Governor of Alaska
| Alaska Governor | |
 | |
| General information | |
| Office Type: | Partisan |
| Office website: | Official Link |
| Compensation: | $145,000 |
| 2024 FY Budget: | $30,651,400 |
| Term limits: | 2 consecutive terms |
| Structure | |
| Length of term: | 4 years |
| Authority: | Constitution of Alaska, Article III, Section 1 |
| Selection Method: | Elected |
| Current Officeholder | |
Governor of Alaska
Mike Dunleavy | |
| Elections | |
| Next election: | November 3, 2026 |
| Last election: | November 8, 2022 |
| Other Alaska Executive Offices | |
| Governor•Lieutenant Governor•Attorney General•Comptroller•Education Commissioner•Revenue Commissioner•Agriculture Director•Insurance Director•Natural Resources Commissioner•Labor Commissioner•Regulatory Commission | |
The Governor of Alaska is an elected constitutional officer, the head of the executive branch, and the highest state office in Alaska. The governor is popularly elected every four years by a plurality and is limited to two consecutive terms. A term-limited governor may not be elected again until one complete gubernatorial term has passed following their last term in office.
Alaska has a divided government where neither party holds a trifecta. The Republican Party controls the office of governor and the upper chamber of the state legislature. Control of the lower chamber of the state legislature is split between parties.
Alaska has a Republican triplex. The Republican Party controls the offices of governor and attorney general.
Current officer
The current governor of Alaska is Republican Mike Dunleavy.[1] Dunleavy assumed office on December 3, 2018. Prior to his election as governor, Dunleavy served as a state senator.[2]
Authority
The Constitution of Alaska addresses the office of the governor in Article III, the Executive.
Alaska Constitution, Article III, Section 1:
|
The executive power of the State is vested in the governor. |
Qualifications
| State Executives |
|---|
| Current Governors |
| Gubernatorial Elections |
| 2024 • 2023 • 2022 • 2021 • 2020 • 2019 • 2018 • 2017 • 2016 • 2015 • 2014 |
| Current Lt. Governors |
| Lt. Governor Elections |
| 2024 • 2023 • 2022 • 2021 • 2020 • 2019 • 2018 • 2017 • 2016 • 2015 • 2014 |
Under Article III, Section 6 of the Constitution, the governor may not hold any federal office or any state office in Alaska while serving as governor. Per Section 2 of the same article, the governor must be at least 30 years old, a qualified voter in Alaska, and have been both an American citizen and a resident of Alaska for a minimum of seven years on election day.
Alaska Constitution, Article III, Section 2
|
The governor shall be at least thirty years of age and a qualified voter of the State. He shall have been a resident of Alaska at least seven years immediately preceding his filing for office, and he shall have been a citizen of the United States for at least seven years. |
Alaska Constitution, Article III, Section 6
|
The governor shall not hold any other office or position of profit under the United States, the State, or its political subdivisions. |
Elections
- See also: Gubernatorial election cycles by state
- See also: Election of governors
Alaska elects governors in federal midterm election years (e.g. 2018, 2022, 2026, 2030). General elections are held on the first Tuesday and the first Monday in November.[3] Winners take office at noon on the first Monday in December following the election, per Article III, Section 4 of the state constitution.
2022
General election
General election for Governor of Alaska
The ranked-choice voting election was won by Mike Dunleavy in round 1 .
