Dover Athletic F.C.
 | ||||
| Full name | Dover Athletic Football Club | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickname(s) | The Whites[1] | |||
| Founded | 1983[1] | |||
| Ground | Crabble Athletic Ground[2] | |||
| Capacity | 6,500[3] | |||
| Chairman | Jim Parmenter[4] | |||
| Manager | Jake Leberl | |||
| League | Isthmian League Premier Division | |||
| 2023–24 | National League South, 24th of 24 (relegated) | |||
| Website | http://www.doverathletic.com/ | |||
|
| ||||
Dover Athletic Football Club is a semi-professional association football club based in the town of Dover, Kent, England. The club currently competes in the Isthmian League Premier Division, the seventh tier of the English football league system. The club was formed in 1983 after the dissolution of the town's previous club, Dover F.C., whose place in the Southern League was taken by the new club.
In the 1989–90 season Dover Athletic won the Southern League championship, but failed to gain promotion to the Football Conference as the club's ground did not meet the required standard. Three seasons later the team won the title again and this time gained promotion to the Conference, where they spent nine seasons before being relegated at the end of the 2001–02 season. The club was transferred from the Southern League to the Isthmian League in 2004, competing in that league's Premier Division for one season before mounting financial problems led the club to a further relegation. In the 2007–08 season, Dover won Division One South of the league, before winning the Premier Division in 2008–09 and thus gaining promotion to the Conference South. They spent five seasons in this division, reaching the play-offs three times, before defeating Ebbsfleet United in the 2013–14 play-off final to finally return to the Conference Premier after a twelve-year absence. At the end of the 2021–22 season Dover were relegated back to the National League South, after finishing the season with one point.
The team usually wear white shirts and are consequently nicknamed the Whites. They have played at the Crabble Athletic Ground since the club's formation. The club's best performance in the FA Cup was reaching the third round proper in both the 2010–11 and 2014–15 seasons, while the best performance registered in the FA Trophy, the national competition for higher-level non-league clubs, was a run to the semi-finals in the 1997–98 season.
History
[edit]Dover Athletic F.C. was formed in 1983 after the town's previous club, Dover, folded due to its debts. The new club took Dover's place in the Southern League Southern Division,[2] with former Dover player Alan Jones as manager and a team consisting mainly of reserve players from the old club.[5] Initially Athletic struggled, finishing second from bottom of the table in the 1984–85 season.[5][6] In November 1985 Steve McRae, who had succeeded Jones a year earlier, was sacked and replaced by Chris Kinnear.[5]

Under Kinnear the club's fortunes turned round, with two top-five finishes followed by the Southern Division championship, and with it promotion, in the 1987–88 season.[6] The team started strongly in the Premier Division, finishing in sixth place at the first attempt, and then winning the championship in the 1989–90 season.[7] The club was denied promotion to the Football Conference, however, as the Crabble Athletic Ground did not meet the standard required for that league.[2] After finishing fourth and second in the subsequent two seasons, Dover won the title again in the 1992–93 season and this time were admitted to the Conference.[7]
Although Dover finished in eighth place in their first season in the Conference,[8] the following season saw the club struggling against relegation, and Kinnear was dismissed due to a combination of the team's poor performances and his own personal problems.[5][9] John Ryan was appointed as the club's new manager,[10] but his reign was a short one and he was dismissed when the club lost seven of its first eight matches in the 1995–96 season.[11] The club then appointed former England international Peter Taylor as manager, but he was unable to steer the team away from the foot of the table, and Dover held onto their place in the Conference only because Northern Premier League runners-up Boston United failed to submit their application for promotion before the required deadline.[11]
Bill Williams took over as manager in 1997 and led the club to the FA Trophy semi-finals in the 1997–98 season and a best league finish to date of sixth place in the 1999–2000 season.[7][12] Williams left the club to take a senior position with Conference rivals Kingstonian in May 2001.[12] By now the club was in severe financial difficulties, with a number of directors resigning and debts exceeding £100,000. Amid the crisis the entire board of directors resigned, forcing the club's Supporters' Trust to take over the running of the club,[13] and manager Gary Bellamy was sacked after just six months in the job.[14][15] Former Everton goalkeeper Neville Southall took over but was dismissed just three months later, with Clive Walker taking over in March 2002 with the club rooted to the foot of the table.[16] The club finished the season bottom of the Conference and was relegated back to the Southern League Premier Division.[17] The club's ongoing financial problems led to it entering a Company Voluntary Arrangement (CVA), a process by which insolvent companies offset their debts against future profits, due to debts that were now estimated at £400,000.[18]

