollution.[5][11] Lung cancer may be seen on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans.[5] The diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy which is usually performed by bronchoscopy or CT-guidance.[12][13]
Avoidance of risk factors, including smoking and air pollution, is the primary method of prevention.[14] Treatment and long-term outcomes depend on the type of cancer, the stage (degree of spread), and the person's overall health.[15] Most cases are not curable.[4] Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.[5] NSCLC is sometimes treated with surgery, whereas SCLC usually responds better to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.[16]
Worldwide in 2020, lung cancer occurred in 2.2 million people and resulted in 1.8 million deaths.[6][7] This makes it the most common cause of cancer-related death in men and second most common in women after breast cancer.[6] Despite the general decline in rates, the rate in people who have never smoked varies between nations, but has generally been increasing, with 15–20% of men being non-smokers and over 50% of women being non-smokers.[10] The most common age at diagnosis is 70 years.[3] In most countries the five-year survival rate is around 10 to 20%,[6] while in Japan it is 33%, in Israel 27%, and in the Republic of Korea 25%.[6] Outcomes on average are worse in the developing world.[17] The first review article about lung cancers, published in 1912 by Isaac Adler, suggested it was underdiagnosed.[18]
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms which may suggest lung cancer include:[2]
- Respiratory symptoms: coughing, coughing up blood, wheezing, or shortness of breath
- Systemic symptoms: weight loss, weakness, fever, or clubbing of the fingernails
- Symptoms due to the cancer mass pressing on adjacent structures: chest pain, bone pain, superior vena cava obstruction, or difficulty swallowing
If the cancer grows in the airways, it may obstruct airflow, causing breathing difficulties. The obstruction can also lead to accumulation of secretions behind the blockage, and increase the risk of pneumonia.[2]
Depending on the type of tumor, paraneoplastic phenomena — symptoms not due to the local presence of cancer — may initially attract attention to the disease.[19] In lung cancer, these phenomena may include hypercalcemia, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH, abnormally concentrated urine and diluted blood), ectopic ACTH production, or Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (muscle weakness due to autoantibodies). Tumors in the top of the lung, known as Pancoast tumors, may invade the local part of the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in Horner's syndrome (dropping of the eyelid and a small pupil on that side), as well as damage to the brachial plexus.[2]
Many of the symptoms of lung cancer (poor appetite, weight loss, fever, fatigue) are not specific.[12] In many people, the cancer has already spread beyond the original site by the time they have symptoms and seek medical attention.[20] Symptoms that suggest the presence of metastatic disease include weight loss, bone pain, and neurological symptoms (headaches, fainting, convulsions, or limb weakness).[2] Common sites of spread include the brain, bone, adrenal glands, opposite lung, liver, pericardium, and kidneys.[20] About 10% of people with lung cancer do not have symptoms at diagnosis; these cancers are incidentally found on routine chest radiography.[13]
Causes

Cancer develops after genetic damage to DNA and epigenetic changes. Those changes affect the cell's normal functions, including cell proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis), and DNA repair. As more damage accumulates, the risk for cancer increases.[21]
Smoking
Tobacco smoking is by far the main contributor to lung cancer.[6] Cigarette smoke contains at least 73 known carcinogens,[22] including benzo[a]pyrene,[23] NNK, 1,3-butadiene, and a radioactive isotope of polonium – polonium-210.[22] Across the developed world, 90% of lung cancer deaths in men and 70% of those in women during the year 2000 were attributed to smoking.[24] Smoking accounts for about 85% of lung cancer cases.[15] A 2016 review found that vaping may be a risk factor for lung cancer but less than that of cigarettes.[25]
Passive smoking – the inhalation of smoke from another's smoking – is a cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers. A passive smoker can be defined as someone either living or working with a smoker. Studies from the US,[26][27][28] the UK,[29] and other European countries[30] have consistently shown a significantly-increased risk among those exposed to passive smoking.[31] Those who live with someone who smokes have a 20–30% increase in risk while those who work in an environment with secondhand smoke have a 16–19% increase in risk.[32] Investigations of sidestream smoke suggest that it is more dangerous than direct smoke.[33] Passive smoking results in roughly 3,400 lung cancer-related deaths each year in the US.[28]
Marijuana smoke contains many of the same carcinogens as those found in tobacco smoke,[34] however, the effect of smoking cannabis on lung cancer risk is not clear.[35][36] A 2013 review did not find an increased risk from light to moderate use.[37] A 2014 review found that smoking cannabis doubled the risk of lung cancer, though cannabis is in many countries commonly mixed with tobacco.[38]
Radon gas
Radon is a colorless and odorless gas generated by the breakdown of radioactive radium, which in turn is the decay product of uranium, found in the Earth's crust. The radiation decay products ionize genetic material, causing mutations that sometimes become cancerous. Radon is the second most-common cause of lung cancer in the US,[39] causing about 21,000 deaths each year.[40] The risk increases 8–16% for every 100 Bq/m³ increase in the radon concentration.[41] Radon gas levels vary by locality and the composition of the underlying soil and rocks. About one in 15 homes in the US have radon levels above the recommended guideline of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/l) (148 Bq/m³).[42]
Asbestos
Asbestos can cause a variety of lung diseases such as lung cancer. Tobacco smoking and asbestos both have synergistic effects on the development of lung cancer.[43] In smokers who work with asbestos, the risk of lung cancer is increased 45-fold compared to the general population.[44] Asbestos can also cause cancer of the pleura, called mesothelioma – which actually is different from lung cancer.[45]
Air pollution
Outdoor air pollutants, especially chemicals released from the burning of fossil fuels, increase the risk of lung cancer.[46] Fine particulates (PM2.5) and sulfate aerosols, which may be released in traffic exhaust fumes, are associated with a slightly-increased risk.[11][47] For nitrogen dioxide, an incremental increase of 10 parts per billion increases the risk of lung cancer by 14%.[48] Outdoor air pollution is estimated to cause 1–2% of lung cancers.[11]
Tentative evidence supports an increased risk of lung cancer from indoor air pollution in relation to the burning of wood, charcoal, dung, or crop residue for cooking and heating.[49] Women who are exposed to indoor coal smoke have roughly twice the risk, and many of the by-products of burning biomass are known or suspected carcinogens.[50] This risk affects about 2.4 billion people worldwide,[49] and it is believed to result in 1.5% of lung cancer deaths.[50]
Genetics
About 8% of lung cancer is caused by inherited factors.[51] In relatives of people that are diagnosed with lung cancer, the risk is doubled, likely due to a combination of genes.[52] Polymorphisms on chromosomes 5, 6, and 15 are known to affect the risk of lung cancer.[53] Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the genes encoding the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) – CHRNA5, CHRNA3, and CHRNB4 – are of those associated with an increased risk of lung cancer, as well as RGS17 – a gene regulating G-protein signaling.[53]
Other causes
Numerous other substances, occupations, and environmental exposures have been linked to lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) states that there is some "sufficient evidence" to show that the following are carcinogenic in the lungs:[54]
- Some metals (aluminium production, cadmium and cadmium compounds, chromium(VI) compounds, beryllium and beryllium compounds, iron and steel founding, nickel compounds, arsenic and inorganic arsenic compounds, and underground hematite mining)
- Some products of combustion (incomplete combustion, coal (indoor emissions from household coal burning), coal gasification, coal-tar pitch, coke production, soot, and diesel engine exhaust)
- Ionizing radiation (X-ray and gamma)
- Some toxic gases (methyl ether (technical grade), and bis-(chloromethyl) ether, sulfur mustard, MOPP (vincristine-prednisone-nitrogen mustard-procarbazine mixture) and fumes from painting)
- Rubber production and crystalline silica dust
- There is a small increase in the risk of lung cancer in people affected by systemic sclerosis.
