Abstract
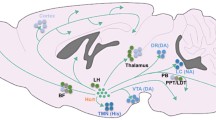
Sleep and wakefulness are instinctive behaviours that are present across the animal species. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is a unique biological phenomenon expressed during sleep. It evolved about 300 million years ago and is noticed in the more evolved animal species. Although it has been objectively identified in its present characteristic form about half a century ago, the mechanics of how REM is generated, and what happens upon its loss are not known. Nevertheless, extensive research has shown that norepinephrine plays a crucial role in its regulation. The present knowledge that has been reviewed in this manuscript suggests that neurons in the brain stem are responsible for controlling this state and presence of excess norepinephrine in the brain does not allow its generation. Furthermore, REM sleep loss increases levels of norepinephrine in the brain that affects several factors including an increase in Na-K ATPase activity. It has been argued that such increased norepinephrine is ultimately responsible for REM sleep deprivation, associated disturbances in at least some of the physiological conditions leading to alteration in behavioural expression and settling into pathological conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- EMG:
-
electromyogram
- LC:
-
locus coeruleus
- NE:
-
norepinephrine
- PGO:
-
pontogeniculooccipital
- REM:
-
rapid eye movement
References
Adya H V A and Mallick B N 2000 Uncompetitive stimulation of rat brain Na-K ATPase activity by rapid eye movement sleep;Neurochem. Int. 36 249–253
Aghajanian G K, Cedarbaum J M and Wang R Y 1977 Evidence for norepinephrine-mediated collateral inhibition of locus coeruleus neurons;Brain Res. 136 570–577
Albanese A and Butcher L L 1980 Actelycholine esterase and catecholamine distribution in the locus coeruleus of the rat;Brain Res. Bull. 5 127–134
Alam M N, Kumari S and Mallick B N 1993 Role of GABA in acetylcholine induced locus coeruleus mediated increase in REM sleep;Sleep Res. 22 541
Ali M, Jha S K, Kaur S and Mallick B N 1999 Medial preoptic area mediated regulation of rapid eye movement sleep is a function of GABA-A receptor;Neurosci. Res. 33 245–250
Amatruda T T, Black D A, McKenna T M, McCarely R W and Hobson J A 1975 Sleep cycle control and cholinergic mechanisms: Differential effects of carbachol injections at pontine brainstem site;Brain Res. 98 501–515
Aserinsky E 1999 Eyelid condition at birth: relationship to adult sleep-waking patterns; inRapid eye movement sleep (eds) B N Mallick and S Inoue (New York: Marcel Dekker) pp 1–16
Aserinsky E and Kleitman N 1953 Regularly occurring periods of eye motility and concomitant phenomena during sleep;Science 118 273–274
Aston-Jones G and Bloom F E 1981 Activity of norepinephrine containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats anticipates fluctuations in the sleep-waking cycle;J. Neurosci. 13 876–886
Aston-Jones G, Ennis M, Pieribone V A, Nickell W T and Shipley M T 1986 The brain nucleus locus coeruleus: restricted afferent control of a broad efferent network;Science 234 734–737
Aston-Jones G, Shipley M T, Chouvet G, Ennis M, van Bockstaele E, Pieribone V, Shiekhattar R, Akaoka H, Drolet G, Astier B, Charlety P, Valentino R J and Williams J T 1991 Afferent regulation of locus coeruleus neurons: anatomy, physiology and pharmacology;Prog. Brain Res. 88 47–75
Baghdoyan H A, Mallios V J, Duckrow R B and Mash D C 1994 Localization of muscarinic receptor subtypes in brain stem areas regulating sleep;Neuroreport 5 1631–1634
Baghdoyan H A, Rodrigo-Angulo M L, McCarley R W and Hobson J A 1984 Site-specific enhancement and suppression of desynchronized sleep signs following cholinergic stimulation of three brainstem regions;Brain Res. 306 39–52