In Dover's first season back in the Southern League Premier Division the Whites finished in third place, albeit 17 points adrift of Tamworth, who claimed the one promotion place available that season.[6] A poor start to the following season saw Walker replaced by Richard Langley.[19] Dover finished the season in 19th place, before being switched to the Isthmian League Premier Division in the summer of 2004 following a re-organisation of the English football league system.[7] The new season started with six successive defeats, which saw Langley sacked, and the financial problems continued, with the club coming within two months of being closed down.[20][21] Dover were relegated to the Isthmian League Division One at the end of the season,[7] but were saved from possible extinction in January 2005 when former director Jim Parmenter returned to head up a consortium that took over the club.[22] Parmenter quickly sacked manager Steve Browne and convinced Clive Walker to return to the club to replace him,[23] and also arranged for the club's outstanding CVA debts to be cleared, putting the club on a firm financial footing for the first time in many years.[24]
Dover Athletic narrowly missed out on an immediate return to the Premier Division in the 2005–06 season, reaching the play-offs for promotion but losing out to Tonbridge Angels.[25] The following season Dover again reached the play-offs but lost in the semi-final to Hastings United,[26] after which Walker did not have his contract renewed and was replaced by former Gillingham manager Andy Hessenthaler.[4] In his first season in charge he led the club to the Division One South championship and promotion to the Isthmian League Premier Division.[27] The following season Dover won a second consecutive championship and thus gained promotion to Conference South.[28] In the 2009–10 season, Dover reached the play-offs for promotion to the Conference National, but lost at the semi-final stage to Woking.[29] The following season the club reached the third round of the FA Cup for the first time after wins over Kent rivals Gillingham in the first round[30] and another League Two club, Aldershot Town, in the second round.[31] In the 2012–13 season the club again reached the play-offs, but this time lost in the final to Salisbury City.[32]
During the following season, the team reached the second round of the FA Cup, losing 1–0 to Milton Keynes Dons.[7] They also made the last 16 of the FA Trophy, narrowly losing 3–2 to Eastleigh, and reached the play-offs once more.[33] A 4–1 aggregate victory over Sutton United in the semi-final set up a match with fellow Kent team Ebbsfleet United in the final.[34] On 10 May 2014, Dover beat Ebbsfleet 1–0 at Stonebridge Road with a goal from Nathan Elder, enough to seal the club's return to the top flight of non-league football for the first time since 2002.[35] In the 2014–15 season, Dover went on another FA Cup run, beating Morecambe 1–0 in the first round and Cheltenham Town 1–0 in the second, to reach the third round proper for only the second time ever.[36] However, they lost 4–0 at home to Premier League side Crystal Palace.[37] During the following season, the team qualified for the play-offs for promotion to League Two.[38]
During the 2020–21 season, the team only played 15 fixtures, with none played after 30 January 2021, due to staff being furloughed because of the costs associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, the club had all of its results expunged in March and was fined £40,000. In addition, the club was handed a 12-point deduction for the 2021–22 season and fined £40,000 by the National League.[39][40] As of 29 May 2021[update], the club had released all but four players, who were reduced from full to part-time.[40] The 2021–22 season saw Dover start with the points deduction and after picking up only eight points in 33 matches, a 2–0 home defeat to Yeovil Town confirmed Dover's relegation back to the National League South after eight seasons in the top flight of non-league football.[41] In their second season back in the sixth tier, they were relegated to the Isthmian League, finishing bottom of the table having only won four games all season.[42][43]
Colours and crest
[edit]Dover Athletic's traditional colours are white and black,[44] which were also the colours worn by the earlier Dover club.[45] Away colours worn by the club have included red,[44] yellow and green, pink, and blue.[1] The club's crest contains a stylised representation of the town's two most famous landmarks, Dover Castle and the white cliffs, enclosed in a circle bearing the club's name. The club's shirts have been sponsored by companies including Criccieth Homes, Paul Brown of Dover, Jenkins and Pain, cross-channel ferry operators Hoverspeed and SeaFrance, local car dealership Perry's, and Gomez, the company owned by Dover Athletic chairman Jim Parmenter.[1][44][46]