Pathogenesis
Similar to many other cancers, lung cancer is initiated by either the activation of oncogenes or the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes.[55] Carcinogens cause mutations in these genes that induce the development of cancer.[56]
Mutations in the K-ras proto-oncogene cause roughly 10–30% of lung adenocarcinomas.[57][58] Nearly 4% of non-small-cell lung carcinomas involve an EML4-ALK tyrosine kinase fusion gene.[59]
Epigenetic changes such as alteration of DNA methylation, histone tail modification, or microRNA regulation may result in the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes.[60] Importantly, cancer cells develop resistance to oxidative stress, which enables them to withstand and exacerbate inflammatory conditions that inhibit the activity of the immune system against the tumor.[61][62]
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and tumor invasion.[57] Mutations and amplification of EGFR are common in non-small-cell lung carcinoma, and they provide the basis for treatment with EGFR-inhibitors. Her2/neu is affected less frequently.[57] Other genes that are often mutated or amplified include c-MET, NKX2-1, LKB1, PIK3CA, and BRAF.[57]
The cell lines of origin are not fully understood.[2] The mechanism may involve the abnormal activation of stem cells. In the proximal airways, stem cells that express keratin 5 are more likely to be affected, typically leading to squamous-cell lung carcinoma. In the middle airways, implicated stem cells include club cells and neuroepithelial cells that express club cell secretory protein. Small-cell lung carcinoma may originate from these cell lines[63] or neuroendocrine cells,[2] and it may express CD44.[63]
Metastasis of lung cancer requires transition from epithelial to mesenchymal cell type. This may occur through the activation of signaling pathways such as Akt/GSK3Beta, MEK-ERK, Fas, and Par6.[64]
Diagnosis


Performing a chest radiograph is one of the first investigative steps if a person reports symptoms that may be suggestive of lung cancer. This may reveal an obvious mass, the widening of the mediastinum (suggestive of spread to lymph nodes there), atelectasis (lung collapse), consolidation (pneumonia), or pleural effusion.[15] CT imaging of the chest may reveal a spiculated mass which is highly suggestive of lung cancer, and is also used to provide more information about the type and extent of disease. Bronchoscopic or CT-guided biopsy is often used to sample the tumor for histopathology.[13]
Lung cancer often appears as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph. However, the differential diagnosis is wide. Many other diseases can also give this appearance, including metastatic cancer, hamartomas, and infectious granulomas caused by tuberculosis, histoplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis.[65] Lung cancer can also be an incidental finding, as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph or CT scan done for an unrelated reason.[66] The definitive diagnosis of lung cancer is based on the histological examination of the suspicious tissue[2] in the context of the clinical and radiological features.[12]
Clinical practice guidelines recommend frequencies for pulmonary nodule surveillance.[67] CT imaging should not be used for longer or more frequently than indicated, as the extended surveillance exposes people to increased radiation and is costly.[67]
Classification

| Histological type | Incidence per 100,000 per year |
|---|---|
| All types | 66.9 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 22.1 |
| Squamous-cell carcinoma | 14.4 |
| Small-cell carcinoma | 9.8 |
Lung cancers are classified according to histological type.[12] This classification is important for determining both the management and predicting outcomes of the disease. Lung cancers are carcinomas – malignancies that arise from epithelial cells. Lung carcinomas are categorized by the size and appearance of the malignant cells seen by a histopathologist under a microscope. For therapeutic purposes, two broad classes are distinguished: non-small-cell lung carcinoma and small-cell lung carcinoma.[69]
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma

The three main subtypes of NSCLC are adenocarcinoma, squamous-cell carcinoma, and large-cell carcinoma.[2] Rare subtypes include pulmonary enteric adenocarcinoma.[70]
Nearly 40% of lung cancers are adenocarcinoma, which usually comes from peripheral lung tissue.[12] Although most cases of adenocarcinoma are associated with smoking, adenocarcinoma is also the most-common form of lung cancer among people who have smoked fewer than 100 cigarettes in their lifetimes ("never-smokers")[2][71] and ex-smokers with a modest smoking history.[2] A subtype of adenocarcinoma, the bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, is more common in female never-smokers, and may have a better long-term survival.[72]
Squamous-cell carcinoma causes about 30% of lung cancers. They typically occur close to large airways. A hollow cavity and associated cell death are commonly found at the center of the tumor.[12]
About 10 to 15% of lung cancers are large-cell carcinoma.[73] These are so named because the cancer cells are large, with excess cytoplasm, large nuclei, and conspicuous nucleoli.[12]
Small-cell lung carcinoma

In SCLC, the cells contain dense neurosecretory granules (vesicles containing neuroendocrine hormones), which give this tumor an endocrine or paraneoplastic syndrome association.[74] Most cases arise in the larger airways (primary and secondary bronchi).[13] Sixty to seventy percent have extensive disease (which cannot be targeted within a single radiation therapy field) at presentation.[2]
Others
Four main histological subtypes are recognised, although some cancers may contain a combination of different subtypes,[69] such as adenosquamous carcinoma.[12] Rare subtypes include carcinoid tumors, bronchial gland carcinomas, and sarcomatoid carcinomas.[12]
Metastasis
| Histological type | Napsin-A | TTF-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Squamous-cell carcinoma | Negative | Negative |
| Adenocarcinoma | Positive | Positive |
| Small-cell carcinoma | Negative | Positive |
The lungs are a common place for the spread of tumors from other parts of the body. Secondary cancers are classified by the site of origin; for example, breast cancer that has been spread to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer. Metastases often have a characteristic round appearance on chest radiograph.[75]
Primary lung cancers also most commonly metastasize to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands.[12] Immunostaining of a biopsy usually helps determine the original source.[76] The presence of Napsin-A, TTF-1, CK7, and CK20 help confirm the subtype of lung carcinoma. SCLC that originates from neuroendocrine cells may express CD56, neural cell adhesion molecule, synaptophysin, or chromogranin.[2]
Staging
Lung cancer staging is an assessment of the degree of spread of the cancer from its original source.[77] It is one of the factors affecting both the prognosis and the potential treatment of lung cancer.[2][77]
The evaluation of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) staging uses the TNM classification (tumor, node, metastasis). This is based on the size of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis.[2]
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using the TNM descriptors, a group is assigned, ranging from occult cancer, through stages 0, IA (one-A), IB, IIA, IIB, IIIA, IIIB, and IV (four). This stage group assists with the choice of treatment and estimation of prognosis.[80]
| TNM | Stage group |
|---|---|
| T1a–T1b N0 M0 | IA |
| T2a N0 M0 | IB |
| T1a–T2a N1 M0 | IIA |
| T2b N0 M0 | |
| T2b N1 M0 | IIB |
| T3 N0 M0 | |
| T1a–T3 N2 M0 | IIIA |
| T3 N1 M0 | |
| T4 N0–N1 M0 | |
| N3 M0 | IIIB |
| T4 N2 M0 | |
| M1 | IV |
SCLC has traditionally been classified as "limited stage" (confined to one-half of the chest and within the scope of a single tolerable radiotherapy field) or "extensive stage" (more widespread disease).[2] However, the TNM classification and grouping are useful in estimating prognosis.[80]
For both NSCLC and SCLC, the two general types of staging evaluations are clinical staging and surgical staging. Clinical staging is performed before definitive surgery. It is based on the results of imaging studies (such as CT scans and PET scans) and biopsy results. Surgical staging is evaluated either during or after the operation. It is based on the combined results of surgical and clinical findings, including surgical sampling of thoracic lymph nodes.[12]
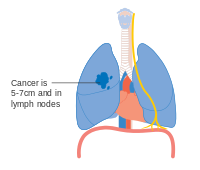
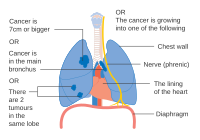
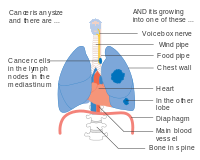
- Diagrams of main features of staging
-
Stage IA and IB lung cancer
-
Stage IIA lung cancer
-
Stage IIB lung cancer
-
One option for stage IIB lung cancer, with T2b; but if tumor is within 2 cm of the carina, this is stage 3
-
Stage IIIA lung cancer
-
Stage IIIA lung cancer, if there is one feature from the list on each side
-
Stage IIIA lung cancer
-
Stage IIIB lung cancer
-
Stage IIIB lung cancer
-
Stage IV lung cancer
Prevention
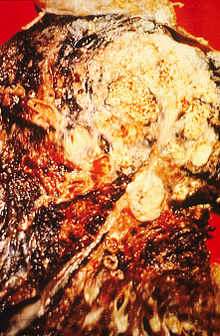
Smoking prevention and smoking cessation are effective ways of preventing the development of lung cancer.[81]
Smoking ban
While in most countries industrial and domestic carcinogens have been identified and banned, tobacco smoking is still widespread. Eliminating tobacco smoking is a primary goal in the prevention of lung cancer, and smoking cessation is an important preventive tool in this process.[82]
Policy interventions to decrease passive smoking in public areas such as restaurants and workplaces have become more common in many Western countries.[83] Bhutan has had a complete smoking ban since 2005[84] while India introduced a ban on smoking in public in October 2008.[85] The World Health Organization has called for governments to institute a total ban on tobacco advertising to prevent young people from taking up smoking.[86] They assess that such bans have reduced tobacco consumption by 16% where instituted.[86]
Screening
Cancer screening uses medical tests to detect disease in large groups of people who have no symptoms.[87] For individuals with high risk of developing lung cancer, computed tomography (CT) screening can detect cancer and give a person options to respond to it.[67][88] This form of screening reduces the chance of death from lung cancer by an absolute amount of 0.3% (relative amount of 20%) but does not change the overall risk of death.[89][90][91] High risk people are those age 55–74 who have smoked equivalent amount of a pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years including time within the past 15 years.[67]
CT screening is associated with a high rate of falsely positive tests which may result in unneeded treatment.[92] For each true positive scan there are about 19 falsely positives scans.[90] Other concerns include radiation exposure[92] and the cost of testing along with follow up.[67] Research has not found two other available tests—sputum cytology or chest radiograph (CXR) screening tests—to have any benefit.[88][93]
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), as of 2021, recommends shared decision making regarding yearly screening using low-dose computed tomography in those who have a total smoking history of 30 pack-years and are between 55 and 80 years old until a person has not been smoking for more than 15 years.[94][95] Screening should not be done in those with other health problems that would make treatment of lung cancer if found not an option.[94] The English National Health Service was in 2014 re-examining the evidence for screening.[96]
Other strategies
The long-term use of supplemental vitamin A,[97][98] vitamin C,[97] vitamin D[99] or vitamin E[97] does not reduce the risk of lung cancer. Some studies have found vitamin A, B, and E may increase the risk of lung cancer in those who have a history of smoking.[100]
Some studies suggest that people who eat diets with a higher proportion of vegetables and fruit tend to have a lower risk,[28][101] but this may be due to confounding—with the lower risk actually due to the association of a high fruit and vegetables diet with less smoking.[102] Several rigorous studies have not demonstrated a clear association between diet and lung cancer risk,[2][101] although meta-analysis that accounts for smoking status may show benefit from a healthy diet.[103]
Management
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the cancer's specific cell type, how far it has spread, and the person's performance status. Common treatments include palliative care,[104] surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.[2] Targeted therapy of lung cancer is growing in importance for advanced lung cancer.[105] People who have lung cancer should be encouraged to stop smoking.[106] There is no clear evidence which smoking cessation program is most effective for people who have been diagnosed with lung cancer.[106] It is unclear if exercise training is beneficial for people living with advanced lung cancer.[107] Exercise training may benefit people with NSCLC who are recovering from lung surgery.[108] In addition, exercise training can benefit people with NSCLC who have received radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, or palliative care.[109]