Basheer R, Magner M, McCarley R W and Shiromani P J 1998 REM sleep deprivation increases the levels of tyrosine hydroxylase and norepinephrine transporter mRNA in the locus coeruleus;Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 57 235–240
Bergmann B M, Everson C A, Kushida C A, Fang V S, Leitch C A, Schoeller D A, Refetoff S and Rechtschaffen A 1989 Sleep deprivation in rat: V. energy use and mediation;Sleep 12 31–41
Bert J, Saier J, Tognetti P and Toure M F 1977 Effect of chlorimipramine on the so-called ponto-geniculo-occipital (PGO) activity in a primate,Papio hamadryas (author’s transl);Psychopharmacology (Berl.)51 301–304
Braun C M J and Pivik R T 1981 Effects of locus coeruleus lesions upon sleeping and waking in the rabbit;Brain Res. 230 133–151
Carli G and Zanchetti A 1965 A study of pontine lesions suppressing deep sleep in the cat;Arch. Ital. Biol. 103 751–788
Cespuglio R, Gomez M E, Faradji H and Jouvet M 1982 Alterations in the sleep-waking cycle induced by cooling of the locus coeruleus area;EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 54 570–578
Cirelli C 2002 Invited Review: How sleep deprivation affects gene expression in the brain: a review of recent findings;J. Appl. Physiol. 92 394–400
Cirelli C, Pompeiano M and Tononi G 1996 Neuronal gene expression in the waking state: a role for the locus coeruleus;Science 274 1211–1215
Crochet S and Sakai K 1999 Alpha-2 adrenoreceptor mediated paradoxical (REM) sleep inhibition in the cat;Neuro Rep. 10 2199–2204
Chu N S and Bloom F E 1974 Activity patterns of catecholamine pontine neurons in the dorsal-lateral tegmentum of unrestrained cat;J. Neurobiol. 5 527–544
Datta S 1995 Neuronal activity in the peribrachial area: relationship to behavioural state control;Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 19 67–84
Depoortere H 1985 Adrenergic agonists and antagonists and sleep wakefulness stages; inSleep: Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (eds) A Wauquier, J M Gaillard, J M Monti and M Radulovacki (New York: Raven Press) pp 79–92
Drucker-Colin R R and Pedraza J G B 1983 Kainic acid lesions of gigantocellularis tegmental field (FTG) neurons do not abolish REM sleep;Brain Res. 272 387–391
Egan T M and North R A 1986 Actions of acetylcholine and nicotine on rat locus coeruleus neuronsin vitro;Neuroscience 19 565–571
Ennis M and Aston-Jones G 1989 GABA-mediated inhibition of locus coeruleus from the dorsomedial rostral medulla;J. Neurosci. 9 2973–2981
Farber J, Miller J D, Craford K A and McMillen B A 1983 Dopamine metabolism and receptor sensitivity in rat brain after REM sleep deprivation;Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 18 509–513
Foote S L, Bloom F E and Aston-Jones G 1983 Nucleus locus coeruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity;Physiol. Rev. 63 844–913
Friedman L and Jones B E 1984 Study of sleep-wakefulness states by computer graphics and cluster analysis before and after lesions of the pontine tegmentum in the cat;Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 57 43–56
Gaillard J M 1985 Involvement of noradrenaline in wakefulness and pradoxical sleep; inSleep: Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (eds) A Wauquier, J M Gaillard, J M Monti and M Radulovacki (New York: Raven Press) pp 57–67
Gallopin T, Fort P, Eggermann E, Cauli B, Luppi P H, Rossier J, Audinat E, Muhlethaler M and Serafin M 2000 Identification of sleep-promoting neuronsin vitro;Nature (London)404 992–995
Gervasoni D, Darracq L, Fort P, Souliere F, Chouvet G and Luppi P H 1998 Electrophysiological evidence that noradrenergic neurons of the rat locus coeruleus are tonically inhibited by GABA during sleep;Eur. J. Neurosci. 10 964–970
Gillin J C, Sitaram N, Janowsky D, Risch C, Huey L and Storch F I 1985 Cholinergic mechanisms in REM sleep; inSleep: Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (eds) A Wauquier, J M Gaillard, J M Monti and M Radulovacki (New York: Raven Press) pp 153–163