Stadium
[edit]
Dover Athletic's home ground since the club's foundation has been the Crabble Athletic Ground, which was also the home of the former Dover club.[2] The word Crabble, which is also found in the name of a local corn mill,[47] may derive from the Old English crabba hol, meaning a hole in which crabs are found.[48] The stadium, commonly known simply as "Crabble"[49] or, imprecisely, as "The Crabble",[50][51] forms part of a larger council-owned complex,[52] and the earlier Dover club originally shared the lower pitch with a rugby club, but moved to the upper pitch in the 1950s, adding a grandstand in 1951, followed soon after by terracing and floodlights.[2]
Dover Athletic continued to make improvements to the ground, although not in time to allow the club to take its place in the Football Conference in 1990. Subsequently, new turnstiles were installed and two new terraces and a second grandstand added. These improvements meant that the club was able to gain promotion after its second Southern League title in 1993.[2] The stadium's modern capacity is 5,745[53]
In 2007 the club announced that under the new sponsorship deal with SeaFrance, the stadium would be known officially as the SeaFrance Crabble Stadium,[44] but a year later it was announced that the deal would not be renewed due to the ferry operator's financial constraints.[54] On 1 July 2008 local car dealership Perry's was announced as the club's new main sponsor and the stadium rebranded as the Perry's Crabble Stadium,[55] an arrangement which lasted until 2012. Between 2003 and 2004 it was known as the Hoverspeed Stadium under the terms of another such agreement.[56] Margate played their home matches at Crabble for two seasons from 2002 until 2004, while their own Hartsdown Park ground was being redeveloped.[57] The stadium had further development in 2016, when a new family stand was built.[58]
Supporters
[edit]In the club's early days Athletic struggled to attract crowds of over 150,[5] but by the time the club reached the Conference, crowds at Crabble were averaging around 1,000.[59][60][61] After the club's relegation to the Isthmian League Division One South, the average attendance fell to just over 800,[62] but when the club returned to the Premier Division for the 2008–09 season, the average attendance at Crabble was 1,293, the highest in the division.[63] The highest home attendance in the club's history was 5,645 for the match against Crystal Palace in the third round of the FA Cup on 4 January 2015. Although Athletic's improved monetary position means that the Supporters' Trust is no longer required to financially support the club, it remains active as a fundraising organisation.[64]
Statistics and records
[edit]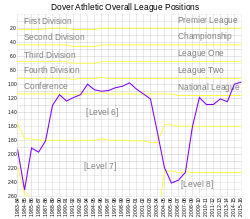
Dover Athletic's highest finish in the English football league system was in the 2015–16 season, in which the team finished in fifth place in the National League, the highest level of non-League football and the fifth level overall. The Whites have made 13 appearances in the final qualifying round of the FA Cup, but have only progressed to the first round proper three times. In the 2010–11 season, Dover reached the third round for the first time, defeating Football League Two teams Gillingham and Aldershot Town in the first two rounds before losing to Huddersfield Town of Football League One. In the 1997–98 season the Whites reached the semi-finals of the FA Trophy but missed out on an appearance at Wembley, losing to Cheltenham Town. The largest number of points the team has accrued is 104 in the 2008–09 season, and the highest total number of goals scored in a season is 89, scored in 40 matches in the 1985–86 season.[7] The team's biggest ever win was an 8–0 defeat of East Preston in September 2009,[65] and the heaviest defeat was by six goals when they lost 7–1 to Poole Town in April 1984[66] and 6–0 to Grimsby Town in October 2021.[67]
The holder of the record for most appearances for Dover Athletic is Jason Bartlett, who played in 539 matches, and the all-time top goalscorer is Lennie Lee, with 160 goals.[68] The club's record signing is Dave Leworthy, who joined the club from Farnborough Town in 1993 for £50,000,[1] which at the time was the highest transfer fee ever paid between non-league clubs.[69] The highest confirmed fee received by the club was also £50,000, paid by Brentford in 1997 for Ricky Reina.[1]
Players
[edit]Current squad
[edit]- As of 13 October 2024[70]
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Former players
[edit]Managers
[edit]Alan Jones was the first manager of Dover Athletic. Chris Kinnear's first stint as manager was the longest in the club's history. The shortest stay was that of Ian Hendon, who was announced as manager on 28 May 2010 and resigned only 18 days later to join Andy Hessenthaler at Gillingham.