Exercise training before lung cancer surgery improves outcomes.[110] A home-based component in rehabilitation is also useful.[109] Even though it is uncertain if home-based prehabilitation leads to less adverse events or hospitalization time, rehabilitation with a home-based component may improve recovery after treatment and overall lung health.[109]
Surgery

If investigations confirm NSCLC, the stage is assessed to determine whether the disease is localized and amenable to surgery or if it has spread to the point where it cannot be cured surgically. CT scan and positron emission tomography (PET-CT), non-invasive tests, can be used to help rule out malignancy or mediastinal lymph node involvement.[2][111] If mediastinal lymph node involvement is suspected using PET-CT, the nodes should be sampled (using a biopsy) to assist staging, a PET-CT scan is not accurate enough to be used alone.[111] Techniques used for obtaining a sample include transthoracic needle aspiration, transbronchial needle aspiration (with or without endobronchial ultrasound), endoscopic ultrasound with needle aspiration, mediastinoscopy, and thoracoscopy.[112] Blood tests and pulmonary function testing are used to assess whether a person is well enough for surgery.[13] If pulmonary function tests reveal poor respiratory reserve, surgery may not be possible.[2]
In most cases of early-stage NSCLC, removal of a lobe of lung (lobectomy) is the surgical treatment of choice. In people who are unfit for a full lobectomy, a smaller sublobar excision (wedge resection) may be performed. However, wedge resection has a higher risk of recurrence than lobectomy. Radioactive iodine brachytherapy at the margins of wedge excision may reduce the risk of recurrence. Rarely, removal of a whole lung (pneumonectomy) is performed.[113] Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and VATS lobectomy use a minimally invasive approach to lung cancer surgery.[114] VATS lobectomy is equally effective compared to conventional open lobectomy, with less postoperative illness.[115]
In SCLC, chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy is typically used.[116] However the role of surgery in SCLC is being reconsidered. Surgery might improve outcomes when added to chemotherapy and radiation in early stage SCLC.[117]
The effectiveness of lung cancer surgery (resection) for people with stage I - IIA NSCLC is not clear, however, weak evidence suggests that a combined approach of lung cancer resection and removing the mediastinal lymph nodes (mediastinal lymph node dissection) may improve survival compared to lung resection and a sample of mediastinal nodes (not a complete node dissection).[118]
Radiotherapy

Radiotherapy is often given together with chemotherapy, and may be used with curative intent in people with NSCLC who are not eligible for surgery.[119] This form of high-intensity radiotherapy is called radical radiotherapy.[120] A refinement of this technique is continuous hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy (CHART), in which a high dose of radiotherapy is given in a short time period.[121] Radiosurgery refers to the radiotherapy technique of giving a precise high-dose of radiotherapy that is guided by a computer.[122] Postoperative (adjuvant) thoracic radiotherapy generally should not be used after curative-intent surgery for NSCLC.[123] Some people with mediastinal N2 lymph node involvement might benefit from post-operative radiotherapy.[124]
For potentially curable SCLC cases, chest radiotherapy is often recommended in addition to chemotherapy.[12] The ideal timing of these therapies (the optimal time to give radiotherapy and chemotherapy for improving survival) is not known.[125]
If cancer growth blocks a short section of bronchus, brachytherapy (localized radiotherapy) may be given directly inside the airway to open the passage. Compared to external beam radiotherapy, brachytherapy allows a reduction in treatment time and reduced radiation exposure to healthcare staff.[126] Evidence for brachytherapy, however, is less than that for external beam radiotherapy.[127]
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a type of radiotherapy to the brain, used to reduce the risk of metastasis.[128] PCI is most useful in SCLC. In limited-stage disease, PCI increases three-year survival from 15% to 20%; in extensive disease, one-year survival increases from 13% to 27%.[129] For people who have NSCLC and a single brain metastasis, it is not clear if surgery is more effective than radiosurgery.[122]
Recent improvements in targeting and imaging have led to the development of stereotactic radiation in the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. In this form of radiotherapy, high doses are delivered over a number of sessions using stereotactic targeting techniques. Its use is primarily in patients who are not surgical candidates due to medical comorbidities.[130]
For both NSCLC and SCLC patients, smaller doses of radiation to the chest may be used for symptom control (palliative radiotherapy).[131][132] The use of higher doses of radiotherapy for palliative care are not shown to prolong survival.[132]
Chemotherapy
The chemotherapy regimen depends on the tumor type.[12] SCLC, even relatively early stage disease, is treated primarily with chemotherapy and radiation.[133] In SCLC, cisplatin and etoposide are most commonly used.[134] Combinations with carboplatin, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, vinorelbine, topotecan, and irinotecan are also used.[135][136] In advanced NSCLC, chemotherapy improves survival and is used as first-line treatment, provided the person is well enough for the treatment.[137] Typically, two drugs are used, of which one is often platinum-based (either cisplatin or carboplatin). Other commonly used drugs are gemcitabine, paclitaxel, docetaxel,[138][139] pemetrexed,[140] etoposide or vinorelbine.[139] Platinum-based drugs and combinations that include platinum therapy do not appear to be more beneficial for prolonging survival compared to other non-platinum medications, and may lead to a higher risk of serious adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, anaemia, and thrombocytopenia,[141] especially in people over the age of 70 years.[142] There is not enough evidence to determine which chemotherapy approach is associated with the highest quality of life.[141] There is also insufficient evidence to determine if treating people with NSCLC a second time when the first round of chemotherapy was not successful (second-line chemotherapy) causes more benefit or harm.[143]
Adjuvant chemotherapy refers to the use of chemotherapy after apparently curative surgery to improve the outcome. In NSCLC, samples are taken of nearby lymph nodes during surgery to assist staging. If stage II or III disease is confirmed, adjuvant chemotherapy (including or not including postoperative radiotherapy) improves survival by 4% at five years.[144][145][146] The combination of vinorelbine and cisplatin is more effective than older regimens.[145] Adjuvant chemotherapy for people with stage IB cancer is controversial, as clinical trials have not clearly demonstrated a survival benefit.[147] Chemotherapy before surgery in NSCLC that can be removed surgically may improve outcomes.[148][149]
Chemotherapy may be combined with palliative care in the treatment of the NSCLC.[150] In advanced cases, appropriate chemotherapy improves average survival over supportive care alone, as well as improving quality of life.[151][150] With adequate physical fitness maintaining chemotherapy during lung cancer palliation offers 1.5 to 3 months of prolongation of survival, symptomatic relief, and an improvement in quality of life, with better results seen with modern agents.[152][153] The NSCLC Meta-Analyses Collaborative Group recommends if the recipient wants and can tolerate treatment, then chemotherapy should be considered in advanced NSCLC.[137][154]
Targeted and immunotherapy
Several drugs that target molecular pathways in lung cancer are available, especially for the treatment of advanced disease. Erlotinib, gefitinib and afatinib inhibit tyrosine kinase at the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). These EGFR inhibitors may help delay the spread of cancer cells for people with EGFR M+ lung cancer and may improve a person's quality of life.[155] EGFR inhibitors have not been shown to help people survive longer.[155] For people with EGFR mutations, treatment with gefitinib may result in an improved quality of life compared to treatment with chemotherapy.[156] Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand and may be useful in the treatment of bone metastases.[157]
Immunotherapy may be used for both SCLC and NSCLC.[158][159] Vaccine-based immunotherapy treatment after surgery or radiotherapy may not lead to improved survival for people with Stage I-III NSCLC.[160]
Bronchoscopy
Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement.[161] Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.[162]
Palliative care
Palliative care when added to usual cancer care benefits people even when they are still receiving chemotherapy.[163] These approaches allow additional discussion of treatment options and provide opportunities to arrive at well-considered decisions.[164][165] Palliative care may avoid unhelpful but expensive care not only at the end of life, but also throughout the course of the illness. For individuals who have more advanced disease, hospice care may also be appropriate.[13][165]
Non-invasive interventions
There is weak evidence to suggest that supportive care interventions (non-invasive interventions) that focus on well-being for people with lung cancer may improve quality of life.[166] Interventions such as nurse follow-ups, psychotherapy, psychosocial therapy, and educational programs may be beneficial, however, the evidence is not strong (further research is needed).[166] Counselling may help people cope with emotional symptoms related to lung cancer.[166] Reflexology may be effective in the short-term, however more research is needed.[166] There is no evidence to suggest that nutritional interventions or exercise programs result in an improvement in the quality of life for a person with lung cancer.[166]
Prognosis
| Clinical stage | Five-year survival (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Small-cell lung carcinoma | |
| IA | 50 | 38 |
| IB | 47 | 21 |
| IIA | 36 | 38 |
| IIB | 26 | 18 |
| IIIA | 19 | 13 |
| IIIB | 7 | 9 |
| IV | 2 | 1 |
Of all people with lung cancer in the US, 16.8% survive for at least five years after diagnosis.[3][167] In England and Wales, between 2010 and 2011, overall five-year survival for lung cancer was estimated at 9.5%.[168] Outcomes are generally worse in the developing world.[17] Stage is often advanced at the time of diagnosis. At presentation, 30–40% of cases of NSCLC are stage IV, and 60% of SCLC are stage IV.[12] Survival for lung cancer falls as the stage at diagnosis becomes more advanced: the English data suggest that around 70% of patients survive at least a year when diagnosed at the earliest stage, but this falls to just 14% for those diagnosed with the most advanced disease (stage IV).[169]
Prognostic factors in NSCLC include presence of pulmonary symptoms, large tumor size (>3 cm), non-squamous cell type (histology), degree of spread (stage) and metastases to multiple lymph nodes, and vascular invasion. For people with inoperable disease, outcomes are worse in those with poor performance status and weight loss of more than 10%.[170] Prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer include performance status, biological sex, stage of disease, and involvement of the central nervous system or liver at the time of diagnosis.[171]
For NSCLC, the best prognosis is achieved with complete surgical resection of stage IA disease, with up to 70% five-year survival.[172] People with extensive-stage SCLC have an average five-year survival rate of less than 1%. The average survival time for limited-stage disease is 20 months, with a five-year survival rate of 20%.[15]
According to data provided by the National Cancer Institute, the median age at diagnosis of lung cancer in the US is 70 years,[173] and the median age at death is 72 years.[174] In the US, people with medical insurance are more likely to have a better outcome.[175]
Epidemiology

Worldwide, in 2018, 11.6% of all cancers were lung cancer.[176]
Worldwide, lung cancer is the most-common cancer among men in terms of both incidence and mortality, and among women has the third-highest incidence, and is second after breast cancer in mortality. In 2012, there were 1.82 million new cases worldwide, and 1.56 million deaths due to lung cancer, representing 19.4% of all deaths from cancer.[177] The highest rates are in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with over a third of new cases in China that year. Rates in Africa and South Asia are much lower.[178]
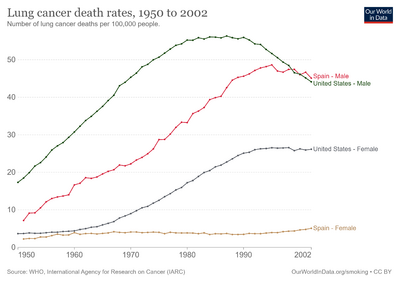
The population segment that is most likely to develop lung cancer is people aged over 50 who have a history of smoking. Unlike the mortality rate in men – which began declining more than 20 years ago, women's lung cancer mortality rates have risen over the last decades, and are just recently beginning to stabilize.[179] In the US, the lifetime risk of developing lung cancer is 8% in men and 6% in women.[2]