Greene R W and Carpenter D O 1985 Actions of neurotransmitters on pontine medial reticular formation neurons of the cat;J. Neurophysiol. 54 520–531
Guilleminault C 1989 Narcolepsy syndromes; inPrinciples and practice of sleep medicine (eds) M H Kryger, T Roth and W C Dement (Philadelphia; W B Saunders) pp 338–346
Gulyani S, Majumdar S and Mallick B N 2000 Rapid Eye Movement Sleep and significance of its deprivation studies -A review;Sleep Hypnosis 2 49–68
Gulyani S and Mallick B N 1993 Effect of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on rat brain Na-K ATPase activity;J. Sleep Res. 2 45–50
Gulyani S and Mallick B N 1995 Possible mechanism of REM sleep deprivation induced increase in Na-K ATPase activity;Neuroscience 64 255–260
Henley K and Morrison A R 1974 A re-evaluation of the effects of lesions of the pontine tegmentum and locus coeruleus on phenomena of paradoxical sleep in the cat;Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Warsz)34 215–232
Hilakivi I, Leppavuori A and Putkonen P T 1980 Prazosin increases paradoxical sleep;Eur. J. Pharmacol. 65 417–420
Hobson J A, McCarley R W, Pivik R T and Freedman R 1974 Selective firing by cat pontine brain stem neurons in desynchronized sleep;J. Neurophysiol. 37 497–511
Hobson J A, McCarley R W and Wyzinski P W 1975 Sleep cycle oscillation: Reciprocal discharge by two brainstem neuronal groups;Science 189 55–58
Iijima K and Ohtomo K 1988 Immunohistochemical study using a GABA antiserum for demonstration of inhibitory neurons in the rat locus coeruleus;Am. J. Anat. 181 43–52
Inoue S 1989Biology of sleep substances (Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press)
Jacobs B L 1986 Single unit activity of locus coeruleus neurons in behaving animals;Prog. Neurobiol. 27 183–194
Jones B E 1979 Elimination of paradoxical sleep by lesions of the pontine gigantocellular tegmental field in the cat;Neurosci. Lett. 13 285–293
Jones B E 1990 Immunohistochemical study of choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive processes and cells innervating the pontomedullary reticular formation in the rat;J. Comp. Neurol. 295 485–514
Jones B E 1991 Paradoxical sleep and its chemical/structural substrates in the brain;Neuroscience 40 637–656
Jones B E, Harper S T and Halaris A E 1977 Effects of locus coeruleus lesions upon cerebral monoamine content, sleep wakefulness states and the response to amphetamine in the cat;Brain Res. 124 473–496
Jones B E and Moore R Y 1974 Catecholamine-containing neurons of the nucleus locus coeruleus in the cat;J. Comp. Neurol. 157 43–51
Jouvet M 1972 The role of monoamines and acetylcholinecontaining neurons in the regulation of the sleep-waking cycle;Ergeb. Physiol. 64 166–307
Jouvet M 1999 Around the discovery of REM sleep in cats; inRapid eye movement sleep (eds) B N Mallick and S Inoue (New York: Marcel Dekker) v-ix
Jouvet M and Delorme F 1965 Locus coeruleus et sommeil paradoxal;Comp. Ren. Soc. Biol. 159 895–899
Jouvet M and Mounier D 1960 Effects des lesions de la formation reticulee pontique sur le sommeil du chat;C. R. Soc. Biol. 154 2301–2305
Kaur S, Saxena R N and Mallick B N 1997 GABA in locus coeruleus regulates spontaneous rapid eye movement sleep by acting on GABA-A receptors in freely moving rats;Neurosci. Lett. 223 105–108
Kaur S, Saxena R N and Mallick B N 2001 GABAergic neurons in prepositus hypoglossi regulate REM sleep by its action on locus coeruleus in freely moving rats;Synapse 42 141–150
Kodama T, Takahashi Y and Honda Y 1990 Enhancement of acetylcholine release during paradoxical sleep in the dorsal tegmental field of the cat brain stem;Neurosci. Lett. 114 277–282
Laguzzi R F, Adrien J, Bourgoin S and Hamon M 1979 Effects of intraventricular injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in the developing kitten I. On the sleep-waking cycles;Brain Res. 160 445–459