| From | To | Manager | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1983 | 1984 | Alan Jones | [5] |
| 1984 | 1984 | Graham Sawyer (caretaker) | [71] |
| 1984 | 1985 | Steve McRae | [5] |
| 1985 | 1995 | Chris Kinnear | [9] |
| 1995 | 1995 | Nigel Donn and Dave Leworthy (caretakers) |
[9] |
| 1995 | 1995 | John Ryan | [10][11] |
| 1995 | 1996 | Peter Taylor | [72] |
| 1996 | 1997 | Joe O'Sullivan | [73] |
| 1997 | 2001 | Bill Williams | [74] |
| 2001 | 2001 | Gary Bellamy | [75] |
| 2001 | 2001 | Clive Walker (caretaker) | [15] |
| 2001 | 2002 | Neville Southall | [16] |
| 2002 | 2003 | Clive Walker | [16][19] |
| 2003 | 2004 | Richard Langley | [20] |
| 2004 | 2004 | Gary Whittle (caretaker) | [20] |
| 2004 | 2005 | Steve Browne | [76][77] |
| 2005 | 2007 | Clive Walker | [23] |
| 2007 | 2010 | Andy Hessenthaler | [78] |
| 2010 | 2010 | Ian Hendon | [79][80] |
| 2010 | 2011 | Martin Hayes | [81][82] |
| 2011 | 2013 | Nicky Forster | [83] |
| 2013 | 2018 | Chris Kinnear | [84][85] |
| 2018 | 2023 | Andy Hessenthaler | [86] |
| 2023 | 2023 | Mitch Brundle and Mike Sandmann (interim) | [87] |
| 2023 | 2023 | Mitch Brundle | [88][89] |
| 2023 | Present | Jake Leberl |
Honours
[edit]
- Conference South (level 6)
- Play-off winners: 2014
- Southern League Premier Division (level 6)
- Southern League Southern Division (level 7)
- Champions: 1987–88
- Isthmian League Premier Division (level 7)
- Champions: 2008–09
- Isthmian League Division One South (level 8)
- Champions: 2007–08
- Kent Senior Cup
- Winners: 1990–91, 2016–17
Rivalries
[edit]Dover Athletic's main rivalry is with nearby Folkestone Invicta.[91] A meeting between the two teams in 2004 was watched by a crowd of 2,278, a record attendance for a league match at Invicta's ground.[92] The club also has a rivalry with Margate.[93] In the 2001–02 season, when both teams were in the Football Conference, the two games between Margate and Dover were watched by a combined total of more than 6,000 spectators. The game played at Margate's Hartsdown Park stadium drew a crowd of 3,676, and 2,325 watched the game at Dover.[94]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g Williams, Tony; Mike Williams (2007). Non-League Club Directory 2007. Tony Williams Publications Ltd. p. 515. ISBN 978-1-869833-55-8.
- ^ a b c d e f "Dover Athletic F.C." Pyramid Passion. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "The Perrys Crabble Stadium". Grimsby Town F.C. Retrieved 3 July 2024.