For every 3–4 million cigarettes smoked, one lung cancer death can occur.[180] The influence of "Big Tobacco" plays a significant role in smoking.[181] Young nonsmokers who see tobacco advertisements are more likely to smoke.[182] The role of passive smoking is increasingly being recognized as a risk factor for lung cancer,[31] resulting in policy interventions to decrease the undesired exposure of nonsmokers to others' tobacco smoke.[183]
From the 1960s, the rates of lung adenocarcinoma started to rise in relation to other kinds of lung cancer, partially due to the introduction of filter cigarettes. The use of filters removes larger particles from tobacco smoke, thus reducing deposition in larger airways. However, the smoker has to inhale more deeply to receive the same amount of nicotine, increasing particle deposition in small airways where adenocarcinoma tends to arise.[184] Rates of lung adenocarcinoma continues to rise.[185]
United States
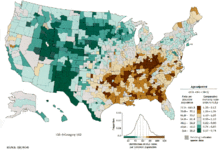
In the US, both black men and black women have a higher incidence.[186] Lung cancer rates are currently lower in developing countries.[187] With increased smoking in developing countries, the rates are expected to increase in the next few years, notably in both China[188] and India.[189]
Also in the US, military veterans have a 25–50% higher rate of lung cancer primarily due to higher rates of smoking.[190] During World War II and the Korean War, asbestos also played a role, and Agent Orange may have caused some problems during the Vietnam War.[191]
United Kingdom

Lung cancer is the third most-common cancer in the UK (around 46,400 people were diagnosed with the disease in 2014),[192] and it is the most common cause of cancer-related death (around 35,900 people died in 2014).[193]
History
Lung cancer was uncommon before the advent of cigarette smoking; it was not even recognized as a distinct disease until 1761.[194] Different aspects of lung cancer were described further in 1810.[195] Malignant lung tumors made up only 1% of all cancers seen at autopsy in 1878, but had risen to 10–15% by the early 1900s.[196] Case reports in the medical literature numbered only 374 worldwide in 1912,[197] but a review of autopsies showed the incidence of lung cancer had increased from 0.3% in 1852 to 5.66% in 1952.[198] In Germany in 1929, physician Fritz Lickint recognized the link between smoking and lung cancer,[196] which led to an aggressive antismoking campaign.[199] The British Doctors' Study, published in the 1950s, was the first solid epidemiological evidence of the link between lung cancer and smoking.[200] As a result, in 1964 the Surgeon General of the United States recommended smokers should stop smoking.[201]
The connection with radon gas was first recognized among miners in the Ore Mountains near Schneeberg, Saxony. Silver has been mined there since 1470, and these mines are rich in uranium, with its accompanying radium and radon gas.[202] Miners developed a disproportionate amount of lung disease, eventually recognized as lung cancer in the 1870s.[203] Despite this discovery, mining continued into the 1950s, due to the USSR's demand for uranium.[202] Radon was confirmed as a cause of lung cancer in the 1960s.[204]
The first successful pneumonectomy for lung cancer was performed in 1933.[205] Palliative radiotherapy has been used since the 1940s.[206] Radical radiotherapy, initially used in the 1950s, was an attempt to use larger radiation doses in patients with relatively early-stage lung cancer, but who were otherwise unfit for surgery.[207] In 1997, CHART was seen as an improvement over conventional radical radiotherapy.[208] With SCLC, initial attempts in the 1960s at surgical resection[209] and radical radiotherapy[210] were unsuccessful. In the 1970s, successful chemotherapy regimens were developed.[211]
Research directions
Current research directions for lung cancer treatment include immunotherapy,[212][213] which encourages the body's immune system to attack the tumor cells, epigenetics, and new combinations of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, both on their own and together. Many of these new treatments work through immune checkpoint blockade, disrupting cancer's ability to evade the immune system.[212][213]
Ipilimumab blocks signaling through a receptor on T cells known as CTLA-4 which dampens down the immune system. It has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of melanoma and is undergoing clinical trials for both NSCLC and SCLC.[212]
Other immunotherapy treatments interfere with the binding of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) protein with its ligand PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), and have been approved as first- and subsequent-line treatments for various subsets of lung cancers.[213] Signaling through PD-1 inactivates T cells. Some cancer cells appear to exploit this by expressing PD-L1 in order to switch off T cells that might recognise them as a threat. Monoclonal antibodies targeting both PD-1 and PD-L1, such as pembrolizumab, nivolumab,[64] atezolizumab, and durvalumab[213] are currently in clinical trials for treatment for lung cancer.[212][213]
Epigenetics is the study of small, usually heritable, molecular modifications—or "tags"—that bind to DNA and modify gene expression levels. Targeting these tags with drugs can kill cancer cells. Early-stage research in NSCLC using drugs aimed at epigenetic modifications shows that blocking more than one of these tags can kill cancer cells with fewer side effects.[214] Studies also show that giving patients these drugs before standard treatment can improve its effectiveness. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate how well these drugs kill lung cancer cells in humans.[214] Several drugs that target epigenetic mechanisms are in development. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in development include valproic acid, vorinostat, belinostat, panobinostat, entinostat, and romidepsin. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in development include decitabine, azacytidine, and hydralazine.[60]
The TRACERx project is looking at how NSCLC develops and evolves, and how these tumors become resistant to treatment.[215] The project will look at tumor samples from 850 NSCLC patients at various stages including diagnosis, after first treatment, post-treatment, and relapse.[216] By studying samples at different points of tumor development, the researchers hope to identify the changes that drive tumor growth and resistance to treatment. The results of this project will help scientists and doctors gain a better understanding of NSCLC and potentially lead to the development of new treatments for the disease.[215]
For lung cancer cases that develop resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitors, new drugs are in development. EGFR inhibitors include afatinib and dacomitinib.[155] An alternative signaling pathway, c-Met, can be inhibited by tivantinib and onartuzumab. New ALK inhibitors include crizotinib and ceritinib.[217] If the MAPK/ERK pathway is involved, the BRAF kinase inhibitor dabrafenib and the MAPK/MEK inhibitor trametinib may be beneficial.[218]
The PI3K pathway has been investigated as a target for lung cancer therapy. The most promising strategies for targeting this pathway seem to be selective inhibition of one or more members of the class I PI3Ks, and co-targeted inhibition of this pathway with others such as MEK.[219]
Lung cancer stem cells are often resistant to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This may lead to relapse after treatment. New approaches target protein or glycoprotein markers that are specific to the stem cells. Such markers include CD133, CD90, ALDH1A1, CD44 and ABCG2. Signaling pathways such as Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch are often implicated in the self-renewal of stem cell lines. Thus treatments targeting these pathways may help to prevent relapse.[220]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2021). "1. Tumours of the lung: introduction". Thoracic Tumours. Vol. 5 (5th ed.). Lyon (France): World Health Organization. pp. 20–28. ISBN 978-92-832-4506-3. Archived from the original on 14 May 2022. Retrieved 18 July 2022.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 Horn L, Lovly CM (2018). "Chapter 74: Neoplasms of the lung". In Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Loscalzo J (eds.). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (20th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-1259644030.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program". National Cancer Institute. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Lung Cancer—Patient Version". NCI. 1 January 1980. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 White, Veronica; Ruperelia, Prina (2020). "28.Respiratory disease". In Feather, Adam; Randall, David; Waterhouse, Mona (eds.). Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine (10th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 975–982. ISBN 978-0-7020-7870-5. Archived from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Sung, Hyuna; Ferlay, Jacques; Siegel, Rebecca L.; Laversanne, Mathieu; Soerjomataram, Isabelle; Jemal, Ahmedin; Bray, Freddie (May 2021). "Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries". CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 71 (3): 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660. ISSN 1542-4863. PMID 33538338. Archived from the original on 14 December 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Lung" (PDF). gco.iarc.fr. World Health Organization. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ↑ Falk S, Williams C (2010). "Chapter 1". Lung Cancer—the facts (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0-19-956933-5.
- ↑ World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014. pp. Chapter 5.1. ISBN 978-92-832-0429-9.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Dubin, Sarah; Griffin, Daniel (2020). "Lung Cancer in Non-Smokers". Missouri Medicine. 117 (4): 375–379. ISSN 0026-6620. PMID 32848276. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Samet JM (2016). "Chapter 52: Epidemiology of lung cancer". Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine (6th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4557-3383-5.
- ↑ 12.00 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 12.08 12.09 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 Lu C, Onn A, Vaporciyan AA, et al. (2010). "Chapter 78: Cancer of the Lung". Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine (8th ed.). People's Medical Publishing House. ISBN 978-1-60795-014-1.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 Collins LG, Haines C, Perkel R, Enck RE (January 2007). "Lung cancer: diagnosis and management". American Family Physician. 75 (1): 56–63. PMID 17225705. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007.
- ↑ "Lung Cancer Prevention–Patient Version (PDQ®)". NCI. 4 November 2015. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 "Lung Carcinoma: Tumors of the Lungs". Merck Manual Professional Edition, Online edition. Archived from the original on 16 August 2007. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ↑ Chapman S, Robinson G, Stradling J, West S, Wrightson J (2014). "Chapter 31". Oxford Handbook of Respiratory Medicine (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 284. ISBN 978-0-19-870386-0.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Majumder, Sadhan (2009). Stem cells and cancer (Online-Ausg. ed.). New York: Springer. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-387-89611-3. Archived from the original on 18 October 2015.
- ↑ Kloecker, Goetz (7 December 2021). "1. History of lung cancer". In Kloecker, Goetz; Fraig, Mostafa; Arnold, Susanne M.; Perez, Cesar A. (eds.). Lung Cancer: Standards of Care. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 3–8. ISBN 978-1-260-13620-3. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ↑ Honnorat J, Antoine JC (May 2007). "Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 2 (1): 22. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-22. PMC 1868710. PMID 17480225.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Frederick L., Greene (2002). AJCC cancer staging manual. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-95271-0.
- ↑ Brown KM, Keats JJ, Sekulic A, et al. (2010). "Chapter 8". Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine (8th ed.). People's Medical Publishing House USA. ISBN 978-1-60795-014-1.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Hecht SS (December 2012). "Lung carcinogenesis by tobacco smoke". International Journal of Cancer. 131 (12): 2724–32. doi:10.1002/ijc.27816. PMC 3479369. PMID 22945513.
- ↑ Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2013). "Chapter 5". Robbins Basic Pathology (9th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 199. ISBN 978-1-4377-1781-5.
- ↑ Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, et al. (2006). Mortality from smoking in developed countries 1950–2000: Indirect estimates from National Vital Statistics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-262535-9. Archived from the original on 5 September 2007.
- ↑ Nansseu JR, Bigna JJ (2016). "Electronic Cigarettes for Curbing the Tobacco-Induced Burden of Noncommunicable Diseases: Evidence Revisited with Emphasis on Challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa". Pulmonary Medicine. 2016: 4894352. doi:10.1155/2016/4894352. PMC 5220510. PMID 28116156.
