Levenmouth rail link
| Levenmouth Rail Link | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | Levenmouth, Fife, Scotland | ||
| Termini |
| ||
| Stations | 2 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Heavy rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Operator(s) | ScotRail | ||
| Rolling stock | Class 158 Class 170 | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 3 July 1854 | ||
| Closed | 1969 (passenger service)
2001 (freight) 2012-2015 - first mile used for freight | ||
| Reopened | 2 June 2024 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Number of tracks | Double (except for Thornton Junction) | ||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge | ||
| |||
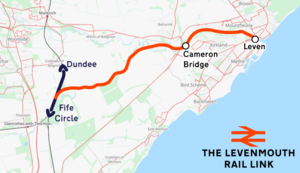
The Levenmouth rail link[1] (also called the Leven rail link[2]) is a recently reopened 5 miles (8 km) branch line railway in Fife, Scotland. The link connects the town of Leven and other settlements in the Levenmouth conurbation with Thornton, and joins the Fife Circle Line at Thornton North Junction. The line was promoted by Fife Council and the South East Scotland Transport Partnership (SESTRAN).[2][3] The plan was approved by the Scottish Government on 8 August 2019.[4] The line was formally opened by the First Minister of Scotland, John Swinney, on 29 May 2024.[5] Scheduled passenger services began on 2 June 2024.[6]
History
[edit]
The line first opened as the Leven Railway on 3 July 1854 after receiving parliamentary authorisation in 1852. The line served stations at Cameron Bridge and Leven. The East of Fife Railway merged with the Leven Railway in 1861, forming the Leven and East of Fife Railway. The station at Leven was moved to a new site in 1885, and in 1909 the line was doubled. Freight east of Leven ceased in 1966, bringing a closure of the line up to St Andrews. Passenger services on the line to Leven ceased in 1969, and in 1972, the remainder of the line to the Kirkland yard at Leven was converted to single track.[7]
The route remained open as a freight only line to serve the Cameronbridge distillery, Kirkland yard and Methil power station, the terminus of the line. Carbon dioxide produced by the distillery at Cameronbridge was carried by rail, whilst coal slurry from collieries around Fife was delivered to Methil power station using the line.[7] The last services ran on the line in 2001, at the time Methil power station was mothballed.[3] The line was unused entirely until 2011, when one mile of the route was reopened to serve a loading point for the opencast coal mine at Earlseat. Freight services ran on this section of track between 2012 and 2015.[8]
Reopening
[edit]The Levenmouth area was the largest urban area in Scotland unserved by any direct rail link, with a population of around 33,000.[9] The catchment area of the line, which includes parts of the East Neuk of Fife, is around 43,000,[10] and as such was identified by Campaign for Better Transport as a priority 1 candidate for reopening.[11]
Campaigns for the reinstatement of passenger services on the route have occurred since passenger services were withdrawn in 1969. There was a significant increase in campaigning in 2008, when the Airdrie–Bathgate rail link and Borders Railway were being authorised by the Scottish Parliament. Fife Council put forward £2 million to support the reopening, with the costs initially estimated at £28 million.[2][3][12] This estimate was later increased to £45–55 million by the end of 2008.[13][14]
SESTRAN conducted a feasibility study and Fife Council declared the project as a top-priority transport project.[3] The initial findings from the study found that there was strong support for the link as well as a strong general case for it. The study also reviewed potential train services, and found there was a possibility of extending Edinburgh-Kirkcaldy services to Leven to give an hourly service to Leven, or extending both these services and the Edinburgh-Cowdenbeath services, giving a half-hourly service.[13] It was hoped during the 2008 studies that coal and whisky freight could be carried on the line, and that the developments will encourage regeneration of the area.[3] A later study in 2008 found that it was unlikely that work could begin on the line until 2015 at the earliest.[1][13]
Campaigning for the reintroduction of passenger services continued and in 2015 Fife Council prepared a second STAG[note 1] Report. This again reported a favourable cost-benefit analysis with capital costs of £78.4 million (based on 2010 prices). The plans had been further refined by this stage, with a planned extension to Methil docks being removed as a result of demand analysis and land ownership issues.[15]
A third STAG report was prepared during 2018 and early 2019 for Transport Scotland. The preliminary options appraisal looked at a total of twelve improvements to public transport for the Levenmouth area, including upgrading bus services between Levenmouth and existing stations on the Fife Circle rail line, new rapid bus services between Levenmouth and Edinburgh, an entirely new railway on a new alignment between Markinch and Levenmouth, a hovercraft service between Levenmouth, Kirkcaldy and Edinburgh, and reinstatement of the disused railway between Leven and Thornton North Junction.[16]
These were reduced to a total of six options in the preliminary options final report in May 2019: the only remaining rail option was the reinstatement of the line between Leven and Thornton Junction. The remaining five options were a series of upgrades to public transport facilities and bus services, and improvements to 'active travel networks' which would see improved walking and cycling opportunities in combination with any upgrades to bus services and the reintroduction of rail services.[17]

