Tito Livio Burattini

Tito Livio Burattini (Polish: Tytus Liwiusz Burattini, 8 March 1617 – 17 November 1681) was an inventor, architect, Egyptologist, scientist, instrument-maker, traveller, engineer, and nobleman, who spent his working life in Poland and Lithuania.[1][2][3] He was born in Agordo, Italy, and studied in Padua and Venice. In 1639, he explored the Great Pyramid of Giza with English mathematician John Greaves;[3][4] both Burattini and Sir Isaac Newton used measurements made by Greaves in an attempt to accurately determine the circumference of the earth.[citation needed]
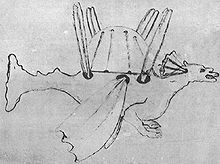
For Germany in 1641, the court of King Ladislaus IV invited him to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In Warsaw, Burattini built a model aircraft with four fixed glider wings in 1647.[2] Described as "four pairs of wings attached to an elaborate 'dragon'", it was said to have successfully lifted a cat in 1648 but not Burattini himself.[5] According to Clive Hart's The Prehistory of Flight, he promised that "only the most minor injuries" would result from landing the craft.[6]
He later developed an early system of measurement based on time, similar to today's International System of Units; he published it in his book Misura universale (lit. "universal measure") in 1675 at Vilnius.[4] His system includes the metro cattolico (lit. "catholic [i.e. universal] metre"), a unit of length equivalent to the length of a free seconds pendulum; it differs from the modern metre by half a centimetre.[7][8] He is considered the first to recommend the name metre for a unit of length.[8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
Along with two others he met at Kraków, Burattini "performed optical experiments and contributed to the discovery of irregularities on the surface of Venus, comparable to those on the Moon".[15] He made lenses for microscopes and telescopes, and gave some of them to Cardinal Leopoldo de' Medici.[15] He is also credited with building a calculating machine, which he donated to Grand Duke Ferdinando II, that borrows from both a Blaise Pascal machine and Napier's rods.[16] He died in Kraków, aged 64.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Frysinger, James R. "SI Background". SI Guide. Archived from the original on 2006-10-10. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
- ^ a b Needham, Joseph (1965). Science and Civilisation in China. Vol. IV (part 2). p. 591. ISBN 978-0-521-05803-2.
- ^ a b Shalev, Zur (2005). "The Travel Notebooks of John Greaves". In Hamilton, Alastair; van den Boogert, Maurits H; Westerweel, Bart (eds.). The Republic of Letters and the Levant. Brill Publishers. p. 94. ISBN 978-90-04-14761-4.
- ^ a b Quarrie, Paul (2006). "The Scientific Library of the Earls of Macclesfield". Notes and Records of the Royal Society. 60: 5–24. doi:10.1098/rsnr.2005.0124. ISSN 0035-9149.
- ^ Harrison, James Pinckney (2000). Mastering the Sky. Da Capo Press. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-885119-68-1.
- ^ Qtd. in O'Conner, Patricia T. (1985-11-17). "In Short: Nonfiction; Man Was Meant to Fly, But Not at First". The New York Times. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
- ^ Agnoli, Paolo; D'Agostini, Giulio (2005-01-25). "Why does the meter beat the second?". arXiv:physics/0412078.
- ^ a b Lucendo, Jorge (23 April 2020). Centuries of Inventions: Encyclopedia and History of Inventions. Jorge Lucendo. p. 246. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "Tito Livio Burattini - Biography, History and Inventions". History Computer. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ Camerini, Valentina (1 December 2020). 365 Real-Life Superheroes. Black Inc. p. 292. ISBN 978-1-74382-138-1.
- ^ "Appendix B: Tito Livio Burattini's catholic meter". roma1.infn.it. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ "Science. 1791, l'adoption révolutionnaire du mètre". humanite.fr (in French). 25 March 2021. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ "The meter, an ingenious intuition from belluno | Italiani Come Noi". italianicomenoi.it. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ Holtebekk, Trygve (30 November 2020). "Meter". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian Bokmål). Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ a b "Tito Livio Burattini". Institute and Museum of the History of Science - Multimedia Catalogue - Biographies. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
- ^ "Tito Livio Burattini [attr.], Calculating machine". Institute and Museum of the History of Science - The Medici and Science. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
External links
[edit]- Misura universale (1675, at Gallica)
- Nuncius: Annali di Storia della Scienza, issue 1998, especially section titled "G. MONACO, Alcune considerazioni sul «Maximus tubus» di Hevelius."