| Total votes: 263,752 |
||||
 = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. | ||||
Nonpartisan primary election
Nonpartisan primary for Governor of Alaska
The following candidates ran in the primary for Governor of Alaska on August 16, 2022.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ |  | Mike Dunleavy (R) | 40.4 | 76,534 |
| ✔ |  | Les Gara (D)  | 23.1 | 43,660 |
| ✔ |  | Bill Walker (Independent) | 22.8 | 43,111 |
| ✔ |  | Charlie Pierce (R) | 6.6 | 12,458 |
 | Christopher Kurka (R) | 3.9 | 7,307 | |
 | John Howe (Alaskan Independence Party) | 0.9 | 1,702 | |
 | Bruce Walden (R) | 0.9 | 1,661 | |
 | William Toien (L) | 0.7 | 1,381 | |
 | David Haeg (R) | 0.6 | 1,139 | |
 | William Nemec II (Independent) | 0.2 | 347 | |
| Total votes: 189,300 | ||||
 = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Withdrawn or disqualified candidates
- Jim Cottrell (R)
2018
General election
General election for Governor of Alaska
Mike Dunleavy defeated Mark Begich, incumbent Bill Walker, and William Toien in the general election for Governor of Alaska on November 6, 2018.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ |  | Mike Dunleavy (R) | 51.4 | 145,631 |
 | Mark Begich (D) | 44.4 | 125,739 | |
 | Bill Walker (Independent) | 2.0 | 5,757 | |
 | William Toien (L) | 1.9 | 5,402 | |
| Other/Write-in votes | 0.2 | 605 | ||
| Total votes: 283,134 | ||||
 = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Democratic primary election
Democratic primary for Governor of Alaska
Mark Begich advanced from the Democratic primary for Governor of Alaska on August 21, 2018.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ |  | Mark Begich | 100.0 | 33,451 |
| Total votes: 33,451 | ||||
 = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Republican primary election
Republican primary for Governor of Alaska
The following candidates ran in the Republican primary for Governor of Alaska on August 21, 2018.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ |  | Mike Dunleavy | 61.5 | 43,802 |
 | Mead Treadwell | 32.0 | 22,780 | |
 | Michael Sheldon | 2.3 | 1,640 | |
 | Merica Hlatcu | 1.5 | 1,064 | |
 | Thomas Gordon | 1.4 | 994 | |
 | Gerald Heikes | 0.7 | 499 | |
 | Darin Colbry | 0.6 | 416 | |
| Total votes: 71,195 | ||||
 = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. = candidate completed the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection survey. | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Withdrawn or disqualified candidates
- Jacob Kern (R)
- Scott Hawkins (R)
2014
- See also: Alaska Gubernatorial election, 2014
| Governor and Lieutenant Governor of Alaska, 2014 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Vote % | Votes | |
| Independent | 48.1% | 134,658 | ||
| Republican | Sean Parnell/Dan Sullivan Incumbent | 45.9% | 128,435 | |
| Libertarian | Carolyn "Care" Clift/Andrew C. Lee | 3.2% | 8,985 | |
| Constitution | J.R. Myers/Maria Rensel | 2.5% | 6,987 | |
| Nonpartisan | Write-in votes | 0.3% | 893 | |
| Total Votes | 279,958 | |||
| Election results via Alaska Division of Elections | ||||
Full history
To view the electoral history dating back to 2002 for the office of Governor/Lt. Governor of Alaska, click [show] to expand the section. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In Alaska, the governor and lieutenant governor run on a single ticket. On November 2, 2010, Parnell/Treadwell won election to the office of Governor/Lt. Governor of Alaska. They defeated Berkowitz/Benson (D), Toien/Brown (L) and Donald R. Wright (I) in the general election.
2006 On November 7, 2006, Palin/Parnell won election to the office of Governor/Lt. Governor of Alaska. They defeated Knowles/Berkowitz (D), Halcro/Von Gemmingen (I), Wright/Welton (AI), Toine/Mirabal (Lib) and David M. Massie (Green) in the general election.
2002 On November 5, 2002, Murkowski/Leman won re-election to the office of Governor/Lt. Governor of Alaska. They defeated Ulmer/Hall (D), Benson/Coburn (Green), Wright/DeNardo (AI), Vinzant/Mendias (MOD) and Toien/Anders (Lib) in the general election.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Term limits
- See also: States with gubernatorial term limits
Alaska governors are restricted to two consecutive terms in office, after which they must wait one term before being eligible to run again.