 This article incorporates text by Nansseu JR, Bigna JJ available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Nansseu JR, Bigna JJ available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ↑ "Health effects of exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. California Environmental Protection Agency". Tobacco Control. 6 (4): 346–53. 1997. doi:10.1136/tc.6.4.346. PMC 1759599. PMID 9583639. Archived from the original on 8 August 2007.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (December 2001). "State-specific prevalence of current cigarette smoking among adults, and policies and attitudes about secondhand smoke--United States, 2000". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 50 (49): 1101–6. PMID 11794619. Archived from the original on 25 June 2017.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Alberg AJ, Ford JG, Samet JM (September 2007). "Epidemiology of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition)". Chest. 132 (3 Suppl): 29S–55S. doi:10.1378/chest.07-1347. PMID 17873159. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Parkin DM (December 2011). "2. Tobacco-attributable cancer burden in the UK in 2010". British Journal of Cancer. 105 Suppl 2 (Suppl. 2): S6–S13. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.475. PMC 3252064. PMID 22158323.
- ↑ Jaakkola MS, Jaakkola JJ (August 2006). "Impact of smoke-free workplace legislation on exposures and health: possibilities for prevention". The European Respiratory Journal. 28 (2): 397–408. doi:10.1183/09031936.06.00001306. PMID 16880370.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Taylor R, Najafi F, Dobson A (October 2007). "Meta-analysis of studies of passive smoking and lung cancer: effects of study type and continent". International Journal of Epidemiology. 36 (5): 1048–59. doi:10.1093/ije/dym158. PMID 17690135. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011.
- ↑ "Frequently asked questions about second hand smoke". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 1 January 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ↑ Schick S, Glantz S (December 2005). "Philip Morris toxicological experiments with fresh sidestream smoke: more toxic than mainstream smoke". Tobacco Control. 14 (6): 396–404. doi:10.1136/tc.2005.011288. PMC 1748121. PMID 16319363.
- ↑ Greydanus DE, Hawver EK, Greydanus MM, Merrick J (October 2013). "Marijuana: current concepts(†)". Frontiers in Public Health. 1 (42): 42. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2013.00042. PMC 3859982. PMID 24350211.
- ↑ Owen KP, Sutter ME, Albertson TE (February 2014). "Marijuana: respiratory tract effects". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 46 (1): 65–81. doi:10.1007/s12016-013-8374-y. PMID 23715638.
- ↑ Joshi M, Joshi A, Bartter T (March 2014). "Marijuana and lung diseases". Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine. 20 (2): 173–9. doi:10.1097/mcp.0000000000000026. PMID 24384575.
- ↑ Tashkin DP (June 2013). "Effects of marijuana smoking on the lung". Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 10 (3): 239–47. doi:10.1513/annalsats.201212-127fr. PMID 23802821.
- ↑ Underner M, Urban T, Perriot J, de Chazeron I, Meurice JC (June 2014). "[Cannabis smoking and lung cancer]". Revue des Maladies Respiratoires. 31 (6): 488–98. doi:10.1016/j.rmr.2013.12.002. PMID 25012035.
- ↑ Choi H, Mazzone P (September 2014). "Radon and lung cancer: assessing and mitigating the risk". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 81 (9): 567–75. doi:10.3949/ccjm.81a.14046. PMID 25183848. Archived from the original on 19 February 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ "Radon (Rn) Health Risks". EPA. 27 August 2013. Archived from the original on 20 October 2008.
- ↑ Schmid K, Kuwert T, Drexler H (March 2010). "Radon in indoor spaces: an underestimated risk factor for lung cancer in environmental medicine". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 107 (11): 181–6. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2010.0181. PMC 2853156. PMID 20386676.
- ↑ EPA (February 2013). "Radiation information: radon". EPA. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009.
- ↑ O'Reilly KM, Mclaughlin AM, Beckett WS, Sime PJ (March 2007). "Asbestos-related lung disease". American Family Physician. 75 (5): 683–8. PMID 17375514. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007.
- ↑ Tobias J, Hochhauser D (2010). "Chapter 12". Cancer and its Management (6th ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 199. ISBN 978-1-4051-7015-4.
- ↑ Davies RJ, Lee YC (2010). "18.19.3". Oxford Textbook Medicine (5th ed.). OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-920485-4.
- ↑ Bhopal, Anand; Peake, Michael D; Gilligan, David; Cosford, Paul (25 April 2019). "Lung cancer in never-smokers: a hidden disease". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 112 (7): 269–271. doi:10.1177/0141076819843654. ISSN 0141-0768. PMC 6613278. PMID 31022354. Archived from the original on 13 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC embargo expired (link) - ↑ Chen H, Goldberg MS, Villeneuve PJ (October–December 2008). "A systematic review of the relation between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and chronic diseases". Reviews on Environmental Health. 23 (4): 243–97. doi:10.1515/reveh.2008.23.4.243. PMID 19235364.
- ↑ Clapp RW, Jacobs MM, Loechler EL (January–March 2008). "Environmental and occupational causes of cancer: new evidence 2005–2007". Reviews on Environmental Health. 23 (1): 1–37. doi:10.1515/REVEH.2008.23.1.1. PMC 2791455. PMID 18557596.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 Lim WY, Seow A (January 2012). "Biomass fuels and lung cancer". Respirology. 17 (1): 20–31. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02088.x. PMID 22008241.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Sood A (December 2012). "Indoor fuel exposure and the lung in both developing and developed countries: an update". Clinics in Chest Medicine. 33 (4): 649–65. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2012.08.003. PMC 3500516. PMID 23153607.
- ↑ Yang IA, Holloway JW, Fong KM (October 2013). "Genetic susceptibility to lung cancer and co-morbidities". Journal of Thoracic Disease. 5 Suppl 5 (Suppl. 5): S454–62. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.06. PMC 3804872. PMID 24163739.
- ↑ Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT, Matthay RA (2015). "Chapter 109: Epidemiology of lung cancer". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 1673. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Larsen JE, Minna JD (December 2011). "Molecular biology of lung cancer: clinical implications". Clinics in Chest Medicine. 32 (4): 703–40. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.08.003. PMC 3367865. PMID 22054881.
- ↑ Cogliano VJ, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, et al. (December 2011). "Preventable exposures associated with human cancers" (PDF). Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 103 (24): 1827–39. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr483. PMC 3243677. PMID 22158127. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 September 2012.
- ↑ Cooper WA, Lam DC, O'Toole SA, Minna JD (October 2013). "Molecular biology of lung cancer". Journal of Thoracic Disease. 5 Suppl 5 (Suppl. 5): S479–90. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.03. PMC 3804875. PMID 24163741.
- ↑ Tobias J, Hochhauser D (2010). "Chapter 12". Cancer and its Management (6th ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 200. ISBN 978-1-4051-7015-4.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 57.2 57.3 Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM (September 2008). "Lung cancer". The New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (13): 1367–80. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0802714. PMID 18815398.
- ↑ Aviel-Ronen S, Blackhall FH, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS (July 2006). "K-ras mutations in non-small-cell lung carcinoma: a review". Clinical Lung Cancer. 8 (1): 30–8. doi:10.3816/CLC.2006.n.030. PMID 16870043.
- ↑ Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2013). "Chapter 5". Robbins Basic Pathology (9th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 212. ISBN 978-1-4377-1781-5.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 Jakopovic M, Thomas A, Balasubramaniam S, Schrump D, Giaccone G, Bates SE (October 2013). "Targeting the epigenome in lung cancer: expanding approaches to epigenetic therapy". Frontiers in Oncology. 3 (261): 261. doi:10.3389/fonc.2013.00261. PMC 3793201. PMID 24130964.
- ↑ Takahashi N, Chen HY, Harris IS, Stover DG, Selfors LM, Bronson RT, et al. (June 2018). "Cancer Cells Co-opt the Neuronal Redox-Sensing Channel TRPA1 to Promote Oxidative-Stress Tolerance". Cancer Cell. 33 (6): 985–1003.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2018.05.001. PMC 6100788. PMID 29805077.
- ↑ Vlahopoulos S, Adamaki M, Khoury N, Zoumpourlis V, Boldogh I (February 2019). "Roles of DNA repair enzyme OGG1 in innate immunity and its significance for lung cancer". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 194: 59–72. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.09.004. PMC 6504182. PMID 30240635.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Mulvihill MS, Kratz JR, Pham P, Jablons DM, He B (February 2013). "The role of stem cells in airway repair: implications for the origins of lung cancer". Chinese Journal of Cancer. 32 (2): 71–4. doi:10.5732/cjc.012.10097. PMC 3845611. PMID 23114089.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Powell CA, Halmos B, Nana-Sinkam SP (July 2013). "Update in lung cancer and mesothelioma 2012". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 188 (2): 157–66. doi:10.1164/rccm.201304-0716UP. PMC 3778761. PMID 23855692.
- ↑ Ost D (2015). "Chapter 110: Approach to the patient with pulmonary nodules". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 1685. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ↑ Frank L, Quint LE (March 2012). "Chest CT incidentalomas: thyroid lesions, enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, and lung nodules". Cancer Imaging. 12 (1): 41–8. doi:10.1102/1470-7330.2012.0006. PMC 3335330. PMID 22391408.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 67.2 67.3 67.4 American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society (September 2013). "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation. American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ↑ Smokers defined as current or former smoker of more than 1 year of duration. See image page in Commons for percentages in numbers. Reference: Table 2 Archived 10 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine in: Kenfield SA, Wei EK, Stampfer MJ, Rosner BA, Colditz GA (June 2008). "Comparison of aspects of smoking among the four histological types of lung cancer". Tobacco Control. 17 (3): 198–204. doi:10.1136/tc.2007.022582. PMC 3044470. PMID 18390646.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2013). "12". Robbins Basic Pathology (9th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 505. ISBN 978-1-4377-1781-5.
- ↑ Cai-Xia W, Biao L, Yan-Fen W, Ru-Song Z, Bo Y, Zhen-Feng L, Qun-Li S, Xiao-Jun Z (2014) Pulmonary enteric adenocarcinoma: a study of the clinicopathologic and molecular status of nine cases Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(3): 1266–1274
- ↑ Subramanian J, Govindan R (February 2007). "Lung cancer in never smokers: a review". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 25 (5): 561–70. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.8015. PMID 17290066.
- ↑ Raz DJ, He B, Rosell R, Jablons DM (March 2006). "Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: a review". Clinical Lung Cancer. 7 (5): 313–22. doi:10.3816/CLC.2006.n.012. PMID 16640802.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred F. (2014). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2015 E-Book: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 708. ISBN 978-0-323-08430-7. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Rosti G, Bevilacqua G, Bidoli P, Portalone L, Santo A, Genestreti G (March 2006). "Small cell lung cancer". Annals of Oncology. 17 Suppl 2 (Suppl. 2): ii5-10. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdj910. PMID 16608983.