Luppi P H, Aston-Jones G, Akaoka H, Chouvet G and Jouvet M 1995 Afferent projections to the rat locus coeruleus demonstrated by retrograde and anterograde tracing with cholera-toxin B subunit andPhaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin;Neuroscience 65 119–160
Luque J M, Malherbe P and Richards J G 1994 Localization of GABA-A receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat locus coeruleus;Mol. Brain Res. 24 219–226
Mallick B N 1999 Presented in Focus Group, 3 (FG3) titled “Where does REM sleep begin?”,World Fed. Sleep Res. Soc., 3rd Int. Congr., Dresden, Germany
Mallick B N and Adya H V 1999 Norepinephrine induced alphaadrenoceptor mediated increase in rat brain Na-K ATPase activity is dependent on calcium ion;Neurochem. Int. 34 499–507
Mallick B N, Adya H V A and Faisal M 2000 Norepinephrine-stimulated increase in Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the rat brain is mediated through alpha 1A adrenoceptor possibly by dephosphorylation of the enzyme;J. Neurochem. 74 1574–1578
Mallick B N, Adya H V A and Thankachan S 1999a REM sleep deprivation alters factors affecting neuronal excitability: role of norepinephrine and its possible mechanism of action; inRapid eye movement sleep (eds) B N Mallick and S Inoue (New York: Marcel Dekker) pp 338–354
Mallick B N, Kaur S, Jha S K and Siegel J M 1999b Possible role of GABA in the regulation of REM sleep with special reference to REM-OFF neurons; inRapid eye movement sleep (eds) B N Mallick and S Inoue (New York: Marcel Dekker) pp 153–166
Mallick B N, Fahringer H M, Wu M F and Siegel J M 1991 REM sleep deprivation reduces auditory evoked inhibition of dorsolateral pontine neurons;Brain Res. 552 333–337
Mallick B N and Gulyani S 1993 Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation increases chloride sensitive Mg2+-ATPase activity in rat brain;Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 45 359–362
Mallick B N and Gulyani S 1996 Alteration in synaptosomal calcium concentrations after rapid eye movement sleep deprivation in rats;Neuroscience 75 729–736
Mallick B N, Kaur S and Saxena R N 2001 Interactions between cholinergic and GABAergic neurotransmitters in and around the locus coeruleus for the induction and maintenance of rapid eye movement sleep in rats;Neuroscience 104 467–485
Mallick B N, Mohan Kumar V, Chinna G S and Singh B 1986 Comparison of rostro-caudal brain stem influence on preoptic neurons and cortical EEG;Brain Res. Bull. 16 121–125
Mallick B N, Siegel J M and Fahringer H 1989 Changes in pontine unit activity with REM sleep deprivation;Brain Res. 515 94–98
Mallick B N and Thakkar M 1991 Short-term REM sleep deprivation increases acetylcholinesterase activity in the medulla of rats;Neurosci. Lett. 130 221–224
Mallick B N and Thakkar M 1992 Effect of REM sleep deprivation on molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in rats;Neuroreport 3 676–678
Mallick B N, Thakkar M and Gangabhagirathi R 1995 Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation decreases membrane fluidity in the rat brain;Neurosci. Res. 22 117–122
Mallick B N Thakkar M and Gulyani S 1994 Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induced alteration in neuronal excitability: possible role of norepinephrine; inEnvironment and physiology (eds) B N Mallick and R Singh (New Delhi: Narosa) pp 196–203
Mallick B N, Thankachan S and Islam F 1998 Differential responses of brain stem neurons during spontaneous and stimulation induced desynchronization of the cortical EEG in freely moving cats;Sleep Res. Online 1 132–146
Maloney K J, Mainville L and Jones B E 1999 Differential c-Fos expression in cholinergic, monoaminergic, and GABAergic cell groups of the pontomesencephalic tegmentum after paradoxical sleep deprivation and recovery;J. Neurosci. 19 3057–3072
