Abstract
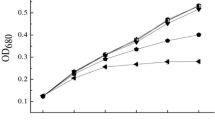
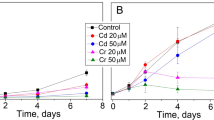
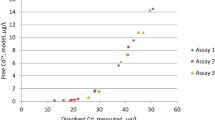
The toxicological response of the cyanophycean algaAnabaena flos- aquae to cadmium was investigated by three integrated approaches: 1) the determination of the incipient lethal concentration of the metal, 2) study of metal incorporation and cellular compartmentalization using X-ray energy dispersive analysis, and 3) the quantification of intracellular structural changes, after metal exposure, using morphometric analysis. After 96 hr of exposure, the incipient lethal concentration was calculated to be 0.118 ± 0.04 μM cadmium. At concentrations three orders of magnitude higher than the incipient lethal concentration, cadmium was incorporated into both the cellular cytoplasm and the cell's polyphosphate bodies. Cadmium also caused the polyphosphate bodies to lose Mg and Ca, resulting in ionic changes in the elemental composition of these cellular inclusions. The utilization of stereological techniques for electron microscopic morphometric analysis established that all concentrations of cadmium tested caused significant reductions in the surface area of the cell's thylakoids. Cadmium induced changes in the numbers and relative volume of the cell occupied by polyhedral bodies, polyphosphate bodies, lipid inclusions, cyanophycin granules, membrane limited crystalline, inclusions, and changes in the volume of the cell wall layers were also documented. The physiological significance of these findings are discussed in terms of the toxic action of cadmium and the cellular mechanisms for detoxification of cations once they enter the cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Baxter, M., and T. E. Jensen: Uptake of magnesium, strontium, barium, and manganese byPlectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) with special reference to polyphosphate bodies. Protoplasma.104, 81 (1980a).
—: A study of methods forin situ X-ray energy dispersive analysis of polyphosphate bodies inPlectonema boryanum. Arch. Microbiol.126, 213 (1980b).
Bliss, C. I.: Statistics of Bioassay. Academic Press, New York, p. 445 (1952).
Carmody, D. J., J. B. Pearce, and W. E. Yasso: Trace metals in sediments of the New York Bight. Mar. Pollut. Bull.4, 132 (1973).
Codd, G. A., K. Okabe, and W. D. P. Stewart: Cellular compartmentation of photosynthetic and photorespiratory enzymes in the heterocystous cyanobacteriumAnabaena cylindrica. Arch. Microbiol.124, 149 (1980).
Codd, G. A., and W. D. P. Stewart: Polyhedral bodies and ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of the blue-green algaAnabaena cylindrica. Planta (Berl)130, 323 (1976).
—: D-ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from the bluegreen alga Aphanocapsa 6308. Arch. Microbiol.113, 105 (1977).
De Filippis, L. F., R. Hampp, and H. Ziegler: The effects of sublethal concentrations of zinc, cadmium, and mercury on Euglena. II. Respiration, photosynthesis, and photochemical activities. Arch. Microbiol.128, 407 (1981).
Doonan, B. B., R. E. Crang, T. E. Jensen, and M. Baxter:In situ X-ray energy dispersive microanalysis of polyphosphate bodies inAureobasidium pullulans. J. Ultrastruct. Res.69, 232 (1979).
Finney, D. J.: Statistical Methods in Biological Assay. Hafner, New York, 668 pp. (1964a).
—: Probit Analysis. Cambridge Univ. Press, England, 318 pp. (1964b).
Fisher, N. S., and D. Frood: Heavy metals and marine diatoms: Influence of dissolved organic compounds on toxicity and selection for metal tolerance among four species. Marine Biol.59, 85 (1980).
Fitzgerald, G. P., G. C. Gerloff, and F. Skoog: Studies on chemicals with selective toxicity to blue-green algae. Sewage Ind. Wastes24, 888 (1952).
Guillard, R. R. L.: Division rates. In: Stein Jr (ed.) Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements. Cambridge Univ. Press, London, p. 289 (1973).
Honig, R. A., M. J. McGinniss, A. L. Buikema, Jr, and J. Cairns Jr.: Toxicity tests of aquatic pollutants using Chilomonas paramecium Ehrenberg (Flagellata) populations. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.25, 169 (1980).
Jensen, T. E. M. Baxter, J. W. Rachlin, and V. Jani: Uptake of heavy metals byPlectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) into cellular components, especially polyphosphate bodies: An X-ray energy dispersive study. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A.27, 119 (1982a).
Jensen, T. E., and L. M. Sicko: Phosphate metabolism in blue-green algae. I. Fine structure of the “polyphosphate overplus” phenomenon inPlectonema boryanum. Can. J. Microbiol.20, 235 (1974).
Jensen, T. E., J. W. Rachlin, V. Jani, and B. Warkentine: An X-ray energy dispersive study of cellular compartmentalization of lead and zinc inChlorella saccharophila (Chlorophyta),Navicula incerta andNitzschia closterium (Bacillariophyta). Environ. Exp. Botany22, 319 (1982b).