- ^ a b "Hessenthaler named Dover manager". BBC. 29 May 2007. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g "John Husk". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ a b c "England – Southern League Final Tables". RSSSF. 4 July 2005. Archived from the original on 21 July 2010. Retrieved 2008-02-04.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Dover Athletic". The Football Club History Database. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ "Football Conference 1993–94". The Football Club History Database. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b c Rupert Metcalf (13 January 1995). "NON-LEAGUE FOOTBALL: Stamco ready to ride the hard road". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ a b Rupert Metcalf (17 February 1995). "Sittingbourne net Lovell". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ a b c "Football: Taylor's a fast mover". The Argus. 15 November 2000. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ a b "Bill Williams Resigns". Dover Athletic F.C. 14 May 2001. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ "Dover appoint Southall". BBC. 18 December 2001. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- ^ Harling, Nicholas (1 November 2001). "Nationwide Conference: Dover on the brink". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b Luscombe, Richard (11 November 2001). "Nationwide Conference: Dover win lifts gloom". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b c "Dover appoint Walker". BBC. 13 March 2002. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Football Conference 2001–02". The Football Club History Database. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ Steve Cattermole (19 June 2002). "CVA Proposal Gets Green Light". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Walker goes at Dover". Non-League Daily. 29 October 2003. Archived from the original on 1 June 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ a b c Simon Wigmore (13 September 2004). "Kemp bows to pressure over Langley". London: Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Club must raise £48,000 or close". BBC. 25 November 2004. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ Justin Allen (6 January 2005). "Jim's Takeover Bid Confirmed". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Whites are Clive and kicking". Dover Athletic F.C. 17 January 2005. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ Justin Allen (1 August 2006). "CVA Agreement Reached". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ "Club History". Tonbridge Angels F.C. Archived from the original on 18 December 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ "Ten-man Hastings reach play-off final". The Argus. 2 May 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Dover ease to Ryman South title". BBC. 5 April 2008. Retrieved 9 April 2008.
- ^ a b Howard, Tom (28 March 2009). "Dover Athletic crowned Ryman Premier champions". Eastern Daily Press. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2009.
- ^ Slavin, Chris (1 May 2010). "Woking book play-off final spot at Dover". Surrey Herald. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ Pritchard, David (6 November 2010). "Dover dump ailing Gills out of FA Cup". Eastern Daily Press. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 6 November 2010.
- ^ "Dover 2 – 0 Aldershot". BBC News. 27 November 2010. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ^ "Blue Square Bet South play-offs: Salisbury promoted". BBC News. 12 May 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ Inkersole, Sam (26 April 2014). "Dramatic Dover clinch last-gasp Conference South play-off spot". Dover Express. Archived from the original on 29 April 2014. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ^ Inkersole, Sam (3 May 2014). "Ten-man Dover Athletic crush Sutton to reach play-off final". Dover Express. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 9 May 2014.
- ^ "Dover promoted to Conference after Ebbsfleet play-off victory". BBC Sport. 10 May 2014.
- ^ "Cheltenham Town 0–1 Dover Athletic". BBC. 7 December 2014. Retrieved 8 December 2014.
- ^ "Dover Athletic 0–4 Crystal Palace". BBC. 4 January 2015. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ^ "Dover Athletic 0–1 Forest Green Rovers". BBC. 30 April 2016. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- ^ "Dover Athletic: National League club hit with fine, points deduction and results expunged". BBC Sport. 26 March 2021. Retrieved 8 April 2021.
- ^ a b Bob Dale (29 May 2021). "Champions League final: Dover Athletic face ruin in 'dog eat dog' football world". BBC Sport. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- ^ "Dover relegated after Yeovil defeat". BBC Sport. 19 March 2022. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ Panting, Matthew (29 March 2024). "Dover Athletic relegated from National League South – Second relegation in three years for Whites". Kent Online. KM Group. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ "Summary – National League N/S". Soccerway. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ a b c d Matthew Clements (1 August 2007). "SeaFrance on board". Dover Athletic F.C. Archived from the original on 4 October 2007. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "Team Photos". The History of Dover Football Club. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "New sponsor deal for Dover". BBC. 25 July 2000. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ "Crabble Corn Mill". Crabble Corn Mill Trust. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "The Origin of Dover's Name". Dover-Kent.co.uk. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ "Visiting Crabble". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- ^ "Dover 1–1 Morecambe". BBC. 20 April 2002. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
The hosts, already relegated, showed plenty of spirit and enjoyed the majority of possession in an entertaining encounter at The Crabble.
- ^ Metcalf, Rupert (21 February 2003). "Slade enraged by Dover defeat". The Independent. London. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
Dover entertain Forest Green Rovers at The Crabble in the fifth round of the Trophy.
- ^ "Crabble Athletic Ground, Dover". Dover District Council. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "Big Preview: Dover Athletic vs Southend United". Southend United F.C. 8 November 2019. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ "Sponsor cutback hits Whites". Dover Athletic F.C. 27 May 2008. Retrieved 5 June 2008.
- ^ "Whites in the fast lane". Dover Athletic F.C. 1 July 2008. Retrieved 2 July 2008.
- ^ "New sponsorship deal for Dover brings new ground name". Non League Daily. 5 July 2003. Archived from the original on 1 June 2012. Retrieved 14 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "The History of Margate Football Club". Margate FC History. Archived from the original on 10 June 2010. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ Hoad, Alex (18 November 2016). "Dover Athletic to open new Family Stand at Crabble". Kent Online. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ "Stats 1999/2000: Dover Athletic". ConfGuide.com. Archived from the original on 6 May 2005. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "Stats 2000/1: Dover Athletic". ConfGuide.com. Archived from the original on 3 May 2005. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "Stats 2001/2: Dover Athletic". ConfGuide.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2005. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "Attendances: Isthmian League Division One South". Tony's English Football Site. Retrieved 21 May 2008.
- ^ "Attendances: Isthmian League Division One South". Tony's English Football Site. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- ^ Paul Harrison. "Trust Statement". Dover Athletic Supporters' Trust. Archived from the original on 12 February 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- ^ Harris, Kevin (26 September 2009). "Record win sends Dover through". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 28 September 2009.
- ^ "Dover Athletic all-time records". Soccerbase. Archived from the original on 26 May 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ "Grimsby Town 6–0 Dover Athletic". BBC Sport. 2 October 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- ^ "Dover Athletic". Non-League Daily. Archived from the original on 1 June 2012. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "He played them both – Spurs: David Leworthy". Vital Football. Archived from the original on 25 January 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ "First Team Squad". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 13 October 2024.
- ^ "Graham Sawyer". margatefchistory.co.uk. 16 September 2006. Archived from the original on 26 August 2009. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Taylor-made for top job". BBC. 14 November 2000. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ Rupert Metcalf (24 January 1997). "Football: Stevenage to take up the cry". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ Triggs, Roger (2001). The Men Who Made Gillingham Football Club. Tempus Publishing Ltd. p. 339. ISBN 0-7524-2243-X.
- ^ "Gary Bellamy". Chesterfield F.C. 2 December 2007. Archived from the original on 20 August 2008. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Browne's the Whites choice". Dover Athletic F.C. 12 October 2004. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ Phil Windeatt (17 January 2005). "Dover Athletic 1 Kingstonian 2". This Is Local London. Archived from the original on 3 November 2005. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Hess unveiled as new Whites manager". Kent Online. 29 May 2007. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- ^ "Hendon takes over Crabble". Dover Athletic F.C. 28 May 2010. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ^ "Hendon Quits". Dover Athletic F.C. 10 June 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2010.
- ^ "Hayes is new Whites boss". Dover Athletic F.C. 16 June 2010. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Hayes released by club". Dover Athletic F.C. 26 September 2011. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- ^ "Nicky Forster unveiled as new Dover Athletic manager". Kent Online. 27 September 2011. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ "Kinnear returns to Crabble". Dover Athletic F.C. 19 January 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2013.
- ^ "Chris Kinnear: Dover Athletic sack manager after one win in 14 games". BBC Sport. 5 October 2018. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ^ "HESS IS BACK AT CRABBLE". www.doverathletic.co.uk. 8 October 2018. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ "Hess Leaves Crabble". Dover Athletic F.C. 5 January 2023. Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ McNicoll, John (16 January 2023). "Brundle Takes the Hotseat". Dover Athletic F.C. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- ^ Reeves, Thomas (5 December 2023). "Mitch Brundle is sacked as boss of struggling National League South side Dover Athletic – a day after his 29th birthday". Kent Online. KM Group. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ "Cup joy for Whites". Kent Online. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- ^ "Dryden breaks Invicta record and Dover's hearts". kentishfootball.co.uk. 28 March 2005. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 6 February 2008.
In the post-match press conference, Folkestone Invicta boss Neil Cugley was delighted with their victory over their local rivals.
- ^ "Folkestone Invicta FC". BBC. 17 July 2007. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ "History/Honours". Margate F.C. Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
... with the highest single attendance being just under 4,000 for the Boxing Day game against local rivals Dover Athletic.
- ^ "Fixtures 2001/2 : Margate". Confguide.com. Archived from the original on 8 April 2007. Retrieved 8 January 2008.
External links
[edit]- Official website
- DAFCtv website (archived)

