Abstract.
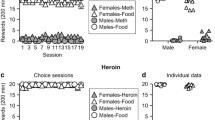
Rationale: Rats selectively bred for high intake of a sweet saccharin solution (HiS) consume more ethanol than their low-saccharin intake (LoS) counterparts. The HiS phenotype may be a predictor of abuse of other drugs via other routes of administration. Objective: HiS and LoS, male and female rats were tested for acquisition of IV cocaine and heroin self-administration under a fixed-ratio 1 (FR1) schedule, and cocaine-reinforced behavior was examined under a progressive-ratio (PR) schedule. Methods: Four groups of rats (HiS males and females and LoS males and females) were trained to self-administer IV cocaine (0.2 mg/kg), and another four groups were trained to self-administer heroin (0.015 mg/kg) using an automated autoshaping procedure. Rats were allowed 30 days to reach a criterion whereby a mean of 100 (cocaine) or 20 (heroin) infusions were self-administered during 6-h sessions over 5 consecutive days. Results: The HiS female rats acquired cocaine self-administration significantly more rapidly than the LoS rats, and females of both phenotypes met the acquisition criteria more rapidly than males. In both HiS and LoS cocaine groups a greater percentage of females (compared with males) met the acquisition criteria within 30 days. The only cocaine group in which 100% met the criterion was the HiS females. The female (compared with male) heroin groups showed a more rapid rate of acquisition, but there was no difference due to saccharin phenotype. In each of the four heroin groups 100% of all rats met the criteria within 30 days. Results of the PR schedule in the HiS females and males and LoS females indicated significantly higher break points in the HiS females (compared with HiS males), but there were no differences in females due to phenotype. Conclusion: Female rats selectively bred for higher saccharin intake show more rapid and successful acquisition of IV self-administration of a low dose of cocaine than those bred for low saccharin intake. Female rats (compared with males) consistently showed accelerated rates of acquisition and maintenance (PR) of cocaine self-administration and acquisition of heroin self-administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carroll, M.E., Morgan, A.D., Lynch, W.J. et al. Intravenous cocaine and heroin self-administration in rats selectively bred for differential saccharin intake: phenotype and sex differences. Psychopharmacology 161, 304–313 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1030-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1030-5