Kuypers, G. A. J., and G. M. Roomans: Mercury-induced loss of K+ from yeast cells investigated by electron probe X-ray microanalysis. J. Gen. Microbiol.115, 13 (1979).
Lanaras, T., and G. A. Codd: Variations in ribulose 1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase protein levels, activities and subcellular distribution during photoautotrophic batch culture ofChlorogloeopsis fritschii. Planta154, 284 (1982).
Lewin, R. A., (ed.): Physiology and Biochemistry of Algae. Academic Press, New York, 929 pp. (1962).
Mori, H., and A. K. Christensen: Morphometric analysis of Leydig cells in the normal rat testis. J. Cell. Biol.84, 340 (1980).
Mueller, J. A., J. S. Jeris, A. R. Anderson, and C. F. Hughes: Contaminant inputs to the New York Bight. NOAA Tech. Memo. ERL-MESA-6, NOAA/ERL, Boulder, Colorado, 347 pp. (1976).
Nakajima, A., T. Horikoshi, and T. Sakaguchi: Uptake of copper ion by green microalgae. Agric. Biol. Chem.43, 1455 (1979).
Passow, H., and A. Rothstein: The binding of mercury by the yeast cell in relation to changes in permeability. J. Gen. Physiol.43, 621 (1960).
Preston, A.: Cadmium in the marine environment of the United Kingdom. Mar. Pollut. Bull.4, 105 (1973).
Rachlin, J. W., T. E. Jensen, M. Baxter, and V. Jani: Utilization of morphometric analysis in evaluating response ofPlectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) to exposure to eight heavy metals. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.11, 323 (1982a).
Rachlin, J. W., and K. Rivlin: Observations of the trace metal load of the Hudson Estuary. In: N. M. Ratcliffe (ed.) New England Intercoll. Geol. Conf. 1975 Guidebook, p. 39 (1975).
Rachlin, J. W., B. Warkentine, and T. E. Jensen: The growth response ofChlorella saccharophila, Navicula incerta andNitzschia closterium to selected concentrations of cadmium. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club.109, 129 (1982b).
Rosko, J. J., and J. W. Rachlin: The effect of copper, zinc, cobalt, and manganese on the growth of the marine diatomNitzschia closterium. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club102, 100 (1975).
—: The effect of cadmium, copper, mercury, zinc, and lead on cell division, growth, and chlorophyll-a content of the chlorophyteChlorella vulgaris. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club104, 226 (1977).
Rothstein, A.: Cell membrane as site of action of heavy metals. Fed. Proc. Fed. Amer. Soc. Exp. Biol.18, 1026 (1959).
Schmitz, R.: Uber die Zusammensetzung der pigmenthaltigen Strukturen aus Prokaryonten. I. Untersuchungen an Thylakoiden von Oscillatoria chalybea Kutz. Arch. Mikrobiol.56, 225 (1967).
Segar, D., and A. Cantillo: Trace metals in the New York Bight. In M. G. Gross (ed.): Middle Atlantic Continental Shelf and The New York Bight. Am. Soc. Limnol. Oceanogr. Spec. Symp. 2, p. 171 (1976).
Sicko-Goad, L., and E. F. Stoermer: A morphometric study of lead and copper effects onDiatoma tenue var. elongatum (Bacillariophyta). J. Phycol.15, 316 (1979).
Sicko-Goad, L., E. F. Stoermer, and B. G. Ladewski: A morphometric method for correcting phytoplankton cell volume estimates. Protoplasma93, 147 (1977).
Simkiss, K.: Metal ions in cells. Endeavour3, 2 (1979).
Simon, R. D., N. H. Lawry, and G. L. McLendon: Structural characterization of the cyanophycin granule polypeptide ofAnabaena cylindrica by circular dichroism and Raman spectroscopy. Biochimi. Biophys. Acta626, 277 (1980).
Starr, R. C.: The culture collection of algae at the University of Texas at Austin. J. Phycol.14, 47 (1978).
Stary, J., and K. Kratzer: The cumulation of toxic metals on alga. J. Environ. Anal. Chem.12, 65 (1982).
Vallee, B. L., and D. D. Ulmer: Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. Ann. Rev. Biochem.41, 91 (1972).
Weibel, E. R., and R. P. Bolender: Stereological techniques for electron microscopic morphometry. In M. A. Hayat (ed.): Principles and Techniques of Electron Microscopy. Van Nostrand-Reinhold, New York, 237 pp. (1973).
Wolk, C. P.: Physiology and cytological chemistry of blue-green algae. Bacteriol. Rev.37, 32 (1973).
Zar, J. H.: Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 620 pp. (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rachlin, J.W., Jensen, T.E. & Warkentine, B. The toxicological response of the algaAnabaena flos- aquae (cyanophyceae) to cadmium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13, 143–151 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055871
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055871