Alaska Constitution, Article III, Section 5
| No person who has been elected governor for two full successive terms shall be again eligible to hold that office until one full term has intervened. |
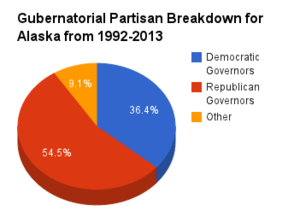
Partisan composition
The chart below shows the partisan breakdown of Alaska governors from 1992 to 2013.
Vacancies
- See also: How gubernatorial vacancies are filled
Details of vacancy appointments are addressed under Article III, Sections 9 to 14.
In the event that the elected governor is unable to complete his or her term, the Lieutenant Governor of Alaska assumes the office. The lieutenant governor also becomes acting governor at any time when the elected incumbent is temporarily unable to discharge the office. If the elected governor is continually unable to discharge the office for six months, the office is deemed vacant and the lieutenant governor succeeds to the office.
In the event that a governor-elect dies, resigns, is disqualified, or otherwise does not take office, the individual elected as lieutenant governor shall become the governor.
If the lieutenant governor takes over as the governor, she or he serves as the governor for the entire remaining term.
Duties
The Governor of Alaska is the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws, and the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Alaska State Legislature, to convene the legislature, and to grant pardons, except in cases of impeachment.
Many offices, such as that of the attorney general, which are elected offices in most states, are gubernatorial appointments in Alaska. The governor has wide latitude in searching for a nominee but must seek legislative confirmation of those nominees. The governor also appoints the officers of most state boards and commissions and has the power to make recess appointments when the legislature is not in session.
The number of departments in Alaska's state government is constitutionally capped at 20; however, the governor may decrease and increase the numbers of departments within that limit. Some reorganization of the government may be done at the governor's discretion. For changes requiring the force of law, the governor issues an executive order; the legislature then has 60 session days to reject the change, done by a majority vote of a joint session. Otherwise, the executive order stands and takes effect on a day chosen by the governor.
Other duties and privileges of the office include:
- upholding the faithful execution of all Alaska laws and forcing compliance when needed, either through the courts or by legislative action
- convening special sessions of the House, the Senate, or both in a joint session
- addressing the legislature at the beginning of each session and at other times he deems necessary, with a description of the current state of Alaska's affairs and with her or his recommendations
- appointing all general and flag officers of Alaska's armed forces
- proclaiming martial law for up to 20 days. (A longer declaration requires a majority vote of the joint legislature.)
Divisions
The Office of the Governor oversees four main divisions: Alaska State Commission for Human Rights, Office of Boards and Commissions, Office of International Trade, and Office of Management and Budget.
Alaska State Commission for Human Rights
- The State Commission for Human Rights has the following mission statement:
- "Discrimination not only threatens the rights and privileges of the inhabitants of the state, but also menaces the institutions of the state and threatens peace, order, health, safety, and general welfare of the state and its inhabitants. Therefore, it is the policy of the state and the purpose of this chapter to eliminate and prevent discrimination. It is also the policy of the state to encourage and enable physically and mentally disabled persons to participate fully in the social and economic life of the state and to engage in remunerative employment."[4]
| Contact Alaska State Commission for Human Rights | |
|---|---|
| Phone: (907) 274-4692 | |
| Phone: (800) 478-4692 | |
| Fax: (907) 278-8588 Department Mailing Address: 800 A Street, Suite 204 | |
Office of Boards and Commissions
- The Office of Boards and Commissions aids the governor in his or her appointments to state boards and commissions. It processes applications for appointments.
| Contact Office of Boards and Commissions | |
|---|---|
| Phone: (907) 269-0006 | |
| Fax: (907) 269-7463 | |
| E-mail: boards@alaska.gov | |
Office of International Trade
- The Office of International Trade works to promote trade between Alaska and other countries.
| Contact Office of International Trade | |
|---|---|
| Phone: (907) 269-7450 | |
Office of Management and Budget
- The Office of Management and Budget prepares annual capital and operating budget, training materials, guidelines, budget submission timetables for executive branch agencies and advises the Governor in the budget review process. It also helps develop the Governor's budget, oversees the automated budget system, and reviews proposed changes for the appropriations bill.
| Contact Office of Management and Budget | |
|---|---|
| Phone: 907-465-4660 | |
| Fax: 907-465-2090 Department Mailing Address: P.O. Box 110020, Juneau, Alaska 99811-0020 | |
State budget
Role in state budget
- See also: Alaska state budget and finances
The state operates on an annual budget cycle, with the fiscal year beginning July 1 and ending June 30. The sequence of key events in the budget process is as follows:[5]
- Budget instructions are sent to state agencies in July.