Mash D C and Potter L T 1986 Autoradiographic localization of M1 and M2 muscarinic receptors in the rat brain;Neuroscience 19 551–564
Matsuzaki M 1969 Differential effects of sodium butyrate and physostigmine upon the activities of para-sleep in acute brain stem preparations;Brain Res. 13 247–265
McCarley R W and Hobson J A 1975 Neuronal excitability modulation over the sleep cycle: a structural and mathematical model;Science 189 58–60
Moore R Y and Bloom F E 1979 Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems;Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2 113–169
Moruzzi G 1972 The sleep waking cycle;Ergeb. Physiol. 64 1–165
Netzer N C, Kristo D, Steinle H, Lehmann M and Strohl K P 2001 REM sleep and catecholamine excretion: a study in elite athletes;Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 84 521–526
Nitz D and Siegel J M 1997 GABA release in the locus coeruleus as a function of sleep/wake state;Neuroscience 78 795–801
Oakson G and Steriade M 1982 Slow rhythmic rate fluctuations of cat midbrain reticular neurons in synchronized sleep and waking;Brain Res. 247 277–288
Olpe H R, Steinmann M W, Hall R G, Brugger F and Pozza M F 1988 GABA-A and GABA-B receptors in locus coeruleus: effect of blockers;Eur. J. Pharmacol. 149 183–185
Pellejero T, Monti J M, Baglietto J, Jantos H, Pazos S, Cichevski V and Hawkins M 1984 Effects of methoxamine and α-adrenoceptor antagonists, prazosin and yohimbine, on the sleep-wake cycle of the rat;Sleep 7 365–372
Porkka-Heiskanen T, Smith S E, Taira T, Urban J H, Levine J E, Turek F W and Stenberg D 1995 Noradrenergic activity in rat brain during rapid eye movement sleep deprivation and rebound sleep;Am. J. Physiol. 268 R1456-R1463
Pujol J F, Mouret J, Jouvet M and Glowinski J 1968 Increased turnover of cerebral norepinephrine during rebound of paradoxical sleep in the rat;Science 159 112–114
Quattrochi J, Datta S and Hobson J A 1998 Cholinergic and non-cholinergic afferents of the caudolateral parabrachial nucleus: a role in the long-term enhancement of rapid eye movement sleep;Neuroscience 83 1123–1136
Reiner P B 1986 Correlational analysis of central noradrenergic neuronal activity and sympathetic tone in behaving cats;Brain Res. 378 86–96
Roussel B, Buguet A, Bobillier P and Jouvet M 1967 Locus coeruleus, paradoxical sleep and cerebral noradrenaline;C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 161 2537–2541
Rye D B 1997 Contributions of the pedunculopontine region to normal and altered REM sleep;Sleep 20 757–788
Sakai K 1980 Some anatomical and physiological properties of ponto-mesencephalic tegmental neurons with special reference to the PGO waves and postural atonia during paradoxical sleep in cat; inThe reticular formation revisited (eds) J A Hobson and M A B Brazier (New York: Raven Press) pp 427–447
Sakai K 1985 Anatomical and physiological basis of paradoxical sleep; inBrain mechanisms of sleep (ed.) D J McGinty (New York: Raven Press) pp 111–137
Sakai K 1988 Executive mechanisms of paradoxical sleep;Arch. Ital. Biol. 126 239–257
Sakai K, Sastre J P, Kanamori N and Jouvet M 1981 Statespecific neurons in the pontomedullary reticular formation with special reference to the postural atonia during paradoxical sleep in the cat; inBrain mechanism and perceptual awareness (eds) O Pompeiano and C Ajmone Marsan (New York: Raven Press) pp 405–429
Sastre J P, Sakai K and Jouvet M 1979 Persistence of paradoxical sleep in the cat after destruction of the pontine gigantocellular tegmental field with kainic acid;C. R. Seances. Acad. Sci. D. 289 959–964
Sastre J P, Sakai K and Jouvet M 1981 Are the gigantocellular tegmental field neurons responsible for paradoxical sleep?;Brain Res. 229 147–161
