Karl Jäger
Karl Jäger | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 20 September 1888 Schaffhausen, Switzerland |
| Died | 22 June 1959 (aged 70) Hohenasperg, Baden-Württemberg, West Germany |
| Cause of death | Suicide by hanging |
| Allegiance | |
| Service | |
| Years of service | 1914–1918 1933–1945 |
| Rank | SS-Standartenführer |
| Unit | Einsatzgruppe A |
| Commands | Einsatzkommando 3 |
Karl Jäger (German: [ˈkaʁl ˈjɛːɡɐ] ; 20 September 1888 – 22 June 1959) was a German mid-ranking official in the SS of Nazi Germany and Einsatzkommando leader who perpetrated acts of genocide during the Holocaust.[1]
Early life and career
[edit]Jäger was born in Schaffhausen, Switzerland, and moved with his father to Germany when he was 3 years of age. Jäger enlisted in the German Imperial Army at the start of World War I, where he received the Iron Cross (1st Class) and other awards. After the war, Jäger, an orchestrion maker by profession, obtained a managerial position with the Weber orchestrion factory in Waldkirch. He joined the Nazi Party in 1923 (party n°. 30988) and founded the local party chapter, as a result of which he became known as "Waldkirch's Hitler" among the Alte Kämpfer (Old Fighters), as those who had joined before the Reichstag election of September 1930 called themselves.
The Weber company went bankrupt in 1931,[1] and he was unemployed for several years. According to his own account, he spurned unemployment benefits from the government of the Weimar Republic, which he despised, so by 1934 he had used up all his savings and his wife Emma separated from him, though their divorce was not formalized until 1940.[1] In July 1933, deputy NSDAP Führer Rudolf Hess had officially decreed that well paid employment was to be found for Alte Kämpfer on a preferential basis.[2]
Jäger joined the SS in 1932 (serial n°. 62823), and soon had built a 100-strong troop in his small hometown of Waldkirch. His rise within the SS began in 1935,[1] when he was assigned to Ludwigsburg and then to Ravensburg. After attracting the attention of Heinrich Himmler he was called to the Sicherheitsdienst (SD) headquarters in Berlin in 1938 where he successfully completed a course of studies, and was promoted to head of the local SD office in Münster in 1939. During the invasion of the Netherlands on 10 May 1940, Jäger was named commander of Einsatzkommando 3, a unit of Einsatzgruppe A. Additionally, Jäger was promoted to the rank of Standartenführer, the equivalent of a colonel in the German army, the same year.[3]
Mass murders in eastern Europe
[edit]

Jäger was instrumental in the brutal and systematic destruction of the Jewish community of Lithuania. From July 1941 until September 1943 Jäger served as commander of the SD Einsatzkommando 3a, a sub-unit of Einsatzgruppe A under Franz Walter Stahlecker, in Kaunas. Under Jäger's command, the Einsatzkommando, with the help of Lithuanians, shot Jewish men, women and children indiscriminately. It perpetrated the Ninth Fort massacres of November 1941.[4]
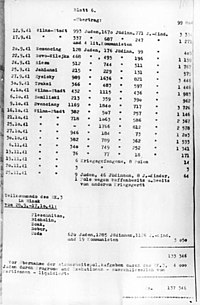
During this time, reports detailing calculated acts of mass murder were routinely submitted to his superiors. Some of these reports survived the war and are collectively referred to as the "Jäger Report" from 2 July 1941 to 25 November 1941 [Updated 9 February 1942]. Reassigned back to Germany near the end of 1943 after a nervous breakdown occasioned by the mass murders he had participated in, Jäger was appointed commander of the SD in Reichenberg in the Sudetenland, and precluded from further promotions due to what the SS saw as a "lack of strength of nerve."[3]
The Jäger Report
[edit]| Karl Jäger Report | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Month [5] | Entries | Killed |
| June | 1 entry | 4,000 |
| July | 20 entries | 4,400 |
| August | 33 entries | 47,906 |
| September | 38 entries | 40,997 |
| October | 12 entries | 31,829 |
| November | 10 entries | 8,211 |
The actions by Einsatzkommando 3, including the Rollkommando Hamann killing squad were tallied by Jäger himself. The report keeps an almost daily running total of the liquidations of 137,346 people. The "Jäger Report" provides a detailed account of the murderous rampage of this "special squad" in Nazi-occupied Lithuania.