- Agencies submit their budget requests to the governor in October.
- The governor submits his or her proposed budget to the state legislature by December 15.
- The legislature adopts a budget by a simple majority in April.
The governor is required by statute to submit a balanced budget. Likewise, the legislature is required by statute to pass a balanced budget.[5]
Alaska is one of 44 states in which the governor has line item veto authority.[5][6]
Governor's office budget
The enacted budget for the Governor's Office in Fiscal Year 2024 was $30,651,400.[7]
Compensation
The governor's salary is determined by the Alaska State Officers Compensation Commission, a four-member board created by the Alaska State Legislature in 2008. This commission meets on a regular basis to evaluate salaries for the governor, lieutenant governor and other state executive officers. State law does not require legislative approval of the salaries, but legislators can vote to prevent salary changes as a veto on the commission's work.[8]
The Alaska Constitution only provides for the compensation of the governor and lieutenant governor by law. Chapter 2, Section 15 of the state constitution prevents changes in salary from taking effect until the next term for the affected office or offices.[9]
2022
In 2022, the officer's salary was $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[10]
2021
In 2021, the governor received a salary of $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[11]
2020
In 2020, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[12]
2019
In 2019, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[13]
2018
In 2018, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[14]
2017
In 2017, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[15]
2016
In 2016, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[16]
2015
In 2015, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[17]
2014
In 2014, the governor's salary remained at $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[18]
2013
In 2013, the governor's salary was $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.[19]
2012
In 2012, the governor was paid an estimated $145,000, according to the Council of State Governments.
Historical officeholders
Since gaining statehood in 1959, Alaska has had 12 governors. Walter J. Hickel served two non-consecutive terms as governor, and William A. Egan served two consecutive terms. [20]
| # | Name | Term | Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | William A. Egan | 1959-1966, 1970-1974 | Democratic |
| 2 | Walter J. Hickel | 1966-1969, 1990-1994 | Republican |
| 3 | Keith H. Miller | 1969-1970 | Republican |
| 4 | Jay S. Hammond | 1974-1982 | Republican |
| 5 | William J. Sheffield | 1982-1986 | Democratic |
| 6 | Steve Cowper | 1986-1990 | Democratic |
| 7 | Tony Knowles | 1994-2002 | Democratic |
| 8 | Frank Murkowski | 2002-2006 | Republican |
| 9 | Sarah Palin | 2006-2009 | Republican |
| 10 | Sean Parnell | 2009-2014 | Republican |
| 11 | Bill Walker | 2014-2018 | Independent |
| 12 | Mike Dunleavy | 2018-present | Republican |
History
Partisan balance 1992-2013
From 1992-2013, there were Democratic governors in office for eight years while there were Republican governors in office for 12 years, including the last 11 of the study period. Alaska was under a Republican trifecta for the last year of the study period.
Across the country, there were 493 years of Democratic governors (44.82 percent) and 586 years of Republican governors (53.27 percent) from 1992 to 2013.
Over the course of the 22-year study, state governments became increasingly more partisan. At the outset of the study period (1992), 18 of the 49 states with partisan legislatures had single-party trifectas and 31 states had divided governments. In 2013, only 13 states had divided governments, while single-party trifectas held sway in 36 states, the most in the 22 years studied.
The chart below shows the partisan composition of the Office of the Governor of Alaska, the Alaska State Senate and the Alaska House of Representatives from 1992 to 2013.