Sherin J E, Elmquist J K, Torrealba F and Saper C B 1998 Innervation of histaminergic tuberomammillary neurons by GABAergic and galaninergic neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus of the rat;J. Neurosci. 18 4705–4721
Shiromani P J and McGinty D J 1986 Pontine neuronal response to local cholinergic infusion: relation to REM sleep;Brain Res. 386 20–31
Shouse M N, Staba R J, Saquib S F and Farber P R 2000 Monoamine and sleep: microdialysis finding in pons and amygdala;Brain Res. 860 181–189
Siegel J M 1983 REM sleep control mechanisms: Evidence from lesion and unit recording studies; inSleep mechanism and functions in humans and animals: an evolutionary perspective (eds) A Mayes and V N Reinhold (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp 217–231
Siegel J M 1989 Brainstem mechanisms generating REM sleep; inPrinciples and practice of sleep medicine (eds) M H Kryger, T Roth and W C Dement (Philadelphia: W B Saunders) pp 104–120
Siegel J M, Tomaszewski K S and Nienhuis R 1986 Behavioral states in the chronic medullary and midpontine cat;EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 63 274–288
Singh S and Mallick B N 1996 Mild electrical stimulation of pontine tegmentum around locus coeruleus reduces rapid eye movement sleep in rats;Neurosci. Res. 24 227–235
Sinha A K, Ciaranello R D, Dement W C and Barchas J D 1973 Tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat brain following “REM” sleep deprivation;J. Neurochem. 20 1289–1290
Steininger T L, Gong H, McGinty D and Szymusiak R 2001 Subregional organization of preoptic area/anterior hypothalamic projections to arousal-related monoaminergic cell groups;J. Comp. Neurol. 429 638–653
Steriade M and McCarley R W 1990Brain stem control of wakefulness and sleep (New York: Plenum Press)
Thakkar M and Mallick B N 1991 Effects of REM sleep deprivation on rat brain acetylcholinesterase;Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 39 211–214
Thakkar M and Mallick B N 1993 Effect of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on rat brain monoamine oxidases;Neuroscience 55 677–683
Thakkar M, Portas C and McCarley R W 1996 Chronic lowamplitude electrical stimulation of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus of freely moving cats increases REM sleep;Brain Res. 723 223–227
Thankachan S, Islam F and Mallick B N 1997 Behavior of brain stem neurons during spontaneous and induced EEG desynchronization during wakefulness and rapid eye movement sleep in free moving cats;Sleep Res. 26 54
Thankachan S, Islam F and Mallick B N 2001 Role of wake inducing brain stem area on rapid eye movement sleep regulation in freely moving cats;Brain Res. Bull. 55 43–49
Tononi G, Pompeiano M and Cirelli C 1991 Effects of local pontine injection of noradrenergic agents on desynchronized sleep of the cat;Prog. Brain Res. 88 545–553
Vanni-Mercier G, Sakai K, Lin J S and Jouvet M 1989 Mapping of cholinoceptive brainstem structures responsible for the generation of paradoxical sleep in the cat;Arch. Ital. Biol. 127 133–164
Velazquez-Moctezuma J, Shalauta M, Gillin J C and Shiromani P J 1991 Cholinergic antagonists and REM sleep generation;Brain Res. 543 175–179
Vogel G W 1975 A review of REM sleep deprivation;Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 32 749–761
Wauquier A, Clincke G H C, Van den Broeck W A E and De Prins E 1985 Active and permissive roles of dopamine in sleep wakefulness regulation; inSleep: Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (eds) A Wauquier, J M Gaillard, J M Monti and M Radulovacki (New York: Raven Press) pp 107–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallick, B.N., Majumdar, S., Faisal, M. et al. Role of norepinephrine in the regulation of rapid eye movement sleep. J. Biosci. 27, 539–551 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705052
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705052