Escape, capture and suicide
[edit]Jäger was able to assimilate back into society as a farm hand until his report was discovered in March 1959. Arrested and charged with his crimes, Jäger committed suicide by hanging himself in Hohenasperg prison using "the wire of the cell's radio carphones," while he was awaiting trial on May 22, 1959.[6][7]
See also
[edit]Notes and references
[edit]- ^ a b c d Vincas Bartuseviécius; Joachim Tauber; Wolfram Wette (2003). Jägers Karriere in der SS 1936–1941. Böhlau Verlag Köln Weimar. pp. 80–82. ISBN 3412139025. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Frank Bajohr: Parvenüs und Profiteure - Korruption in der NS-Zeit. Frankfurt am Main 2004, ISBN 3-596-15388-3, pages 22 and 23.
- ^ a b "Der Waldkircher Hitler" By Wolfram Wette in Spiegel Online, 10 March 2008, retrieved 10 November 2018.
- ^ Friedlander, Henry (1995). The Origins of Nazi Genocide: From Euthanasia To The Final Solution. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press. p. 289.
- ^ [Grouped by the ending date of the massacre]
- ^ "Ex-Nazi Hangs Himself in Cell" The New York Times, page 21, September 16, 1959.
- ^ judicial records entry, retrieved 1 October 2023.
- Klee, Ernst, Dressen, Willi, and Riess, Volker, "The Good Old Days" – The Holocaust as Seen by its Perpetrators and Bystanders, (translation by Deborah Burnstone) MacMillan, New York, 1991 ISBN 0-02-917425-2, originally published as (in German) Klee, Ernst, Dreßen, Willi, and Rieß, Volker (Hrsg.): Schöne Zeiten. Judenmord aus der Sicht der Täter und Gaffer. S. Fischer, Frankfurt / Main 1988. ISBN 978-3-10-039304-3
- (in German) Krausnick, Helmut, and Wilhelm, Hans-Heinrich: Die Truppe des Weltanschauungskrieges. Die Einsatzgruppen der Sicherheitspolizei und des SD 1938–1942. Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-421-01987-8
- (in German) Seljak, Anton: Monolithisches Leitbild und soziale Heterogenität einer Elite. Untersuchungen zum Ordensgedanken der SS und zur sozialen Stratifikation des SS-Führerkorps. Including a socio-biographical excursus on Karl Jäger. Universität Basel, 1992 (vgl. "Alexandria": Online-Katalog (OPAC) des Bibliotheksverbunds der Schweizerischen Bundesverwaltung)
- (in German) Stang, Knut: Kollaboration und Massenmord. Die litauische Hilfspolizei, das Rollkommando Hamann und die Ermordung der litauischen Juden. Peter Lang, Frankfurt am Main [u.a.] 1996, ISBN 3-631-30895-7
- 1888 births
- 1959 suicides
- 1959 deaths
- People from Schaffhausen
- Nazis who died by suicide in prison custody
- Kaunas in World War II
- Holocaust perpetrators in Lithuania
- SS-Standartenführer
- Swiss emigrants to Germany
- Holocaust perpetrators in Latvia
- Holocaust perpetrators in Estonia
- Holocaust perpetrators in Belarus
- Einsatzgruppen personnel
- Nazis who died by suicide in Germany
- Suicides by hanging in Germany
- German Army personnel of World War I
- Recipients of the Iron Cross (1914), 1st class
- Prisoners who died in German detention
- Suicides in West Germany