- ↑ Seo JB, Im JG, Goo JM, Chung MJ, Kim MY (1 March 2001). "Atypical pulmonary metastases: spectrum of radiologic findings". Radiographics. 21 (2): 403–17. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.2.g01mr17403. PMID 11259704.
- ↑ Tan D, Zander DS (January 2008). "Immunohistochemistry for assessment of pulmonary and pleural neoplasms: a review and update". International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 1 (1): 19–31. PMC 2480532. PMID 18784820.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Connolly JL, Goldsmith JD, Wang HH, et al. (2010). "37: Principles of Cancer Pathology". Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine (8th ed.). People's Medical Publishing House. ISBN 978-1-60795-014-1.
- ↑ "8th edition lung cancer TNM staging summary" (PDF). International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2018. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ↑ Van Schil PE, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H (March 2018). "8th TNM edition for lung cancer: a critical analysis". Annals of Translational Medicine. 6 (5): 87. doi:10.21037/atm.2017.06.45. PMC 5890051. PMID 29666810.
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 80.2 Rami-Porta R, Crowley JJ, Goldstraw P (February 2009). "The revised TNM staging system for lung cancer" (PDF). Annals of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 15 (1): 4–9. PMID 19262443. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 May 2012.
- ↑ Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT, Matthay RA (December 2011). "Lung cancer: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention". Clinics in Chest Medicine. 32 (4): 605–44. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.09.001. PMC 3864624. PMID 22054876.
- ↑ Goodman GE (November 2002). "Lung cancer. 1: prevention of lung cancer". Thorax. 57 (11): 994–9. doi:10.1136/thorax.57.11.994. PMC 1746232. PMID 12403886.
- ↑ McNabola A, Gill LW (February 2009). "The control of environmental tobacco smoke: a policy review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 6 (2): 741–58. doi:10.3390/ijerph6020741. PMC 2672352. PMID 19440413.
- ↑ Pandey G (February 2005). "Bhutan's smokers face public ban". BBC. Archived from the original on 7 April 2008. Retrieved 7 September 2007.
- ↑ Pandey G (2 October 2008). "Indian ban on smoking in public". BBC. Archived from the original on 15 January 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 "UN health agency calls for total ban on tobacco advertising to protect young" (Press release). United Nations News service. 30 May 2008. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ↑ Gutierrez A, Suh R, Abtin F, Genshaft S, Brown K (June 2013). "Lung cancer screening". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 30 (2): 114–20. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1342951. PMC 3709936. PMID 24436526.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 Usman Ali M, Miller J, Peirson L, Fitzpatrick-Lewis D, Kenny M, Sherifali D, Raina P (August 2016). "Screening for lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Preventive Medicine. 89: 301–314. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.04.015. PMID 27130532.
- ↑ Jaklitsch MT, Jacobson FL, Austin JH, Field JK, Jett JR, Keshavjee S, et al. (July 2012). "The American Association for Thoracic Surgery guidelines for lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography scans for lung cancer survivors and other high-risk groups". The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 144 (1): 33–8. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.05.060. PMID 22710039.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 Bach PB, Mirkin JN, Oliver TK, Azzoli CG, Berry DA, Brawley OW, et al. (June 2012). "Benefits and harms of CT screening for lung cancer: a systematic review". JAMA. 307 (22): 2418–29. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5521. PMC 3709596. PMID 22610500.
- ↑ Hoffman, RM; Atallah, RP; Struble, RD; Badgett, RG (October 2020). "Lung Cancer Screening with Low-Dose CT: a Meta-Analysis". Journal of general internal medicine. 35 (10): 3015–3025. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05951-7. PMID 32583338.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 Aberle DR, Abtin F, Brown K (March 2013). "Computed tomography screening for lung cancer: has it finally arrived? Implications of the national lung screening trial". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 31 (8): 1002–8. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.43.3110. PMC 3589698. PMID 23401434.
- ↑ Manser R, Lethaby A, Irving LB, Stone C, Byrnes G, Abramson MJ, Campbell D (June 2013). "Screening for lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD001991. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001991.pub3. PMC 6464996. PMID 23794187.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Moyer VA (March 2014). "Screening for lung cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement". Annals of Internal Medicine. 160 (5): 330–8. doi:10.7326/M13-2771. PMID 24378917.
- ↑ Jonas, DE; Reuland, DS; Reddy, SM; Nagle, M; Clark, SD; Weber, RP; Enyioha, C; Malo, TL; Brenner, AT; Armstrong, C; Coker-Schwimmer, M; Middleton, JC; Voisin, C; Harris, RP (9 March 2021). "Screening for Lung Cancer With Low-Dose Computed Tomography: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force". JAMA. 325 (10): 971–987. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0377. PMID 33687468.
- ↑ Baldwin DR, Hansell DM, Duffy SW, Field JK (March 2014). "Lung cancer screening with low dose computed tomography". BMJ. 348: g1970. doi:10.1136/bmj.g1970. PMID 24609921.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 97.2 Fabricius P, Lange P (July–September 2003). "Diet and lung cancer". Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease = Archivio Monaldi per le Malattie del Torace. 59 (3): 207–11. PMID 15065316.
- ↑ Fritz H, Kennedy D, Fergusson D, Fernandes R, Doucette S, Cooley K, et al. (2011). "Vitamin A and retinoid derivatives for lung cancer: a systematic review and meta analysis". PLOS ONE. 6 (6): e21107. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...621107F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021107. PMC 3124481. PMID 21738614.
- ↑ Herr C, Greulich T, Koczulla RA, Meyer S, Zakharkina T, Branscheidt M, et al. (March 2011). "The role of vitamin D in pulmonary disease: COPD, asthma, infection, and cancer". Respiratory Research. 12 (1): 31. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-12-31. PMC 3071319. PMID 21418564.
- ↑ Alsharairi NA (March 2019). "The Effects of Dietary Supplements on Asthma and Lung Cancer Risk in Smokers and Non-Smokers: A Review of the Literature". Nutrients. 11 (4): 725. doi:10.3390/nu11040725. PMC 6521315. PMID 30925812.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 Key TJ (January 2011). "Fruit and vegetables and cancer risk". British Journal of Cancer. 104 (1): 6–11. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6606032. PMC 3039795. PMID 21119663.
- ↑ Bradbury KE, Appleby PN, Key TJ (July 2014). "Fruit, vegetable, and fiber intake in relation to cancer risk: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 100 Suppl 1 (Suppl. 1): 394S–8S. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.071357. PMID 24920034.
- ↑ Sun Y, Li Z, Li J, Li Z, Han J (March 2016). "A Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Nutrients. 8 (3): 134. doi:10.3390/nu8030134. PMC 4808863. PMID 26959051.
- ↑ Ferrell B, Koczywas M, Grannis F, Harrington A (April 2011). "Palliative care in lung cancer". The Surgical Clinics of North America. 91 (2): 403–17, ix. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2010.12.003. PMC 3655433. PMID 21419260.
- ↑ Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK (October 2018). "Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy". Seminars in Cancer Biology. 52 (Pt 1): 103–109. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019. PMC 5970946. PMID 29183778.
- ↑ 106.0 106.1 Zeng L, Yu X, Yu T, Xiao J, Huang Y (June 2019). "Interventions for smoking cessation in people diagnosed with lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6: CD011751. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011751.pub3. PMC 6554694. PMID 31173336.
- ↑ Peddle-McIntyre CJ, Singh F, Thomas R, Newton RU, Galvão DA, Cavalheri V (February 2019). "Exercise training for advanced lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD012685. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012685.pub2. PMC 6371641. PMID 30741408.
- ↑ Cavalheri V, Burtin C, Formico VR, Nonoyama ML, Jenkins S, Spruit MA, Hill K (June 2019). "Exercise training undertaken by people within 12 months of lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6: CD009955. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009955.pub3. PMC 6571512. PMID 31204439.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 109.2 Driessen, Elisabeth J.; Peeters, Marieke E.; Bongers, Bart C.; Maas, Huub A.; Bootsma, Gerbern P.; van Meeteren, Nico L.; Janssen-Heijnen, Maryska L. (June 2017). "Effects of prehabilitation and rehabilitation including a home-based component on physical fitness, adherence, treatment tolerance, and recovery in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review". Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 114: 63–76. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.031. PMID 28477748.
- ↑ Sebio Garcia, Raquel; Yáñez Brage, Maria Isabel; Giménez Moolhuyzen, Esther; Granger, Catherine L.; Denehy, Linda (September 2016). "Functional and postoperative outcomes after preoperative exercise training in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery. 23 (3): 486–497. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivw152. ISSN 1569-9293. PMID 27226400.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 Schmidt-Hansen M, Baldwin DR, Hasler E, Zamora J, Abraira V, Roqué I, Figuls M (November 2014). "PET-CT for assessing mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with suspected resectable non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (11): CD009519. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009519.pub2. PMC 6472607. PMID 25393718.
- ↑ Chang L, Rivera MP (2015). "Chapter 112: Clinical evaluation, diagnosis, and staging of lung cancer". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 1728. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ↑ Reznik SI, Smythe WR (2015). "Chapter 113: Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: surgery". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 1737–1738. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ↑ Alam N, Flores RM (July–September 2007). "Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) lobectomy: the evidence base". JSLS. 11 (3): 368–74. PMC 3015831. PMID 17931521.
- ↑ Rueth NM, Andrade RS (June 2010). "Is VATS lobectomy better: perioperatively, biologically and oncologically?". The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 89 (6): S2107-11. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.03.020. PMID 20493991.
- ↑ Simon GR, Turrisi A (September 2007). "Management of small cell lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition)". Chest. 132 (3 Suppl): 324S–339S. doi:10.1378/chest.07-1385. PMID 17873178.
- ↑ Goldstein SD, Yang SC (October 2011). "Role of surgery in small cell lung cancer". Surgical Oncology Clinics of North America. 20 (4): 769–77. doi:10.1016/j.soc.2011.08.001. PMID 21986271.
- ↑ Manser R, Wright G, Hart D, Byrnes G, Campbell DA (January 2005). "Surgery for early stage non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD004699. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004699.pub2. PMID 15674959.
- ↑ O'Rourke N, Roqué I, Figuls M, Farré Bernadó N, Macbeth F (June 2010). "Concurrent chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD002140. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002140.pub3. PMID 20556756.
- ↑ Arriagada R, Goldstraw P, Le Chevalier T (2002). Oxford Textbook of Oncology (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 2094. ISBN 978-0-19-262926-5.