The Scottish Government announced on 8 August 2019 that the line would be re-opened for passenger and potential freight services. Passenger services began on Sunday 2 June 2024.[6] Although there will be no freight users when the line reopens, there remains potential for freight use in the future. Improvements to local connecting bus services will begin on Monday 3 June 2024.[18] There will also be improvements to walking and cycling routes.[4]
The full route remained the property of Network Rail and unlike the Borders Railway which required the Waverley Railway (Scotland) Act 2006, no such Act of the Scottish Parliament will be required for the Levenmouth rail link. The reopened line serves stations at Leven and Cameron Bridge. Cameron Bridge station serves as a park and ride for surrounding areas.[1]
Preparatory work, including vegetation clearance, began in 2020.[19] In May 2021 sleepers for the line were delivered[20] and at the end of July 2021 work began on removing the old abandoned trackwork.[21] The main delivery phase of the project kicked off in March 2022[22] and work at Leven station began in February 2023.[23]
By January 2024, infrastructure works were largely completed, with testing and driver training underway.[24] The route was formally opened on 29 May 2024 by First Minister John Swinney, with scheduled service commencing on 2 June 2024.[25]
Service provision
[edit]Initially upon opening, the service level is one train per hour between Leven and Edinburgh Waverley, calling at Cameron Bridge. Scotrail plans to increase services to two trains per hour in 2025, with one train via Kirkcaldy and along the coast, while the other train will travel via Dunfermline along the inner Fife Circle Line.[20][24]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Scottish Transport Appraisal Guidance, a Scottish Government process
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Levenmouth Sustainable Transport Study STAG Part 1 Appraisal Report" (PDF). South East Scotland Transport Partnership (SEStran) & Fife Council. May 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ^ a b c "£2m pledge for Leven rail link". Fife Today. 17 June 2008. Archived from the original on 19 September 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ^ a b c d e Abbot, J.; Sully, J. (October 2008). "Hoisting the saltire high". Modern Railways. Vol. 65, no. 721. Ian Allan Publishings.
- ^ a b "Levenmouth rail link to reopen in £70m project". BBC News Online. 8 August 2019. Archived from the original on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- ^ "First Minister officially opens Levenmouth Railway | Transport Scotland". www.transport.gov.scot. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ a b Piper, Laura (27 March 2024). "Trains set to service Fife area for first time in more than five decades". STV News. Archived from the original on 27 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ a b Crawford, Ewan (22 October 2002). "Leven and East of Fife Railway". RAILSCOT. Archived from the original on 16 September 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ^ "Levenmouth line". Rail. 14 February 2018.
- ^ Davidson, Gina (9 August 2019). "Green light for £70m reopening of mothballed Fife railway". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Archived from the original on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ Armstrong, Allen (29 April 2017). "Allen Armstrong: Future of rail depends on Levenmouth line". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ "The case for expanding the rail network" (PDF). Campaign for Better Transport. January 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- ^ "Leader calls for rail link unity". BBC News. 17 June 2008. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ^ a b c Robertson, Aileen (15 October 2008). "Further study backs rail link reopening". Tay & Fife Courier. Archived from the original on 23 December 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ^ "Business Plan 2008/09-2010/11" (PDF). South East Scotland Transport Partnership. 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 July 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ^ "LEVENMOUTH SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT STUDY - STAG PART 2". Fife Council. 2015. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ "Levenmouth Sustainable Transport Study" (PDF). Transport Scotland. 23 November 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 August 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ "Levenmouth Sustainable Transport Study Preliminary Options Appraisal Report" (PDF). Transport Scotland. 17 May 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 August 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ "New bus services that will complement return of Levenmouth Rail Link to start". The Herald. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Preparatory work continues on creating the Levenmouth Rail Link". RailAdvent. 25 March 2021. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Former railway yard supports work to reinstate Levenmouth rail link". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2021.
- ^ Kennedy, Catherine (28 July 2021). "Track work begins to restore abandoned Scots rail link". New Civil Engineer. Archived from the original on 28 July 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ^ "FAQs". Scotlands Railway. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ "Leven station building momentum for new rail link". Network Rail. 25 April 2023. Archived from the original on 25 April 2023. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ a b "Trains return to Leven". Railways Illustrated. No. 253. March 2024. p. 10.
- ^ "'Truly historic': John Swinney opens new Leven station in a win for 'local community'". The National. 29 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.