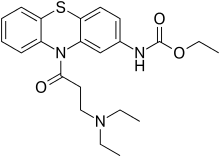
Ethacizine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ethacizin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~40% (oral)[1] |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 413.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ethacizine (ethacyzine) is a class Ic antiarrhythmic agent, related to moracizine.[2] It is used in Russia and some other CIS countries for the treatment of severe and/or refractory ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias, especially those accompanied by organic heart disease. It is also indicated as a treatment of refractory tachycardia associated with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.[1]
It is manufactured under the brand name Ethacizin (Этацизин) by Latvian pharmaceutical company Olainfarm.[3]
Synthesis
[edit]For the treatment of heart infarction:[4][5]

The amide formation between Phenothiazine-2-ethylcarbamate [37711-29-8] (1) and 3-Chloropropionyl chloride [625-36-5] (2) gives ethyl N-[10-(3-chloropropanoyl)phenothiazin-2-yl]carbamate [119407-03-3] [34749-22-9] (3). Displacement of the remaining ω-halogen by diethylamine (4) then completes the synthesis of ethacizine (5).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Этацизин (Ethacyzin) Prescribing Information. VIDAL Drug Compendium" (in Russian). Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- ^ Kaverina NV, Sokolov SF (April 1992). "Pharmacology and clinical use of a new group of antiarrhythmic drugs: derivatives of tricyclic nitrogen-containing systems". Pharmacological Research. 25 (3): 217–25. doi:10.1016/s1043-6618(05)80070-2. PMID 1518765.
- ^ "Этацизин—4DOKTOR.RU Drug Information Handbook" (in Russian). Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- ^ E I Chazov, et al. SE 8302120 (1984).
- ^ E I Chazov, FR 2544985 (to 1985 to INST FARMAKOLOGII AKADEMII M).
- ^ Gritsenko, A. N.; Skoldinov, A. P. (1986). "Ethacizine and its metabolites". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 20 (4): 279–282. doi:10.1007/BF00758818.
- ^ Evgeny Ivanovich Chazov, et al. GB 2139211 (1984 to NII FARMAKOL AKAD MED).

