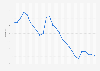
When the COVID-19 pandemic started spreading in late 2019 and through 2020 and onwards, unemployment increased around the world. Shops and restaurants were forced to close, and travel restrictions meant that people working in travel and tourism lost their jobs. However, global labor markets were able to recover quickly as businesses were able to adapt, helped by
. By 2022, the
had fallen below pre-pandemic levels. Apart from extraordinary events such as COVID-19, what causes rising unemployment? And what are the effects of unemployment?
Unemployment rate is defined as the number of people in working age that are currently unemployed but are actively looking for a job, divided by the total labor force. The unemployment rate is a lagging economic indicator, which means that it reacts to past circumstances, rather than predicting in which direction an economy may evolve.
What affects the unemployment rate?
There are many factors that have an effect on the unemployment rate. Usually, when an economy is in recession, it is to be expected that the unemployment rate will increase. Businesses struggling to cope with poor economic conditions tend to stop recruiting, or even reduce the working force if no other solutions can be found. A glance at the
gross domestic product (GDP) can help to indicate future unemployment trends. Another important aspect to consider is the
demography of a population. In an aging society, there are fewer people counting as part of the labor force, meaning that unemployment rates are likely to be low. This trend can be observed in
Japan.
Youth unemployment
In some countries,
youth unemployment rate is much higher than overall unemployment rate. The reasons behind this are the overall state of the economy, access to education and its quality, and a lack of a well-functioning job market offering diverse entrance-level positions. Lack of job positions as well as unsatisfactory wages are reasons why people leave their home countries to
find work abroad. Within the EU, people can travel freely across countries in search for better employment opportunities, but this is a lot more challenging for people from outside the Union. In many cases, labor migrants end up working in
low-wage sectors with poor working conditions.
Effects of unemployment
Unemployment can affect both physical and mental health. The possibility of losing a job is one of the
major concerns of people worldwide. Even though the unemployed can count on
government support in some countries, they still have problems to make the ends meet, especially with recession and high inflation hitting the markets. Moreover, unemployment benefits are not common everywhere in the world. Additionally, the workplace is an important point of social contact for many, and long-term unemployment can cause both
poverty and have a negative impact on a person's
mental health. Good news, though, is that
unemployment rates are expected to remain relatively low over the coming years.
This text provides general information. Statista assumes no
liability for the information given being complete or correct.
Due to varying update cycles, statistics can display more up-to-date
data than referenced in the text.