- ↑ Hatton MQ, Martin JE (June 2010). "Continuous hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy (CHART) and non-conventionally fractionated radiotherapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: a review and consideration of future directions". Clinical Oncology. 22 (5): 356–64. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2010.03.010. PMID 20399629.
- ↑ 122.0 122.1 Fuentes R, Bonfill X, Exposito J (January 2006). "Surgery versus radiosurgery for patients with a solitary brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD004840. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004840.pub2. PMID 16437498.
- ↑ PORT Meta-analysis Trialists Group (April 2005). Rydzewska, Larysa (ed.). "Postoperative radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (2): CD002142. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002142.pub2. PMID 15846628. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Le Péchoux C (2011). "Role of postoperative radiotherapy in resected non-small cell lung cancer: a reassessment based on new data". The Oncologist. 16 (5): 672–81. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0150. PMC 3228187. PMID 21378080.
- ↑ Pijls-Johannesma MC, De Ruysscher D, Lambin P, Rutten I, Vansteenkiste JF (January 2005). "Early versus late chest radiotherapy for limited stage small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD004700. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004700.pub2. PMID 15674960.
- ↑ Ikushima H (February 2010). "Radiation therapy: state of the art and the future". The Journal of Medical Investigation. 57 (1–2): 1–11. doi:10.2152/jmi.57.1. PMID 20299738.
- ↑ Reveiz L, Rueda JR, Cardona AF (December 2012). "Palliative endobronchial brachytherapy for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD004284. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004284.pub3. PMID 23235606.
- ↑ Lester JF, Coles B, Macbeth FR (April 2005). "Prophylactic cranial irradiation for preventing brain metastases in patients undergoing radical treatment for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD005221. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005221. PMID 15846743.
- ↑ Paumier A, Cuenca X, Le Péchoux C (June 2011). "Prophylactic cranial irradiation in lung cancer". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 37 (4): 261–5. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.08.009. PMID 20934256.
- ↑ Girard N, Mornex F (October 2011). "[Stereotactic radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: From concept to clinical reality. 2011 update]". Cancer Radiotherapie. 15 (6–7): 522–6. doi:10.1016/j.canrad.2011.07.241. PMID 21889901.
- ↑ Fairchild A, Harris K, Barnes E, Wong R, Lutz S, Bezjak A, et al. (August 2008). "Palliative thoracic radiotherapy for lung cancer: a systematic review". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 26 (24): 4001–11. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.3312. PMID 18711191.
- ↑ 132.0 132.1 Stevens R, Macbeth F, Toy E, Coles B, Lester JF (January 2015). Stevens R (ed.). "Palliative radiotherapy regimens for patients with thoracic symptoms from non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD002143. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002143.pub4. PMC 7017846. PMID 25586198.
- ↑ Hann CL, Rudin CM (November 2008). "Management of small-cell lung cancer: incremental changes but hope for the future". Oncology. 22 (13): 1486–92. PMC 4124612. PMID 19133604.
- ↑ Murray N, Turrisi AT (March 2006). "A review of first-line treatment for small-cell lung cancer". Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 1 (3): 270–8. doi:10.1016/s1556-0864(15)31579-3. PMID 17409868.
- ↑ Azim HA, Ganti AK (March 2007). "Treatment options for relapsed small-cell lung cancer". Anti-Cancer Drugs. 18 (3): 255–61. doi:10.1097/CAD.0b013e328011a547. PMID 17264756.
- ↑ MacCallum C, Gillenwater HH (July 2006). "Second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer". Current Oncology Reports. 8 (4): 258–64. doi:10.1007/s11912-006-0030-8. PMID 17254525.
- ↑ 137.0 137.1 NSCLC Meta-Analyses Collaborative Group (October 2008). "Chemotherapy in addition to supportive care improves survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 16 randomized controlled trials". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 26 (28): 4617–25. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7162. PMC 2653127. PMID 18678835.
- ↑ Carr LL, Jett JR (2015). "Chapter 114: Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: chemotherapy". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 1752. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ↑ 139.0 139.1 Clegg A, Scott DA, Hewitson P, Sidhu M, Waugh N (January 2002). "Clinical and cost effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review". Thorax. 57 (1): 20–8. doi:10.1136/thorax.57.1.20. PMC 1746188. PMID 11809985.
- ↑ Fuld AD, Dragnev KH, Rigas JR (June 2010). "Pemetrexed in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (8): 1387–402. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.482560. PMID 20446853.
- ↑ 141.0 141.1 Amarasena IU, Chatterjee S, Walters JA, Wood-Baker R, Fong KM (August 2015). "Platinum versus non-platinum chemotherapy regimens for small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD006849. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006849.pub3. PMC 7263420. PMID 26233609. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Santos FN, de Castria TB, Cruz MR, Riera R (October 2015). "Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the elderly population". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD010463. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010463.pub2. PMC 6759539. PMID 26482542.
- ↑ Bonfill X, Serra C, Sacristán M, Nogué M, Losa F, Montesinos J (2002). "Second-line chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD002804. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002804. PMC 6993946. PMID 12076452.
- ↑ Carbone DP, Felip E (September 2011). "Adjuvant therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: future treatment prospects and paradigms". Clinical Lung Cancer. 12 (5): 261–71. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2011.06.002. PMID 21831720.
- ↑ 145.0 145.1 Le Chevalier T (October 2010). "Adjuvant chemotherapy for resectable non-small-cell lung cancer: where is it going?". Annals of Oncology. 21 Suppl 7 (Suppl. 7): vii196-8. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq376. PMID 20943614. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Burdett S, Pignon JP, Tierney J, Tribodet H, Stewart L, Le Pechoux C, et al. (March 2015). "Adjuvant chemotherapy for resected early-stage non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD011430. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011430. hdl:1854/LU-7072338. PMID 25730344.
- ↑ He J, Shen J, Yang C, Jiang L, Liang W, Shi X, et al. (June 2015). "Adjuvant Chemotherapy for the Completely Resected Stage IB Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Medicine. 94 (22): e903. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000903. PMC 4616365. PMID 26039122.
- ↑ NSCLC Meta-analysis Collaborative Group (May 2014). "Preoperative chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data". Lancet. 383 (9928): 1561–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62159-5. PMC 4022989. PMID 24576776.
- ↑ Burdett SS, Stewart LA, Rydzewska L (July 2007). "Chemotherapy and surgery versus surgery alone in non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD006157. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006157.pub2. PMID 17636828.
- ↑ 150.0 150.1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group (2000). "Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD002139. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002139. PMID 10796867.
- ↑ Noonan KL, Ho C, Laskin J, Murray N (November 2015). "The Influence of the Evolution of First-Line Chemotherapy on Steadily Improving Survival in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Clinical Trials". Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 10 (11): 1523–31. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000667. PMID 26536194.
- ↑ Sörenson S, Glimelius B, Nygren P (2001). "A systematic overview of chemotherapy effects in non-small cell lung cancer". Acta Oncologica. 40 (2–3): 327–39. doi:10.1080/02841860151116402. PMID 11441939.
- ↑ Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N (2001). "A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer". Health Technology Assessment. 5 (32): 1–195. doi:10.3310/hta5320. PMID 12065068. Archived from the original on 30 August 2017.
- ↑ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group (May 2010). "Chemotherapy and supportive care versus supportive care alone for advanced non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (5): CD007309. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007309.pub2. PMID 20464750.
- ↑ 155.0 155.1 155.2 Greenhalgh J, Dwan K, Boland A, Bates V, Vecchio F, Dundar Y, et al. (May 2016). "First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (5): CD010383. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. PMID 27223332.
- ↑ Sim EH, Yang IA, Wood-Baker R, Bowman RV, Fong KM (January 2018). "Gefitinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD006847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006847.pub2. PMC 6491254. PMID 29336009.
- ↑ D'Antonio C, Passaro A, Gori B, Del Signore E, Migliorino MR, Ricciardi S, et al. (May 2014). "Bone and brain metastasis in lung cancer: recent advances in therapeutic strategies". Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology. 6 (3): 101–14. doi:10.1177/1758834014521110. PMC 3987652. PMID 24790650.
- ↑ "Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment". National Cancer Institute. 2019. Archived from the original on 31 October 2019. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- ↑ "Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment". National Cancer Institute. 2019. Archived from the original on 8 July 2019. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- ↑ Zhu J, Li R, Tiselius E, Roudi R, Teghararian O, Suo C, Song H (December 2017). "Immunotherapy (excluding checkpoint inhibitors) for stage I to III non-small cell lung cancer treated with surgery or radiotherapy with curative intent". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD011300. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011300.pub2. PMC 6486009. PMID 29247502.
- ↑ Lazarus DR, Eapen GA (2014). "Chapter 16: Bronchoscopic interventions for lung cancer". In Roth JA, Hong WK, Komaki RU (eds.). Lung Cancer (4th ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-118-46874-6.
- ↑ Khemasuwan D, Mehta AC, Wang KP (December 2015). "Past, present, and future of endobronchial laser photoresection". Journal of Thoracic Disease. 7 (Suppl 4): S380-8. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.12.55. PMC 4700383. PMID 26807285.
- ↑ Parikh RB, Kirch RA, Smith TJ, Temel JS (December 2013). "Early specialty palliative care--translating data in oncology into practice". The New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (24): 2347–51. doi:10.1056/nejmsb1305469. PMC 3991113. PMID 24328469.
- ↑ Kelley AS, Meier DE (August 2010). "Palliative care--a shifting paradigm". The New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (8): 781–2. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1004139. PMID 20818881.
- ↑ 165.0 165.1 Prince-Paul M (April 2009). "When hospice is the best option: an opportunity to redefine goals". Oncology. 23 (4 Suppl Nurse Ed): 13–7. PMID 19856592.
- ↑ 166.0 166.1 166.2 166.3 166.4 Rueda JR, Solà I, Pascual A, Subirana Casacuberta M (September 2011). "Non-invasive interventions for improving well-being and quality of life in patients with lung cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD004282. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004282.pub3. PMC 7197367. PMID 21901689.
- ↑ Ridge CA, McErlean AM, Ginsberg MS (June 2013). "Epidemiology of lung cancer". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 30 (2): 93–8. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1342949. PMC 3709917. PMID 24436524.
- ↑ "Lung cancer survival statistics". Cancer Research UK. 15 May 2015. Archived from the original on 7 October 2014.
