Soyuz 7K-OK was the first generation of Soyuz spacecraft and was flown between 1967 and 1971.[2] The 7K-OK was used for the first ferry flights to the Salyut space station program, beginning a long history of space station service that continues with the International Space Station (ISS).
 Soyuz 7K-OK (active) spacecraft with an active docking unit | |
| Manufacturer | Experimental Design Bureau (OKB-1) |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Tested a new crewed space vehicle in orbit and returned to Earth |
| Specifications | |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Production | |
| Status | No longer in service |
| Built | 16 |
| Launched | 16 |
| Maiden launch | Kosmos 133, 1966 |
| Last launch | Soyuz 9, 1970 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz-A (concept only) |
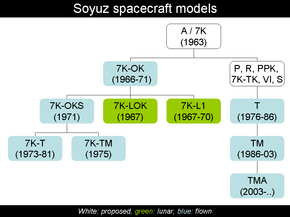
| Derivatives | Soyuz 7K-OKS (Salyut 1 ferry)
Soyuz 7K-L1[1] (lunar) Soyuz 7K-LOK[citation needed] (lunar) Soyuz 7K-T (successor) |
As of 2024[update], the 7K-OK was responsible for the only fatalities of the Soyuz programme, with Soyuz 1 in 1967 (sole crew-member killed by parachute failure) and Soyuz 11 in 1971 (three crew killed by depressurisation during reentry).
The first uncrewed automated docking in the history of spaceflight was achieved between 7K-OK spacecraft Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 in 1967. Additional firsts include the first docking between two crewed spacecraft (Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5), the longest crewed flight involving only one spacecraft (the 18-day flight of Soyuz 9 in 1970), and the first successful transfer of crew to the first space station in the history of space flight (Soyuz 11 and Salyut 1 in 1971).
Description
editThe Soyuz 7K-OK vehicles carried a crew of up to three without space suits. The craft can be distinguished from those following by their bent solar panels and their use of the Igla automatic docking navigation system, which required special radar antennas.
The 7K-OK was primarily intended as a variant of the 7K-LOK (the lunar mission Soyuz) for Earth orbital testing. Mostly the same vehicle, it lacked the larger antenna needed to communicate at lunar distance. The early Soyuz models also sported an external toroidal fuel tank surrounding the engines and meant to store extra propellant for lunar flights, but it was left empty on the first nine flights. After the spacecraft's purpose was changed to space station ferry duties, the tank was removed.
Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft had a "probe and drogue" docking mechanism to connect with other spacecraft in orbit, in order to gather engineering data as a preparation for the Soviet space station program. There were two variants of Soyuz 7K-OK: Soyuz 7K-OK (active) featuring an active "probe" docking port, and Soyuz 7K-OK (passive) featuring a passive "drogue" docking target. The docking mechanisms of 7K-OK and 7K-LOK did not allow internal transfer (this feature was added on the Soyuz 7K-OKS version), thus cosmonauts had to spacewalk between docked modules. This procedure was conducted successfully on the joint Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5 missions, where Aleksei Yeliseyev and Yevgeny Khrunov transferred from their Soyuz 5 to the Soyuz 4 craft.
The first uncrewed test of this version was Kosmos 133, launched on 28 November 1966.
Soyuz 7K-OKS
editThe last two Soyuz space craft of this series were of the designation Soyuz 7K-OKS. The main modification was the addition of the new SSVP docking system that allowed internal crew transfer, which was performed for the first time on the Salyut 1 space station by Soyuz 11. The SSVP docking adapter is still in use today on the International Space Station (ISS).
Uncrewed and test missions
edit- Kosmos 133
- Kosmos 140
- Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188, the first uncrewed automated docking in the history of spaceflight.
- Kosmos 212 and Kosmos 213, uncrewed automated docking mission.
- Kosmos 238
- Soyuz 2, intended docking target for the crewed Soyuz 3.
Crewed missions
edit- Soyuz 1, the first crewed Soyuz flight, commander and sole crew-member killed on re-entry.
- Soyuz 3
- Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5, the first crewed docking and first crew transfer in the history of spaceflight.
- Soyuz 6
- Soyuz 7 and Soyuz 8: Intended docking, to be filmed by Soyuz 6 crew – docking failed due to malfunction.
- Soyuz 9
References
edit- ^ Siddiqi, Asif (March 2003). Simpson, Clive; Owens, Lucy (eds.). "Soyuz variants: a 40-year history" (PDF). British Interplanetary Society. 45 (3): 119.
- ^ Portree, David (March 1995). "Mir Hardware Heritage" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2012. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
External links
edit- RSC Energia: Concept Of Russian Manned Space Navigation Development
- Mir Hardware Heritage
- David S.F. Portree, Mir Hardware Heritage, NASA RP-1357, 1995
- Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource)
- Information on Soyuz spacecraft
- OMWorld's ASTP Docking Trainer Page
- NASA - Russian Soyuz TMA Spacecraft Details
- Space Adventures circum-lunar mission - details
