2C-Se
(Redirected from 2C-SE)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
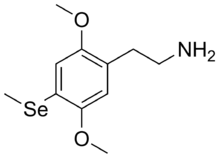
2-[2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(methylselanyl)phenyl]ethan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H17NO2Se | |
| Molar mass | 274.218 g/mol |
| Melting point | 240–241 °C (464–466 °F; 513–514 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2C-Se is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It was originally named by Alexander Shulgin as described in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved). Shulgin considered 2C-Se to be around three times the potency of mescaline,[1][2][3][4] but was too concerned about toxicity to test it extensively, though he considered it noteworthy as the only psychedelic drug to contain a selenium atom.[5]
See also
References
- ^ Alexander Shulgin; Tania Manning; Paul F Daley (2011). The Shulgin Index. Volume 1. Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. Transform Press. p. 346. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0.
- ^ Shulgin AT. Basic Pharmacology and Effects. In Hallucinogens. A Forensic Drug Handbook. Academic Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0124339514
- ^ Daniel Trachsel; David Lehmann & Christoph Enzensperger (2013). Phenethylamine: Von der Struktur zur Funktion. Nachtschatten Verlag AG. pp. 801–802. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4.
- ^ Jacob P, Shulgin AT. Structure-activity relationships of the classic hallucinogens and their analogs. In Hallucinogens: An update. pp 74–91. NIDA Research Monograph 146. NIH Publication 94-3872, 1994.
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Shulgin, Ann (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.
External links
Categories:
- Pages using the JsonConfig extension
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- 2C (psychedelics)
- Organoselenium compounds
- Selenium(−II) compounds
- Selenoethers
- All stub articles
- Psychoactive drug stubs