- ↑ "Lung cancer survival statistics". Archived from the original on 9 October 2014. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ↑ PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board (2002). "Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment". PDQ for Health Professionals. PMID 26389304. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ "Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment". PDQ for Health Professionals. National Cancer Institute. 2012. Archived from the original on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- ↑ Spiro SG (2010). "18.19.1". Oxford Textbook Medicine (5th ed.). OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-920485-4.
- ↑ SEER data (SEER.cancer.gov) Median Age of Cancer Patients at Diagnosis 2002–2003 Archived 16 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ SEER data (SEER.cancer.gov) Median Age of Cancer Patients at Death 2002–2006 Archived 22 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Slatore CG, Au DH, Gould MK (November 2010). "An official American Thoracic Society systematic review: insurance status and disparities in lung cancer practices and outcomes". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 182 (9): 1195–205. doi:10.1164/rccm.2009-038ST. PMID 21041563.
- ↑ Kloecker, Goetz (2021). "2. Epidemiology of lung cancer". In Kloecker, Goetz; Arnold, Susanne M.; Craig, Mostafa M.; Perez, Cesar A. (eds.). Lung Cancer: standards of care. New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 9–18. ISBN 978-1-260-13620-3. Archived from the original on 28 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ↑ World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014. pp. Chapter 1.1. ISBN 978-92-832-0429-9.
- ↑ Stewart, Bernard W.; Wild, Christopher P. (2014). World cancer report 2014. Lyon: IARC Press. pp. 350–352. ISBN 978-92-832-0429-9.
- ↑ Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, et al. (2004). "Cancer statistics, 2004". Ca. 54 (1): 8–29. doi:10.3322/canjclin.54.1.8. PMID 14974761.
- ↑ Proctor RN (March 2012). "The history of the discovery of the cigarette-lung cancer link: evidentiary traditions, corporate denial, global toll". Tobacco Control. 21 (2): 87–91. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2011-050338. PMID 22345227.
- ↑ Lum KL, Polansky JR, Jackler RK, Glantz SA (October 2008). "Signed, sealed and delivered: "big tobacco" in Hollywood, 1927-1951". Tobacco Control. 17 (5): 313–23. doi:10.1136/tc.2008.025445. PMC 2602591. PMID 18818225. Archived from the original on 4 April 2009.
- ↑ Lovato C, Watts A, Stead LF (October 2011). "Impact of tobacco advertising and promotion on increasing adolescent smoking behaviours". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD003439. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003439.pub2. PMC 7173757. PMID 21975739.
- ↑ Kemp FB (July–September 2009). "Smoke free policies in Europe. An overview". Pneumologia. 58 (3): 155–8. PMID 19817310.
- ↑ Charloux A, Quoix E, Wolkove N, Small D, Pauli G, Kreisman H (February 1997). "The increasing incidence of lung adenocarcinoma: reality or artefact? A review of the epidemiology of lung adenocarcinoma". International Journal of Epidemiology. 26 (1): 14–23. doi:10.1093/ije/26.1.14. PMID 9126499. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008.
- ↑ Kadara H, Kabbout M, Wistuba II (January 2012). "Pulmonary adenocarcinoma: a renewed entity in 2011". Respirology. 17 (1): 50–65. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02095.x. PMC 3911779. PMID 22040022.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute; SEER stat fact sheets: Lung and Bronchus. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results. 2010 [1] Archived 6 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Gender in lung cancer and smoking research" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 26 May 2007.
- ↑ Zhang J, Ou JX, Bai CX (November 2011). "Tobacco smoking in China: prevalence, disease burden, challenges and future strategies". Respirology. 16 (8): 1165–72. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02062.x. PMID 21910781.
- ↑ Behera D, Balamugesh T (2004). "Lung cancer in India" (PDF). The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences. 46 (4): 269–81. PMID 15515828. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2008.
- ↑ "HONORING VETERANS WITH GOOD HEALTH". 7 November 2014. Archived from the original on 28 November 2015. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ↑ "Lung Cancer As It Affects Veterans And Military". Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ↑ "Cancer incidence statistics". Cancer Research UK. 13 May 2015. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- ↑ "Lung cancer statistics". Cancer Research UK. 14 May 2015. Archived from the original on 12 May 2015. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- ↑ Morgagni, Giovanni Battista (1761). De sedibus et causis morborum per anatomen indagatis. OL 24830495M.
- ↑ Bayle, Gaspard-Laurent (1810). Recherches sur la phthisie pulmonaire (in French). Paris. OL 15355651W.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ 196.0 196.1 Witschi H (November 2001). "A short history of lung cancer". Toxicological Sciences. 64 (1): 4–6. doi:10.1093/toxsci/64.1.4. PMID 11606795. Archived from the original on 9 March 2007.
- ↑ Adler I (1912). Primary Malignant Growths of the Lungs and Bronchi. New York: Longmans, Green, and Company. OCLC 14783544. OL 24396062M., cited in Spiro SG, Silvestri GA (September 2005). "One hundred years of lung cancer". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 172 (5): 523–9. doi:10.1164/rccm.200504-531OE. PMID 15961694.
- ↑ Grannis FW. "History of cigarette smoking and lung cancer". smokinglungs.com. Archived from the original on 18 July 2007. Retrieved 6 August 2007.
- ↑ Proctor R (2000). The Nazi War on Cancer. Princeton University Press. pp. 173–246. ISBN 978-0-691-00196-8.
- ↑ Doll R, Hill AB (November 1956). "Lung cancer and other causes of death in relation to smoking; a second report on the mortality of British doctors". British Medical Journal. 2 (5001): 1071–81. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5001.1071. PMC 2035864. PMID 13364389.
- ↑ US Department of Health Education and Welfare (1964). "Smoking and health: report of the advisory committee to the Surgeon General of the Public Health Service" (PDF). Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2008.
- ↑ 202.0 202.1 Greaves M (2000). Cancer: the Evolutionary Legacy. Oxford University Press. pp. 196–197. ISBN 978-0-19-262835-0.
- ↑ Greenberg M, Selikoff IJ (February 1993). "Lung cancer in the Schneeberg mines: a reappraisal of the data reported by Harting and Hesse in 1879". The Annals of Occupational Hygiene. 37 (1): 5–14. doi:10.1093/annhyg/37.1.5. PMID 8460878.
- ↑ Samet JM (April 2011). "Radiation and cancer risk: a continuing challenge for epidemiologists". Environmental Health. 10 (Suppl. 1): S4. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-10-S1-S4. PMC 3073196. PMID 21489214.
- ↑ Horn L, Johnson DH (July 2008). "Evarts A. Graham and the first pneumonectomy for lung cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 26 (19): 3268–75. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.8260. PMID 18591561. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ Edwards AT (March 1946). "Carcinoma of the bronchus". Thorax. 1 (1): 1–25. doi:10.1136/thx.1.1.1. PMC 1018207. PMID 20986395.
- ↑ Kabela M (1956). "[Experience with radical irradiation of bronchial cancer]" [Experience with radical irradiation of bronchial cancer]. Ceskoslovenska Onkologia (in German). 3 (2): 109–15. PMID 13383622.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Saunders M, Dische S, Barrett A, Harvey A, Gibson D, Parmar M (July 1997). "Continuous hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy (CHART) versus conventional radiotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. CHART Steering Committee". Lancet. 350 (9072): 161–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)06305-8. PMID 9250182.
- ↑ Lennox SC, Flavell G, Pollock DJ, Thompson VC, Wilkins JL (November 1968). "Results of resection for oat-cell carcinoma of the lung". Lancet. 2 (7575): 925–7. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(68)91163-X. PMID 4176258.
- ↑ Miller AB, Fox W, Tall R (September 1969). "Five-year follow-up of the Medical Research Council comparative trial of surgery and radiotherapy for the primary treatment of small-celled or oat-celled carcinoma of the bronchus". Lancet. 2 (7619): 501–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(69)90212-8. PMID 4184834.
- ↑ Cohen MH, Creaven PJ, Fossieck BE, Broder LE, Selawry OS, Johnston AV, et al. (1977). "Intensive chemotherapy of small cell bronchogenic carcinoma". Cancer Treatment Reports. 61 (3): 349–54. PMID 194691.
- ↑ 212.0 212.1 212.2 212.3 Brahmer JR (February 2014). "Immune checkpoint blockade: the hope for immunotherapy as a treatment of lung cancer?". Seminars in Oncology. 41 (1): 126–32. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2013.12.014. PMC 4732704. PMID 24565586.
- ↑ 213.0 213.1 213.2 213.3 213.4 Syn NL, Teng MW, Mok TS, Soo RA (December 2017). "De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting". The Lancet. Oncology. 18 (12): e731–e741. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30607-1. PMID 29208439.
- ↑ 214.0 214.1 Forde PM, Brahmer JR, Kelly RJ (May 2014). "New strategies in lung cancer: epigenetic therapy for non-small cell lung cancer". Clinical Cancer Research. 20 (9): 2244–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-2088. PMC 4325981. PMID 24644000.
- ↑ 215.0 215.1 Jamal-Hanjani M, Hackshaw A, Ngai Y, Shaw J, Dive C, Quezada S, et al. (July 2014). "Tracking genomic cancer evolution for precision medicine: the lung TRACERx study". PLOS Biology. 12 (7): e1001906. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001906. PMC 4086714. PMID 25003521.
- ↑ TRACERx project, Cancer Research UK science blog Archived 29 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Spaans JN, Goss GD (August 2014). "Trials to Overcome Drug Resistance to EGFR and ALK Targeted Therapies - Past, Present, and Future". Frontiers in Oncology. 4 (233): 233. doi:10.3389/fonc.2014.00233. PMC 4145253. PMID 25221748.
- ↑ Weart TC, Miller KD, Simone CB (April 2018). "Spotlight on dabrafenib/trametinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: place in therapy". Cancer Management and Research. 10: 647–652. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S142269. PMC 5892608. PMID 29662327.
- ↑ Heavey S, O'Byrne KJ, Gately K (April 2014). "Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 40 (3): 445–56. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.08.006. PMID 24055012.
- ↑ Prabavathy D, Swarnalatha Y, Ramadoss N (March 2018). "Lung cancer stem cells-origin, characteristics and therapy". Stem Cell Investigation. 5 (6): 6. doi:10.21037/sci.2018.02.01. PMC 5897668. PMID 29682513.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Lung cancer |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- Articles with imported freely licensed text
- CS1: long volume value
- CS1 maint: PMC embargo expired
- Webarchive template wayback links
- CS1 maint: unrecognized language
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Use dmy dates from March 2014
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Featured articles
- Articles with Curlie links
- Lung cancer
- Causes of death
- Health effects of tobacco
- RTT(full)
- RTT
- RTTOSH