SQLI and partisanship
The chart below depicts the partisanship of the Alaska state government and the state's SQLI ranking for the years studied. For the SQLI, the states were ranked from 1-50, with 1 being the best and 50 the worst. The only trifecta in Alaska, a Republican trifecta, occurred between the years 2003 and 2006, as well as 2013. The state never had a Democratic trifecta between 1992 and 2012. Between 1995-2002 and 2007-2012, Alaska had divided government. Alaska never placed in the top-10 or bottom-10 in the SQLI ranking. Alaska’s highest SQLI ranking (16th) occurred during divided government, in 2002, while its lowest ranking (37th) occurred in 2011, also under divided government.
- SQLI average with Democratic trifecta: N/A
- SQLI average with Republican trifecta: 32
- SQLI average with divided government: 23.27
State profile
| Demographic data for Alaska | ||
|---|---|---|
| Alaska | U.S. | |
| Total population: | 737,709 | 316,515,021 |
| Land area (sq mi): | 570,641 | 3,531,905 |
| Race and ethnicity** | ||
| White: | 66% | 73.6% |
| Black/African American: | 3.4% | 12.6% |
| Asian: | 5.9% | 5.1% |
| Native American: | 13.8% | 0.8% |
| Pacific Islander: | 1.2% | 0.2% |
| Two or more: | 8.4% | 3% |
| Hispanic/Latino: | 6.5% | 17.1% |
| Education | ||
| High school graduation rate: | 92.1% | 86.7% |
| College graduation rate: | 28% | 29.8% |
| Income | ||
| Median household income: | $72,515 | $53,889 |
| Persons below poverty level: | 11.3% | 11.3% |
| Source: U.S. Census Bureau, "American Community Survey" (5-year estimates 2010-2015) Click here for more information on the 2020 census and here for more on its impact on the redistricting process in Alaska. **Note: Percentages for race and ethnicity may add up to more than 100 percent because respondents may report more than one race and the Hispanic/Latino ethnicity may be selected in conjunction with any race. Read more about race and ethnicity in the census here. | ||
Presidential voting pattern
- See also: Presidential voting trends in Alaska
Alaska voted Republican in all six presidential elections between 2000 and 2020.
More Alaska coverage on Ballotpedia
- Elections in Alaska
- United States congressional delegations from Alaska
- Public policy in Alaska
- Endorsers in Alaska
- Alaska fact checks
- More...
Contact information
Juneau Office
Alaska State Capitol Building
Third Floor
Mailing Address:
P.O. Box 110001
Juneau, AK 99811
Phone: 907-465-3500
Fax: 907-465-3532
See also
| Alaska | State Executive Elections | News and Analysis |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
External links
Footnotes
- ↑ Office of the Governor, "Meet Governor Dunleavy," accessed January 13, 2020
- ↑ Anchorage Daily News, "Dunleavy sworn in as governor after a very Alaska travel glitch," December 3, 2018
- ↑ Justia, "Title 15, Chapter 15, Section 020," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Alaska Statutes, "Title 18. HEALTH, SAFETY, AND HOUSING-Sec.18.80.200," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Budget Processes in the States, Spring 2021," accessed January 24, 2023
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "Separation of Powers: Executive Veto Powers," accessed January 26, 2024
- ↑ Alaska Office of Management and Budget, "Department Totals - FY2024," accessed December 6, 2023
- ↑ Alaska State Officers Compensation Commission, "Findings and Recommendations," January 13, 2021
- ↑ Alaska State Legislature, "Alaska's Constitution: A Citizen's Guide," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Book of the States 2022 Table 4.11: Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries," provided to Ballotpedia by CSG personnel
- ↑ Issuu, "The Book of the States 2021," accessed September 22, 2022
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2020," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2019," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2018," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2017," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2016," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2015," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries," accessed January 13, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "CSG Releases 2013 Governor Salaries," January 13, 2021
- ↑ Statewide Library Electronic Doorway, "Governors of Alaska," accessed January 13, 2021
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||
 |
State of Alaska Juneau (capital) |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2024 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |