From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound
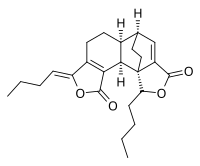
3,8-Dihydrodiligustilide Other names (3Z')-(3a'R,6'R,3R,6R,7R)-3,8-Dihydro-6.6',7.3a'-diligustilide[ 1]
(1S ,2S ,6Z ,10S ,11S )-16-Butyl-6-butylidene-5,15-dioxapentacyclo[9.5.2.01,13 .02,10 .03,7 ]octadeca-3(7),12-diene-4,14-dione
PubChem CID Formula C 24 H 30 O 4 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
CCCCC1[C@]23CC[C@H](C=C2C(=O)O1)[C@H]4[C@@H]3C5=C(CC4)/C(=C/CCC)/OC5=O
InChI=1S/C24H30O4/c1-3-5-7-18-16-10-9-15-14-11-12-24(21(15)20(16)23(26)27-18)17(13-14)22(25)28-19(24)8-6-4-2/h7,13-15,19,21H,3-6,8-12H2,1-2H3/b18-7-/t14-,15+,19?,21-,24+/m1/s1
Key:YTEUTQUNVHWZOR-LGNHLWLRSA-N
3,8-Dihydrodiligustilide is a nonsteroidal phytoprogestogen that is found in Ligusticum chuanxiong [ 1] [ 2] potent agonist of the progesterone receptor (EC50 = 90 nM).[ 1] riligustilide , is also a phytoprogestogen, but is almost 1,000-fold less potent and is very weak in comparison (EC50 ≈ 81 μM).[ 1]
PR Tooltip Progesterone receptor
Agonists
Testosterone derivatives: Progestins: 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate 17α-Allyl-19-nortestosterone Allylestrenol Altrenogest Chloroethynylnorgestrel Cingestol Danazol Desogestrel Dienogest Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethisterone Ethynerone Etonogestrel Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Gestodene Gestrinone Levonorgestrel Levonorgestrel esters (e.g., levonorgestrel butanoate )Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Metynodiol Metynodiol diacetate Norelgestromin Norethisterone (norethindrone) Norethisterone esters (e.g., norethisterone acetate , norethisterone enanthate )Noretynodrel Norgesterone Norgestimate Norgestrel Norgestrienone Norvinisterone Oxendolone Quingestanol Quingestanol acetate Tibolone Tigestol Tosagestin ; Anabolic–androgenic steroids: 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone dodecylcarbonate 19-Nor-5-androstenediol 19-Nor-5-androstenedione 19-Nordehydroepiandrosterone Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Bolandione Dimethisterone Dienedione Dienolone Dimethandrolone Dimethandrolone buciclate Dimethandrolone dodecylcarbonate Dimethandrolone undecanoate Dimethyldienolone Dimethyltrienolone Ethyldienolone Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol) Methyldienolone Metribolone (R-1881) Methoxydienone (methoxygonadiene) Mibolerone Nandrolone Nandrolone esters (e.g., nandrolone decanoate , nandrolone phenylpropionate )Norethandrolone Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethandrolone, normethisterone) RU-2309 Tetrahydrogestrinone Trenbolone (trienolone) Trenbolone esters (e.g., trenbolone acetate , trenbolone enanthate )Trendione Trestolone Trestolone acetate MixedSPRMs Tooltip Selective progesterone receptor modulators ) Antagonists
mPR Tooltip Membrane progesterone receptor PAQR Tooltip Progestin and adipoQ receptor )